BI Analysis in Urban Traffic Management Departments
Business Intelligence (BI) analysis in traffic management departments involves leveraging data to gain insights into traffic patterns, optimize operations, and make informed decisions. Here's an overview of how BI analysis is typically done in traffic management:
- Data Collection and Integration:
- Traffic Sensors and Cameras: Utilizing sensors, cameras, and other IoT devices to collect real-time data on traffic conditions, including vehicle counts, speed, and congestion.
- Weather and Environmental Data: Integrating weather and environmental data to understand how external factors impact traffic.
- Data Warehousing:
- Centralized Storage: Storing data in a centralized data warehouse that allows for efficient management, analysis, and retrieval of traffic-related information.
- Data Cleaning and Transformation:
- Preprocessing: Cleaning and transforming raw data to ensure accuracy and consistency before analysis. This may involve handling missing values, removing outliers, and standardizing data formats.
- Traffic Analytics:
- Traffic Flow Analysis: Examining patterns in traffic flow to identify peak hours, congestion points, and areas with high traffic volume.
- Historical Analysis: Analyzing historical data to identify trends, seasonality, and recurring patterns.
- Predictive Modeling: Using predictive analytics to forecast future traffic conditions based on historical data and external factors.
- Route Optimization:
- GIS Integration: Integrating Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for spatial analysis and optimal route planning.
- Real-Time Navigation: Providing real-time navigation suggestions to drivers based on current traffic conditions and historical patterns.
- Incident Detection and Management:
- Anomaly Detection: Implementing BI algorithms to detect anomalies and incidents, such as accidents or road closures.
- Automated Alerts: Setting up automated alerts to notify authorities and emergency services about incidents that may impact traffic.
- Performance Monitoring:
- KPI Tracking: Defining and tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) related to traffic management, such as average speed, travel time, and congestion levels.
- Dashboard Reporting: Creating interactive dashboards that provide a visual representation of real-time and historical traffic data.
- Public Communication and Engagement:
- Dynamic Message Signs: Using BI insights to update dynamic message signs on roads, providing real-time information to drivers.
- Public Information Portals: Creating portals or mobile apps to share traffic updates, alternative routes, and information on ongoing construction or events.
- Regulatory Compliance and Reporting:
- Compliance Reporting: Generating reports to comply with regulatory requirements and standards.
- Performance Reports: Providing regular performance reports to stakeholders and the public.
- Resource Allocation:
- Optimizing Resources: Analyzing data to determine optimal resource allocation, such as adjusting traffic signal timings or deploying personnel to manage specific areas.
- Machine Learning and AI Integration:
- Predictive Maintenance: Using machine learning algorithms to predict maintenance needs for traffic infrastructure, such as traffic lights or sensors.
- Adaptive Traffic Control Systems: Implementing AI-driven traffic control systems that adapt to changing conditions in real-time.
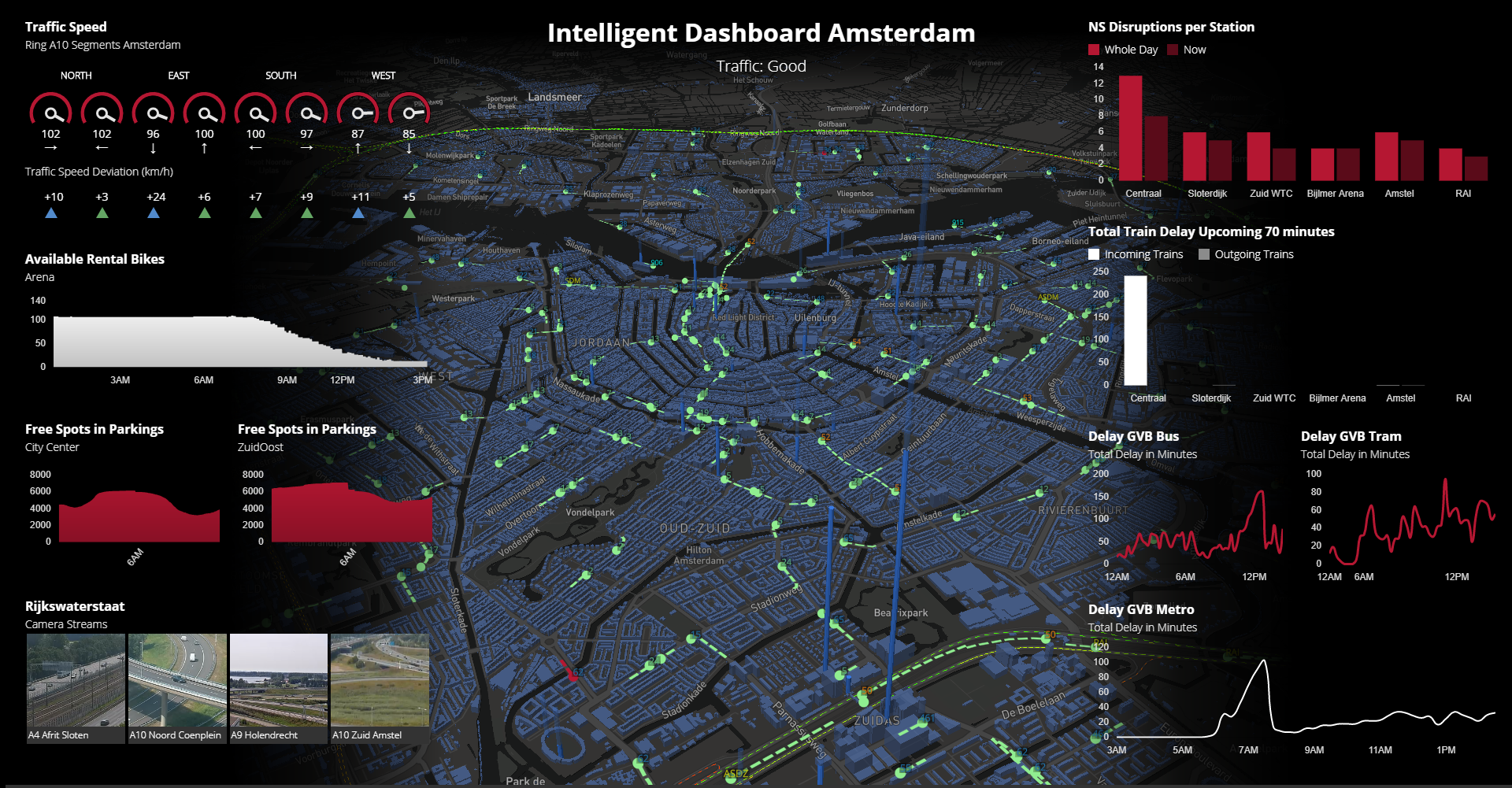
What Are Some Examples of Using AI in Urban Traffic Management?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a significant role in revolutionizing urban traffic management by introducing smart solutions to address congestion, enhance safety, and optimize transportation systems. Here are some examples of using AI in urban traffic management:
- Traffic Prediction and Forecasting:
- AI Algorithms for Prediction: Implementing machine learning algorithms to analyze historical traffic data and predict future traffic patterns.
