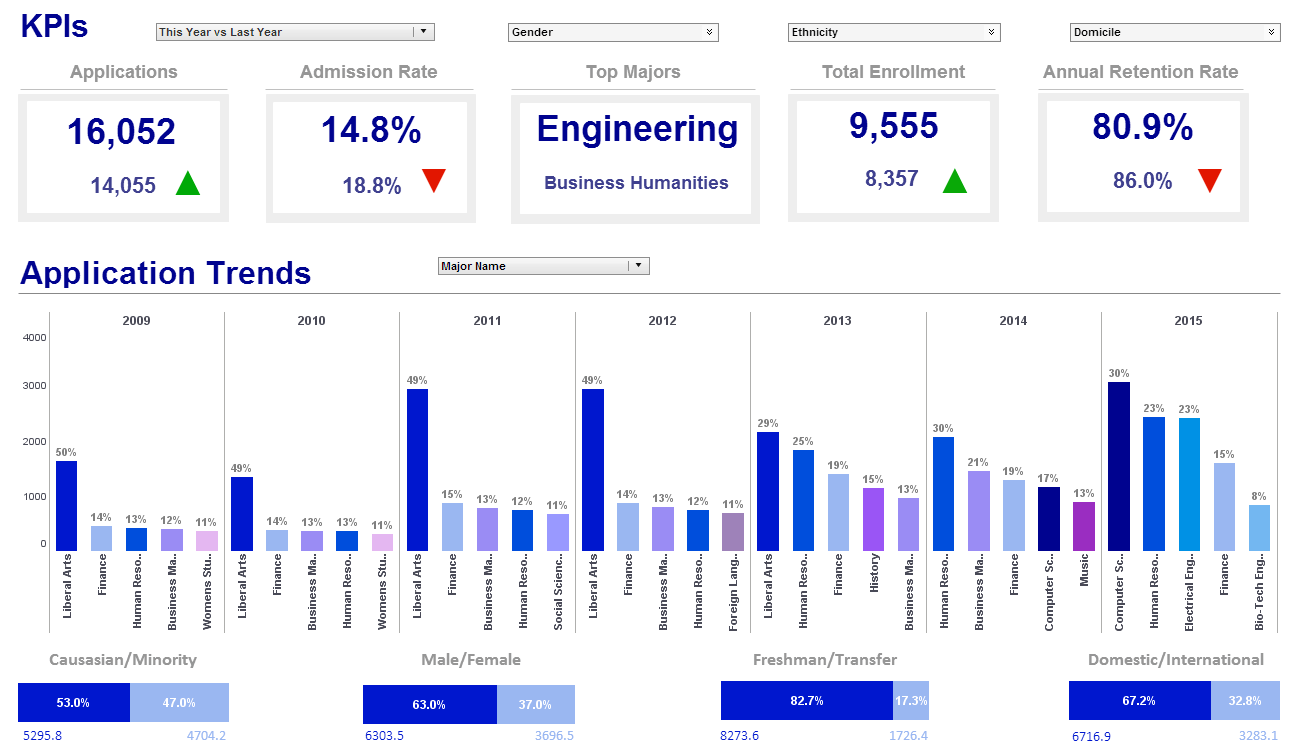
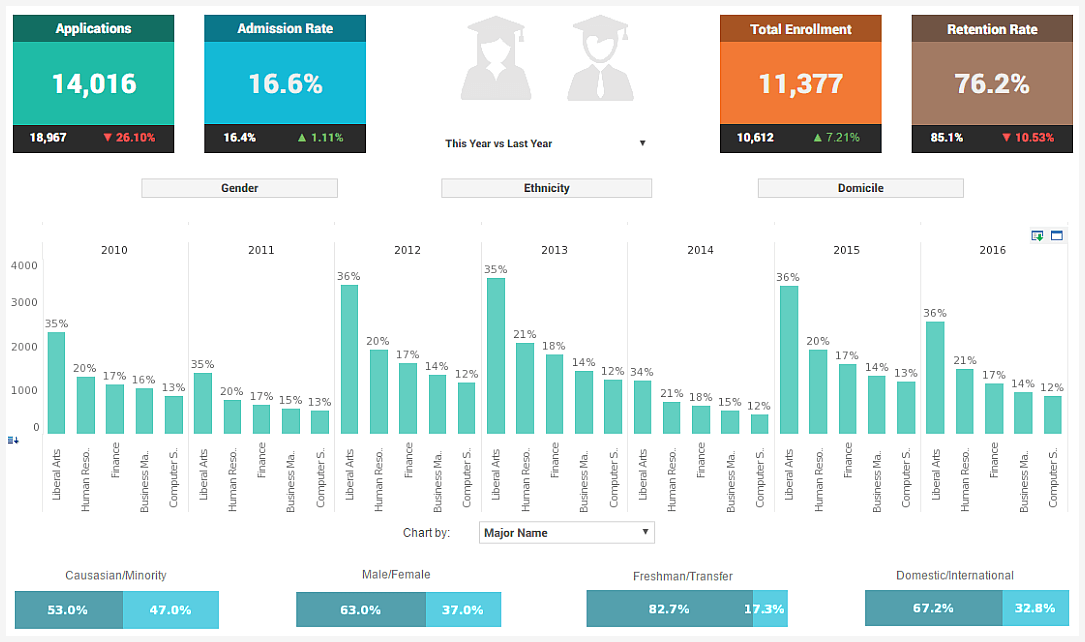
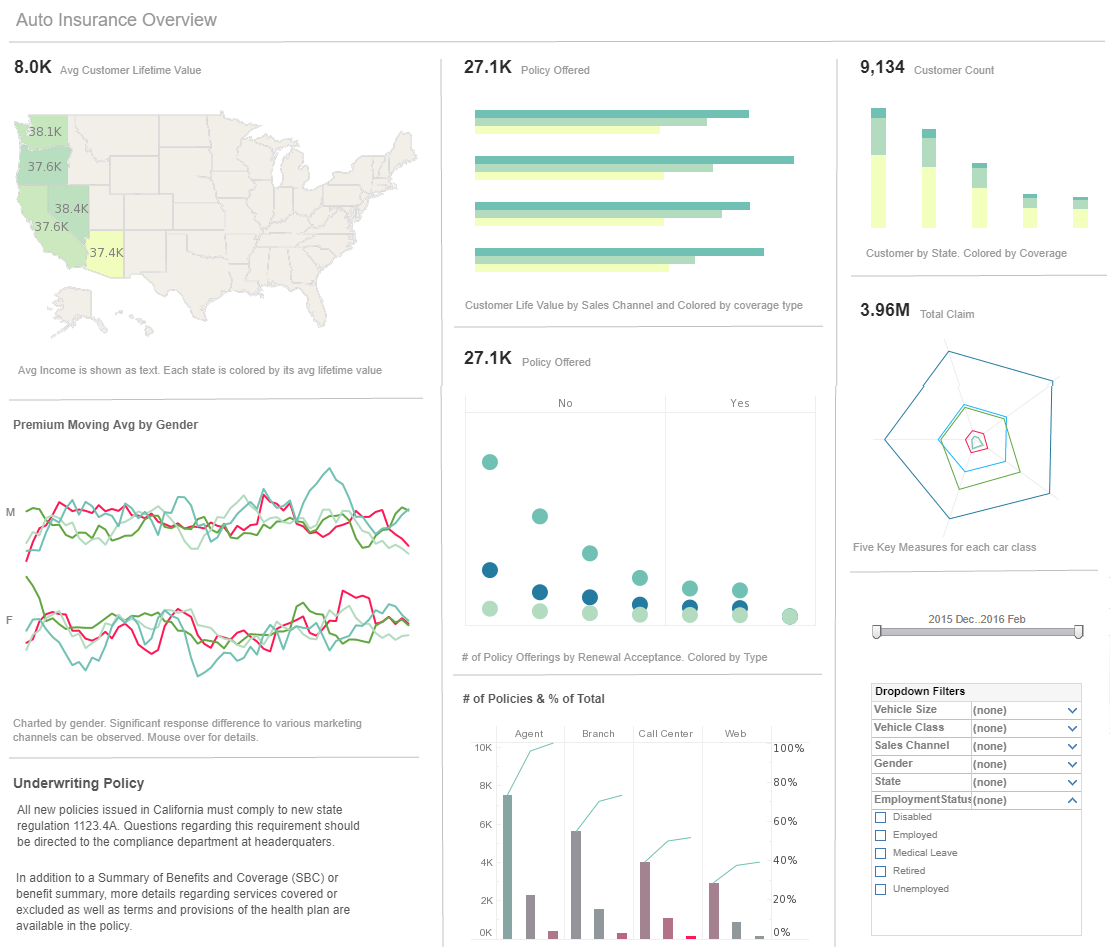
Simple Reporting Tools
Are you searching for a simple reporting tool to help you organize your reports so they can be viewed with ease? InetSoft offers reporting tools through its flagship platform StyleBI and a stand alone reporting tool called Style Report Enterprise.
Easy, Agile, Robust | Self-Service Reporting
Business users require flexibility when it comes to reporting. Like data mashup, creating reports must be an accessible process for both IT and business users, alike. InetSoft empowers both with a combination of powerful authoring tools and a highly scalable deployment environment.
