Case Study: The World Health Organization (WHO)
Anti-tuberculosis (TB) drug resistance is a major public health problem that threatens progress made in TB care and control worldwide. Drug resistance arises due to improper use of antibiotics in chemotherapy of drug-susceptible TB patients. This improper use is a result of a number of actions including, administration of improper treatment regimens and failure to ensure that patients complete the whole course of treatment. Essentially, drug resistance arises in areas with weak TB control programmes. A patient who develops active disease with a drug-resistant TB strain can transmit this form of TB to other individuals.
Style Intelligence Features
Using Style Intelligence, WHO has created a way for website visitors to quickly view indicators of diagnosis and treatment of drug-resistant TB by country and year.
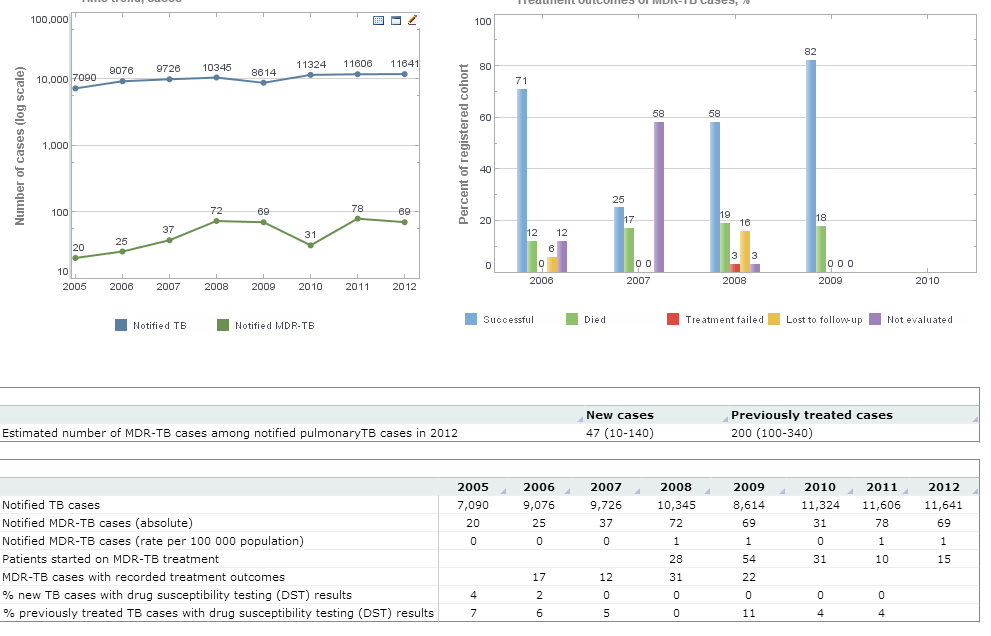
Various components of Style Intelligence are used to create these visualizations. In the first example, line charts and bar charts are among the most obvious, using the "show values" plot property to display data at various points. Each line and bar is individually colored from a selection of over 16 million color choices in order to differentiate one "case" or "cohort" from the next. Below, a crosstab is used to display detailed information that cannot be quickly displayed in a graph.
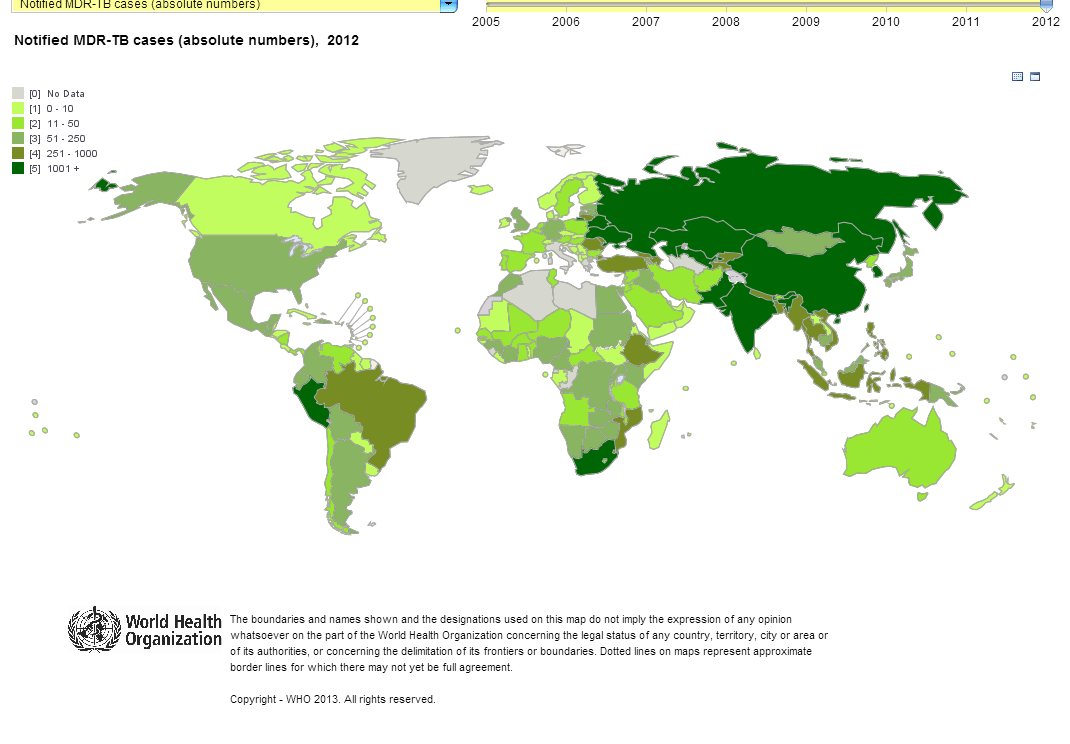
The second visualization uses Style Intelligence's embedded mapping system to create a visual representation of TB data that the user can sort and filter on a number of different levels. The drop-down menu, for example, gives users the option to display various diagnosis and notifications related to multi-drug resistant TB. The date slider allows users to further filter that data down to a relevant time frame.
