The Significance of Local Government Management Dashboards in Terms of Civic Decision Making
The building of a local government dashboard is currently becoming one of the civic management priorities.
The development of high-quality managerial decisions in municipal authorities, in turn, as well as their effective implementation is the key to stability and successful development of municipalities. That is why the problem of improving the quality of management decisions in local governments is now becoming of paramount importance.
The quality of management decisions is understood as the degree to which the parameters of the selected solution correspond to a specific system of characteristics that satisfy its developers, consumers and provide the possibility of effective implementation. The necessary characteristics of the quality of management decisions of local authorities include scientific validity, timeliness, consistency, adaptability, and reality.
In other words, this is a list of requirements for the quality of decisions. In addition to the set of these characteristics, in each management decision there are certain elements of subjectivity, since in practice when making decisions, many interests, desires, and intentions collide. The degree of subjectivity depends on the knowledge, abilities of the decision-maker, on their awareness.
At the same time, objective decisions are taken as the basis for management decisions, which every leader must reckon with. The degree of their use depends on the ability to proceed from objective positions and develop solutions taking into account the scientific foundations of management.
Objectives of Management Decisions in Local Government
The objectives for the development of competent management decisions in local governments are:
- knowledge of real development trends of the managed facility;
- knowledge of the methods of the positive use of emerging trends for the system;
- orientation for the common goals of developing the economy of the country as a whole and the municipality in particular;
- definition of tasks arising from these goals for a managed facility;
- a clear idea of the state of the object, the external environment (the immediate environment), their development trends;
- possession of a set of methods for transferring a managed facility from the actual state to the desired and giving it the necessary directions of development;
- the ability to respond in a timely manner to a changing environment and new challenges posed by the market, the economic policies of the region, the municipality, and the state as a whole.
For municipal employees, these positions are of particular importance, since the object of management is the development of the socio-economic sphere of the municipality, therefore, non-compliance with these objective economic conditions can lead to disorganization of the life of the whole city. Thus, the quality of management decisions of local authorities depends mainly on the level of information support for the activities of this body, the qualifications and training level of municipal employees, the degree of public participation in the development of management decisions of local governments.