InetSoft's easy to use business intelligence tool combines the familiar environment of a word-processor with dynamic data manipulation, enabling sophisticated reports to be created using simple-to-understand software.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
Key features include
- Rapid implementation; minimum specialized IT expertise required
- Shallow learning curve for business users; only Excel-level skills needed
- Make it easy for analysts & administrators; no SQL experience required
- Scale up with zero-client deployment and no per-user licensing
- Accommodate quick, formal, and experimental change
Style Report also provides various report elements that displays data through texts and graphics. Its comprehensive because it allows use of tables, charts, and others advanced report components all in one report, and can be easily modified with individual data binding, formatting, and display properties.
Easy-to-use benefits
- A simple point and click system; the user can simple grab data from any location in any format.
- Two different layouts depending on the report designer's needs:
- The Flow layout treats reports like a word processor document. The report designer can place flow area
into the report, which allows the report elements to flow from one area to the next.
- The Tabular layout allows report designers to divide a report into cellular areas that each contain
different portions of the report.
- Complete control over how data is placed and displayed
- Allows report designers to bind data to any report element and specify grouping and summary rules for every field displayed on that element.
About InetSoft
Since 1996 InetSoft has been delivering easy, agile, and robust business intelligence software that makes it possible for organizations and solution providers of all sizes to deploy or embed full-featured business intelligence solutions. Application highlights include visually-compelling and interactive dashboards that ensure greater end-user adoption plus pixel-perfect report generation, scheduling, and bursting.
InetSoft's patent pending Data Block™ technology enables productive reuse of queries and a unique capability for end-user defined data mashup. This capability combined with efficient information access enabled by InetSoft's visual analysis technologies allows maximum self-service that benefits the average business user, the IT administrator, and the developer. InetSoft solutions have been deployed at over 5,000 organizations worldwide, including 25% of Fortune 500 companies, spanning all types of industries.
What KPIs and Metrics Are Tracked in Emission Testing Reporting Dashboards?
In the realm of environmental management and regulatory compliance, emission testing dashboards play a crucial role in monitoring and managing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics related to emissions from various sources. These dashboards provide real-time insights into pollutant levels, compliance with emissions standards, and operational efficiency. This article explores the essential KPIs and metrics tracked in emission testing dashboards, their definitions, and their significance in performance management.
1. Emission Levels
Definition: The concentration of pollutants emitted from a specific source, measured in parts per million (ppm) or micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m³).
Significance: Monitoring emission levels is fundamental in assessing environmental impact and compliance with regulatory standards. KPIs related to emission levels include measurements of particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other pollutants. These metrics help industries identify sources of emissions, implement mitigation strategies, and demonstrate adherence to environmental regulations to avoid fines and penalties.
2. Compliance Rate
Definition: The percentage of emission tests that meet or exceed regulatory requirements and standards.
Significance: Compliance rate indicates the extent to which emissions from a facility or process comply with legal limits and regulations set by environmental agencies. Maintaining a high compliance rate is essential for avoiding legal liabilities, maintaining operational permits, and fostering trust with stakeholders. Monitoring compliance rate KPIs ensures that corrective actions are taken promptly to address non-compliance issues and improve overall environmental performance.
3. Testing Frequency and Coverage
Definition: The frequency of emission testing conducted on various equipment, processes, or emissions sources within a facility.
Significance: Testing frequency and coverage metrics ensure comprehensive monitoring of emissions to capture variations over time and under different operating conditions. Regular testing helps in detecting equipment malfunctions, process inefficiencies, or changes in emissions patterns that could impact environmental performance. Optimizing testing frequency ensures timely identification of issues and supports proactive maintenance and operational adjustments to minimize emissions and maintain compliance.
4. Calibration and Accuracy
Definition: The accuracy and reliability of emission monitoring equipment and measurement techniques, verified through calibration procedures.
Significance: Calibration and accuracy metrics ensure the validity and precision of emission data collected during testing. KPIs related to calibration include calibration intervals, measurement uncertainty, and adherence to calibration protocols. Accurate measurements are critical for making informed decisions about emission control strategies, evaluating compliance with regulatory limits, and resolving discrepancies in reported emission data. Monitoring calibration and accuracy metrics supports data integrity, credibility, and regulatory acceptance of emission testing results.
5. Emission Reduction Goals
Definition: Targets and benchmarks set by organizations to reduce emissions over specific time frames, typically aligned with environmental sustainability objectives.
Significance: Emission reduction goals KPIs measure progress towards achieving environmental sustainability and corporate responsibility commitments. These metrics include reduction targets for greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs), air pollutants, and other harmful substances. Tracking emission reduction goals encourages continuous improvement in emission control technologies, operational practices, and resource efficiency. Achieving emission reduction targets enhances organizational reputation, supports regulatory compliance, and mitigates environmental impacts associated with industrial operations.