Parameterized Reporting
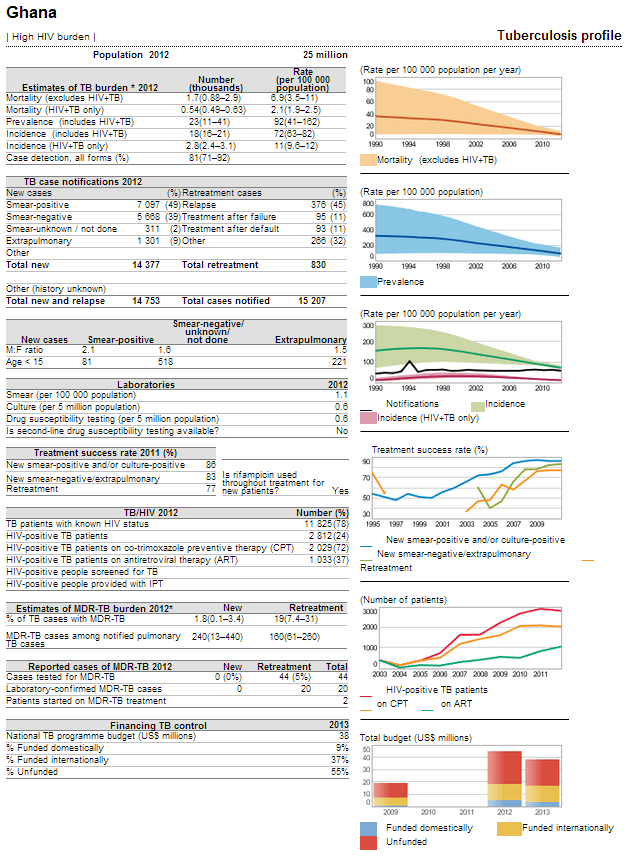
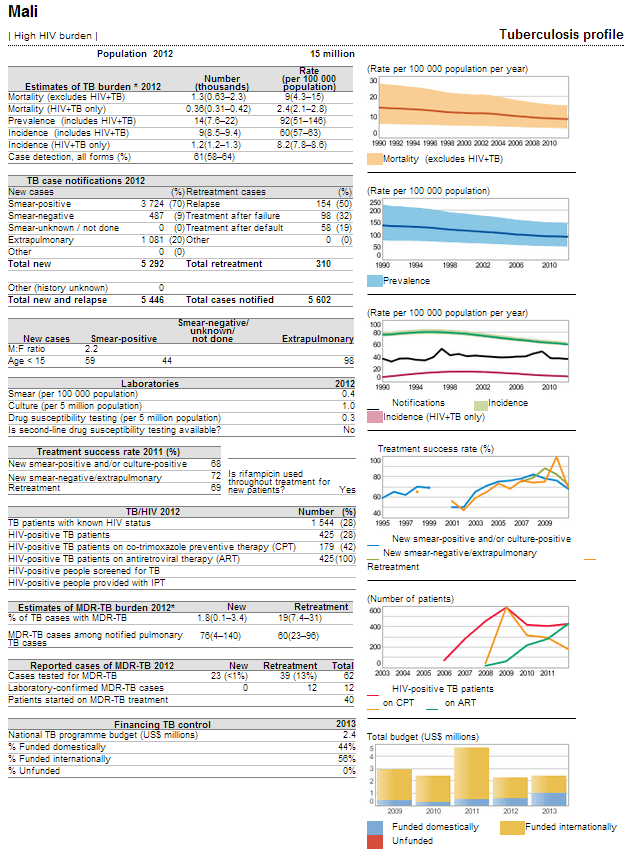
WHO has also used Style Intelligence to create a series of parameterized Web-based reports in the form of its Global Tuberculosis Report. Tuberculosis country profiles are generated automatically based on data reported by countries and which are held in WHO's global TB database. This information is updated on annual basis.
Users can choose what country's data they want to view by inputting a parameter, and the report will be run accordingly. Results can be viewed both on the Web or in .PDF format, as well as in English, Spanish, French, and Russian.