A Report Element Script
A script attached to a report element is evaluated before the element is processed. The script can change the properties of the element, including visibility. Because element script executes after query execution, the script also has access to the element's data.
In fact, an element script can access any element in the report. However, it is not good practice to modify the properties of one element from within the script of another element. See Script Debugging for alternative approaches.
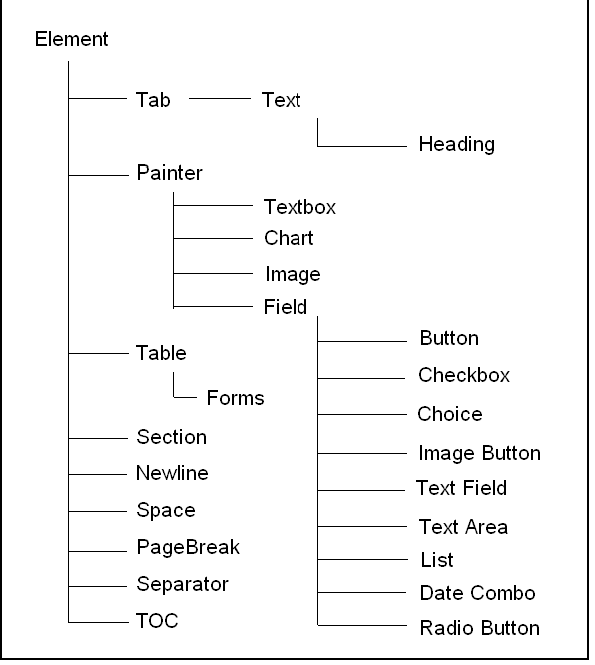
Element Inheritance
Hierarchy Report elements are organized in the object inheritance structure shown below. Properties defined in base classes are inherited by their subclasses.
Common Element Properties
All elements share a basic set of properties, including foreground, background, font, alignment, visibility, etc. The following sections explain how to use these properties.
Color Property
Color properties (foreground/text and background/fill) are frequently used to highlight a text or textbox element. The simplest way to specify a color property is to assign a string containing one of the constants from the java.awt.Color class: black, blue, cyan, darkGray, gray, green, lightGray, magenta, orange, pink, red, white, and yellow.
foreground = 'red';
Since color is a Java type, the class name must be fully qualified. You can also specify a color as java.awt.Color object, an integer (e.g., hexadecimal) representing the RGB value of a color, an array of RGB values, or a JSON object.
foreground = java.awt.Color.red;
background = 0xFF00FF;
// RRGGBB foreground = [255, 255, 0];
foreground = {r:255,g:255,b:0};
Alternatively, you can create a color object by calling the constructor with the the 'new' operator. foreground = new java.awt.Color(0.5, 1, 0); Note that the parameters to the color constructor have type float. Because JavaScript treats all numbers as float by default, you have to explicitly convert them to integer if you want to specify the RGB values in the range of 0-255. The default float parameters pass the RGB value in the range of 0-1, where 1 is equivalent to 255 in the integer version.
Font Property
You can specify the font property with a string containing the font name, style, and size, separated by dashes, or by creating a java.awt.Font object.
font = 'Verdana-BOLD-12';
font = new java.awt.Font('Verdana', java.awt.Font.BOLD, 12);
The name of the font can be a TrueType font name, or a logical font name. Logical font names are not recommended, however, because the logical font may be replaced by a different font in the runtime environment. There are three font styles, Font.PLAIN, Font.BOLD and Font.ITALIC. The styles can be combined with a bitwise OR.
font = new java.awt.Font('Verdana', java.awt.Font.BOLD |
java.awt.Font.ITALIC, 12);
The final parameter specifies the size of the font. Style Intelligence provides an extended font that supports additional styles:
Table 2. Font Styles
|
Font Style |
Description |
|
Underline |
Draw an underline below the text. The line style can be any one of the Style Intelligence Line Styles. |
|
Strikethrough |
Draw a line through the text in the middle. |
|
Superscript |
Draw the text at the upper corner of the previous text. |
|
Subscript |
Draw the text at the lower corner of the previous text. |
|
SMALLCAPS |
Draw all letters in capital letter, but draw the lowercase letters in a smaller size. |
|
Allcaps |
Convert all letters to uppercase. |
|
Shadow |
Draw the text with a shadow effect. |
To create an extended font, you must use the fully qualified name of inetsoft.report.StyleFont class.
font = new inetsoft.report.StyleFont('Verdana',
java.awt.Font.BOLD | inetsoft.report.StyleFont.UNDERLINE, 12,
StyleReport.THIN_LINE);
The final parameter specifies the line style used to draw the underline.
More Articles About Reporting
Bin Capacity Monitoring - Monitoring garbage bin capacity is essential to efficient waste management since it lowers environmental risks, keeps things clean, and prevents overflows. Dashboards for waste collection software use a range of KPIs and analytics to solve this issue: Fill Level Sensors Integration Bins with fill level sensors are a common feature in garbage collection systems. When bins are getting close to capacity, waste management staff can accurately plan pickups thanks to real-time data provided by KPIs linked to fill levels. Overflow Incidents Analysis Areas with a high frequency of overflowing bins may be identified with the use of analytics pertaining to overflow events...
Evaluate InetSoft's Continuous Online Reporting Program - Are you looking for a good continuous online reporting program? InetSoft is a pioneer in offering flexible, enterprise-grade reporting software. Use an easy-to-use drag-and-drop designer to create great-looking web-based dashboards and reports. View a demo and try interactive examples. All new clients and partners get free one-on-one business intelligence expert help to accelerate deployment...
Global Trade Management Dashboard Example - With global firms and complex supply chains, global trade management (GTM) has gotten more complicated. Businesses use Global Trade Management Dashboards with KPIs and analytics to manage international trade operations. These technologies help firms make educated choices and improve their international operations by providing insights on global commerce. This article discusses Global Trade Management Dashboards' key KPIs and analytics...
Insurance Claims Processor KPIs - Here are some common KPIs tracked by an insurance claims processor: Claims Processing Time: Average Processing Time: Measures the average time taken to process a claim from submission to resolution, including initial review, investigation, adjudication, and payment. Cycle Time: Tracks the elapsed time between each stage of the claims processing workflow, identifying bottlenecks and areas for process improvement. Claims Accuracy and Quality: Claims Accuracy Rate: Calculates the percentage of claims processed accurately without errors, discrepancies, or omissions, ensuring compliance with policy terms, regulatory requirements, and industry standards...
Pharmaceutical Analytics Dashboard Example - Dashboards and analytics play a crucial role in the field of pharmaceutical drug testing trials, providing valuable insights and facilitating informed decision-making. InetSoft's pharmaceutical testing dashboard presents complex pharma testing data in a visually appealing and comprehensible format. InetSoft's mashup feature is essential in drug testing trials where large amounts of data are generated from diverse sources, including patient records, laboratory results, and clinical assessments. InetSoft's visualization tools can help researchers and stakeholders easily interpret trends, patterns, and outliers...
School Bus Routing Software Dashboards - One important KPI that has a direct influence on parents' and children' daily routines is on-time performance. The proportion of buses that arrive at schools and other stops on time is commonly shown on charts and graphs on the dashboard of school bus routing software. Administrators may use this information to spot trends, evaluate the effectiveness of their routes, and implement corrective measures to cut down on delays. Bus scheduling may be improved continuously and patterns can be highlighted with the use of visual representations of on-time performance over time...