- Dynamic Route Planning: Providing real-time recommendations to drivers based on predicted traffic conditions, optimizing routes to avoid congestion.
- Adaptive Traffic Signal Control:
- AI-Controlled Traffic Lights: Using AI algorithms to dynamically adjust traffic signal timings based on real-time traffic flow, reducing congestion and improving traffic efficiency.
- Intersection Optimization: Optimizing signal timings at intersections to prioritize high-traffic routes and reduce wait times.
- Smart Traffic Monitoring and Surveillance:
- Computer Vision and Video Analytics: Deploying AI-powered cameras to monitor traffic in real-time, detect incidents, and analyze vehicle movement patterns.
- Anomaly Detection: Using AI algorithms to identify unusual events, such as accidents or road obstructions, and automatically alerting traffic management authorities.
- Parking Management:
- Predictive Parking Availability: Implementing AI models to predict parking space availability based on historical data, sensor inputs, and current demand.
- Smart Parking Solutions: Utilizing AI-powered applications to guide drivers to available parking spaces, reducing traffic caused by searching for parking.
- Public Transportation Optimization:
- Demand Prediction for Public Transit: Using AI to analyze ridership data and predict demand for public transportation services.
- Dynamic Scheduling: Adjusting public transit schedules in real-time based on demand patterns, special events, or unexpected disruptions.
- Intelligent Traffic Control Centers:
- AI-Based Control Centers: Implementing AI-driven traffic control centers that analyze data from various sources to make real-time decisions on traffic management strategies.
- Integrated Data Fusion: Integrating data from sensors, cameras, and other sources to provide a comprehensive view of traffic conditions.
- Emergency Response and Evacuation Planning:
- AI for Emergency Detection: Using AI to identify emergency situations, such as accidents or natural disasters, and automatically adjusting traffic flows to facilitate emergency response.
- Evacuation Route Optimization: Planning and optimizing evacuation routes during emergencies based on real-time conditions.
- Dynamic Toll Pricing:
- AI-Driven Toll Pricing: Implementing dynamic toll pricing based on current traffic conditions to manage congestion and encourage alternative routes.
- Variable Pricing Strategies: Adjusting toll rates dynamically to optimize traffic flow and reduce bottlenecks.
- Pedestrian and Cyclist Safety:
- AI-Powered Crosswalk Monitoring: Using computer vision to detect and monitor pedestrian and cyclist activity at crosswalks, triggering signal adjustments for enhanced safety.
- Predictive Safety Analytics: Analyzing data to predict high-risk areas for pedestrians and cyclists and implementing safety measures accordingly.
- Noise and Pollution Monitoring:
- AI-Based Environmental Sensors: Utilizing AI to analyze data from environmental sensors to monitor noise levels and air quality.
- Adaptive Traffic Management for Environmental Impact: Implementing traffic management strategies to reduce pollution in real-time, such as diverting traffic away from high-pollution areas.
More Articles About BI Analysis
Artificial Neural Networks Based on Biology - In this article, continuing our introduction to machine learning, I am going to write a little bit about real neurons and the real brain which provide the inspiration for the artificial neural networks that we are striving to learn about in this series of articles. In most of the discussion, we won't talk much about real neurons, but I wanted to give you a quick overview at the beginning...
Link All Your Metrics - Here are some of the biggest mistakes I've seen organizations make. Probably one of the most common ones is coming up with some vague vision statement and then trying to link all your metrics and your scorecard to the vision. In fact, some of the books on balanced scorecards even suggest that that's how you should do it...
Measuring Organizational Vision - Number three has to do with being able to clarify and measure organizational vision. So what happens is all these stupid deliberate words go up on the board. The next step is to take all these deliberate words and just bring them together into some awkward sentence. So after six or eight hours of this nonsense, he ends up with some garbled sentence that says our vision is to...
Modern Balanced Scorecard - The balanced scorecard has evolved from its early use as a simple performance measurement framework to a full strategic planning and management system. The "new" balanced scorecard transforms an organization's strategic plan from an attractive but passive document into the "marching orders" for the organization on a daily basis. It provides a framework that not only...