About Operationalizing Business Intelligence
A continuation of eBizQ's Business Intelligence in Action Podcast
Goldstein: Thank you, next Jim, you also spoke about operational business intelligence and operational performance management and database access and Cognos obviously is another pure play BI vendor, so how do you work with BPM? How do you make it operational?
Hare: Well, I guess there are a couple of things to highlight there. Some of the BPM vendors, themselves, have recognized the need to link in key metrics and be able to monitor and measure information and provide that as a base capability in a BPM solution, so several of the BPM vendors have licensed BI technology which speaks to the uniqueness of what BI software can deliver in providing that up to date set of analytics, dashboards, and reporting specifically related to processes.
Information Might Spread Across Multiple Systems
And in answering your question, part of the challenge with deploying a BPM system is not all your processes are being managed by this particular solution. Ad hoc processes within an organization and the data related to those processes is spread across multiple operational data sources that need to have information extracted and correlated and aggregated together to provide a single key metric that the rest of the organization can really determine how well they are performing to.
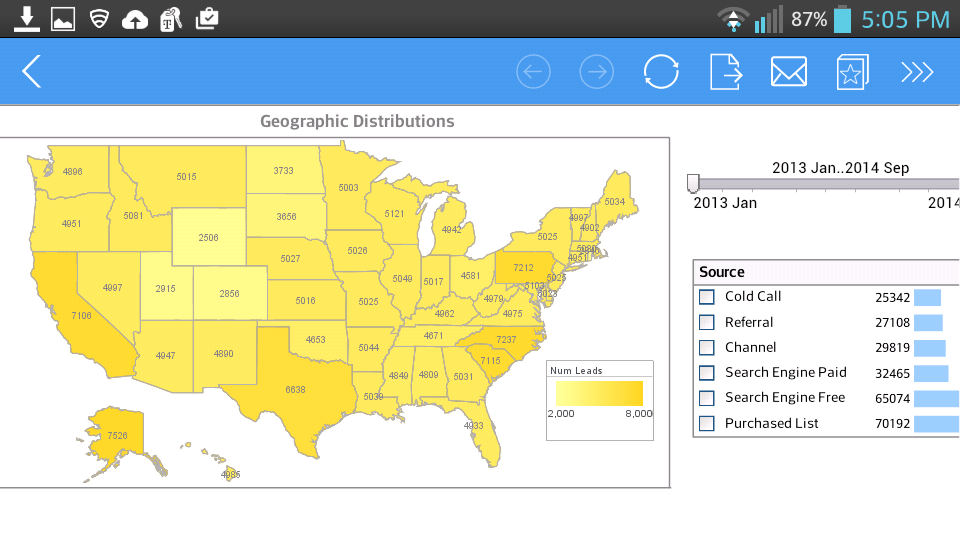
So it is important first of all to make sure that you’re actually pulling that information that might spread across multiple systems and data sources into a centralized system and then be able to process that in real-time, or near real-time in some type of event based system – event based in the sense that you are able to essentially be notified when some piece of information has changed and then be able to notify the respective people giving them that information in their KPI dashboards or management reports.
Then of course if appropriate, be able to create some type of alert to take corrective action. The bottom line is that the people who are actually often the people involved in monitoring dashboards and measuring these processes are the ones that often have not had that information at their finger tips. And they need to have it presented in a way that is related to the way they do their day to day jobs and be able to know how well they are performing their job, and if there is a problem be able to be responsive and be able to be empowered to take corrective action when there is a problem.
Example of Operationalizing Business Intelligence in the Software Development Industry
Operationalizing business intelligence (BI) in the software development industry involves leveraging data-driven insights and analytics to optimize various aspects of the software development lifecycle (SDLC), including planning, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. By harnessing the power of BI, software development organizations can make more informed decisions, improve productivity, enhance product quality, and drive innovation. In this article, we will explore how BI can be operationalized in the software development industry and the benefits it brings to organizations.
Planning and Requirements Gathering
BI plays a crucial role in the planning phase of software development by providing insights into market trends, customer preferences, and competitive landscape. By analyzing data from market research, customer feedback, and past project performance, software development organizations can identify market opportunities, prioritize feature development, and align their product roadmap with business objectives. BI tools such as predictive analytics and data visualization dashboards enable stakeholders to forecast demand, anticipate customer needs, and make data-driven decisions about resource allocation and project prioritization.
Development and Coding
In the development phase, BI helps software development teams optimize their coding processes, identify bottlenecks, and improve code quality. By analyzing code repositories, version control systems, and development workflows, organizations can track developer productivity, identify coding patterns, and detect potential issues early in the development cycle. BI tools can generate code quality metrics, such as code complexity, code coverage, and code churn, to assess the health of the codebase and prioritize refactoring efforts. Additionally, BI can facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing among developers by providing insights into code reuse, best practices, and performance optimizations.
Testing and Quality Assurance
BI is instrumental in optimizing testing and quality assurance processes in software development. By analyzing test data, defect logs, and user feedback, organizations can identify patterns, trends, and root causes of software defects, enabling them to improve testing strategies and prioritize bug fixes. BI tools can generate test coverage reports, defect trend analysis, and regression testing insights to assess the effectiveness of testing efforts and identify areas for improvement. Furthermore, BI can facilitate continuous integration and continuous testing practices by providing real-time feedback on code changes, test results, and quality metrics, enabling teams to deliver high-quality software at a faster pace.
Deployment and Release Management
BI enables software development organizations to streamline deployment and release management processes by providing visibility into deployment pipelines, release cycles, and production environments. By analyzing deployment logs, system performance metrics, and user feedback, organizations can monitor application health, identify performance bottlenecks, and optimize deployment workflows. BI tools can generate deployment analytics, release dashboards, and service-level agreements (SLAs) to track deployment success rates, downtime incidents, and service availability, enabling organizations to improve reliability, scalability, and resilience of their software applications.
Maintenance and Support
BI helps software development organizations optimize maintenance and support processes by providing insights into application usage, performance issues, and customer satisfaction. By analyzing application logs, error reports, and support tickets, organizations can identify recurring issues, prioritize bug fixes, and proactively address customer concerns. BI tools can generate service level reports, incident trend analysis, and customer satisfaction scores to assess the effectiveness of support efforts and identify opportunities for service improvement. Additionally, BI enables organizations to track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as mean time to resolution (MTTR), first call resolution (FCR), and customer retention rate to measure the success of their support operations and drive continuous improvement.
Benefits of Operationalizing BI in Software Development
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: By operationalizing BI, software development organizations can make more informed decisions based on real-time data and actionable insights, leading to improved outcomes and better alignment with business goals.
-
Increased Productivity: BI tools automate data collection, analysis, and reporting tasks, freeing up time for developers, testers, and other stakeholders to focus on more strategic activities and value-added tasks.
-
Improved Quality and Reliability: BI helps organizations identify and address quality issues early in the software development lifecycle, resulting in higher-quality products, reduced defects, and improved customer satisfaction.
-
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication: BI facilitates collaboration and knowledge sharing among cross-functional teams by providing a centralized platform for sharing insights, discussing findings, and making data-driven decisions collaboratively.
-
Faster Time to Market: By optimizing development, testing, and deployment processes, BI enables organizations to deliver software products to market faster, gain a competitive edge, and capitalize on market opportunities more effectively.
-
Continuous Improvement: BI enables organizations to monitor performance, track key metrics, and identify areas for improvement continuously, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within the organization.