6. Operational Efficiency
Definition: The efficiency of emission control technologies and operational processes in minimizing emissions per unit of production or activity.
Significance: Operational efficiency metrics evaluate the effectiveness of emission control measures, such as pollution control devices, process modifications, and operational best practices. KPIs related to operational efficiency include emissions intensity (emissions per unit of output), energy efficiency ratios, and resource utilization efficiencies. Improving operational efficiency reduces environmental footprint, lowers operational costs, and enhances competitiveness by optimizing resource use and reducing emissions intensity.
7. Maintenance and Downtime
Definition: Metrics related to the frequency and duration of maintenance activities and equipment downtime affecting emission control systems.
Significance: Maintenance and downtime metrics assess the reliability and availability of emission control equipment and systems. KPIs include mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair (MTTR), and maintenance costs as a percentage of total operational expenses. Effective maintenance practices minimize unplanned downtime, ensure continuous compliance with emission standards, and prolong the lifespan of emission control infrastructure. Monitoring these metrics supports proactive maintenance planning, risk management, and operational continuity in emission testing and control operations.
8. Cost of Compliance
Definition: The financial expenditure associated with achieving and maintaining compliance with emission regulations and standards.
Significance: Cost of compliance metrics quantify the direct and indirect costs incurred by organizations to meet emission testing requirements, invest in emission control technologies, and manage regulatory obligations. KPIs include compliance-related expenditures, cost per emission test conducted, and cost per unit of emission reduction achieved. Managing the cost of compliance optimizes resource allocation, supports budgetary planning, and enhances financial performance while ensuring adherence to environmental regulations and sustainability commitments.
9. Trend Analysis and Forecasting
Definition: Analyzing historical emission data trends and using predictive models to forecast future emission levels and compliance outcomes.
Significance: Trend analysis and forecasting metrics provide insights into long-term emission patterns, seasonal variations, and potential future regulatory requirements. KPIs include trend analysis of emission levels over time, forecasting models for emissions under different scenarios, and sensitivity analysis of regulatory changes. Understanding emission trends and forecasts enables proactive decision-making, risk assessment, and strategic planning to anticipate compliance challenges, optimize emission control strategies, and capitalize on opportunities for operational improvement.
10. Stakeholder Engagement and Transparency
Definition: Metrics related to stakeholder communication, engagement initiatives, and transparency in reporting emission testing results and environmental performance.
Significance: Stakeholder engagement and transparency metrics measure the effectiveness of communication strategies, stakeholder satisfaction levels, and public trust in emission testing practices. KPIs include stakeholder feedback surveys, frequency of communication on environmental performance, and public disclosure of emission data. Enhancing stakeholder engagement fosters trust, promotes corporate accountability, and supports collaborative efforts to address environmental challenges. Transparent reporting of emission testing results builds credibility, enhances regulatory compliance, and strengthens relationships with regulatory authorities, communities, and industry peers.
 |
View the gallery of examples of dashboards and visualizations. |
More Articles About Simple Reporting
Business Analysts in Government - Trend number 2. This is a really interesting trend, and it couldn't have come at a better time. Now one of the themes that we've heard over the years in state and local federal government agencies, is that we just don't have business analysts, and we don't talk to them as business analysts. I can tell you not too long ago we ran a survey with some of our government customers here, and it's true there are no business analyst types with the exception of one government agency that we are very near and dear, with and they do have them...
Evaluate InetSoft's Software for Tracking Key Performance Measures - Key performance measures (KPMs) are business metrics used to track an organization's performance. Any industry, agency, or organization must measure its performance on a daily, monthly, quarterly basis. InetSoft's pioneering KPM tracking application produces great-looking cloud-based dashboards with an easy-to-use drag-and-drop designer. View a demo and try interactive examples...
Homebuilder Timeline Analytics - Home builders manage several activities at once and complex project timeframes. Project management-specific KPIs and analytics help to optimize workflow and resource allocation. Project Timeline Adherence: Tracking how closely projects follow their schedules helps in anticipating possible setbacks and initiating remedial measures. Task Completion Rates: This Key Performance Indicator evaluates the effectiveness of project teams by monitoring the proportion of tasks completed...
Tie a Strategic Result to a Theme - So now we'll take one of those strategic themes, tie a strategic result to it, so we can answer the question how well we know success when we see it. Right? Because it's not enough to talk about this stuff in the abstract. You have to be able to answer the question, how will we know. So now we have a vision that's built on two pillars. We have a strategic result tied to a theme...