Therefore, to ensure and improve the quality of management decisions in municipal management, the following basic conditions must be created:
- improvement of information support for the activities of local authorities,
- advanced training of municipal employees,
- intensification of public participation in the development of managerial decisions of local authorities.
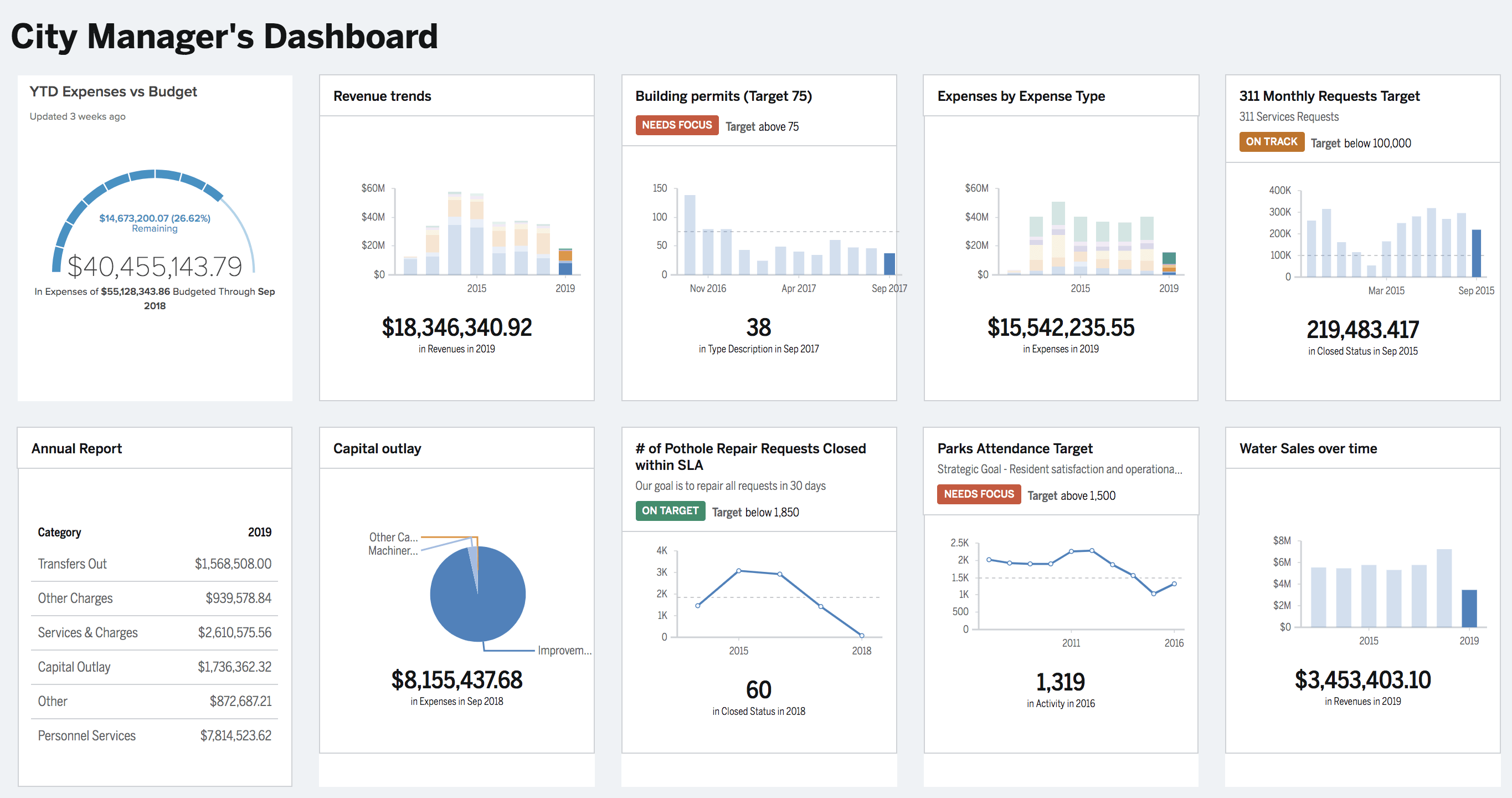
What KPIs and Metrics Does a City Manager Track?
City managers track a wide range of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to assess the overall health, efficiency, and livability of their cities. These metrics help city managers make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and measure progress towards strategic goals. Some of the most common KPIs and metrics tracked by city managers include:
-
Economic Indicators: These metrics provide insights into the economic vitality and growth of the city. Key indicators include gross domestic product (GDP), unemployment rate, job growth, business startups, and tax revenue. City managers monitor economic trends to identify areas of strength and opportunities for economic development initiatives.
-
Infrastructure and Utilities: City managers track metrics related to infrastructure and utilities to ensure that essential services are provided efficiently and reliably. This includes metrics such as water quality, wastewater treatment capacity, road condition index, public transportation ridership, and utility service interruptions. Monitoring infrastructure metrics helps city managers prioritize maintenance and investment projects to enhance the quality of life for residents.
-
Public Safety: Ensuring the safety and security of residents is a top priority for city managers. They track metrics related to crime rates, response times for emergency services, fire incidents, traffic accidents, and public safety complaints. Analyzing these metrics helps city managers allocate resources effectively, identify crime hotspots, and implement targeted interventions to improve public safety.
-
Quality of Life: City managers monitor various metrics related to the quality of life for residents, including housing affordability, access to healthcare, educational attainment, parks and recreation facilities, air and water quality, and cultural amenities. These metrics provide insights into residents' well-being and satisfaction with city services, guiding policy decisions and investments to enhance overall quality of life.
-
Sustainability and Environment: Tracking sustainability metrics is increasingly important for city managers as they work to address climate change and environmental challenges. Metrics such as greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy adoption, waste diversion rates, and air pollution levels help assess progress towards sustainability goals and inform initiatives to promote environmental stewardship and resilience.