What KPIs and Analytics Does a Customer Experience Operations Analyst Use?
Providing outstanding customer experience has become an important difference in today's fiercely competitive corporate environment. Companies use customer experience operations analysts, who are critical in gauging and enhancing customer happiness, to do this.
To acquire insights into consumer behavior, pinpoint problem areas, and enhance the overall customer experience, these analysts use a variety of key performance indicators (KPIs) and analytics. The important KPIs and data that customer experience operations analysts utilize to fuel company performance will be discussed in this article.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
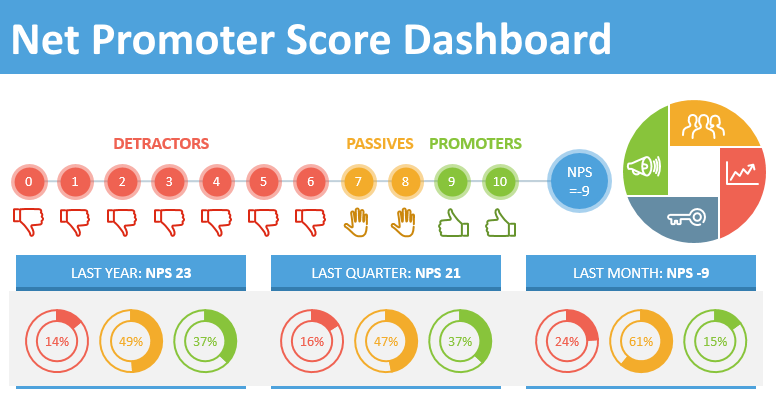
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is one of the key KPIs used by customer experience operations analysts. By calculating the chance that consumers would refer a brand's goods or services to others, NPS calculates customer loyalty. Analysts gather data to compute NPS using surveys and other feedback channels, allowing them to evaluate consumer happiness and spot brand supporters or detractors. Analysts may make strategic judgments based on the effect of their actions on customer loyalty by tracking NPS over time.
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
Customer experience operations analysts also heavily depend on the Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) KPI. CSAT gauges a customer's degree of satisfaction based on certain interactions or experiences with a business. Analysts gather quantitative or qualitative information via surveys or post-interaction comments to construct CSAT scores. By highlighting areas of special customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction, this KPI enables analysts to discover possibilities for development and to take well-informed choices to improve the entire customer experience.
Customer Effort Score (CES)
The Customer Effort Score (CES) KPI measures how simple or complex customer interactions are. It evaluates the effort consumers make to solve problems, make purchases, or interact with a business. Analysts can determine CES ratings and pinpoint pain areas in the customer journey by gathering data via surveys or other feedback channels. Higher CES ratings identify areas that need work, while lower CES scores reflect encounters that are more seamless, enabling analysts to optimize procedures and minimize consumer effort.
First Contact Resolution (FCR) Rate
The proportion of client questions or problems that are addressed at the first contact with customer support or service teams is known as the first contact resolution (FCR) rate. Analysts of customer experience operations use FCR as a KPI to assess the performance of customer care agents and the effectiveness of support procedures. Rapid and satisfactory problem resolution results in higher customer satisfaction and less effort from the customer. This is shown by a high FCR rate.
Customer Churn Rate
Customer experience operations analysts utilize the customer turnover rate as a key KPI to evaluate customer loyalty and retention. It calculates the proportion of clients who end their engagement with a business over a certain time frame. Analysts can pinpoint the causes of customer attrition and take proactive steps to solve them by tracking churn rate trends and studying churn drivers. To reduce churn, this KPI helps create retention strategies and enhances overall customer experience.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
The Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) statistic calculates the overall value a customer contributes to a business over the course of their relationship. CLV is a tool used by customer experience operations analysts to categorize customers based on their long-term profitability. Analysts may identify high-value consumers and provide individualized experiences to optimize their worth by studying CLV. The return on investment (ROI) of client acquisition and retention initiatives may also be calculated using CLV.
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
Text and Sentiment Analysis
Analysts that focus on customer experience use text and sentiment analysis to glean important information from reviews, comments, and social media data. They can classify and analyze unstructured textual data using natural language processing (NLP) methods, giving them a better knowledge of consumer sentiment, preferences, and pain areas. By identifying new trends, reoccurring problems, and sentiment patterns, this research enables analysts to make data-driven choices that will improve the customer experience.
Journey Mapping and Funnel Analysis
Customer experience operations analysts employ tools like customer journey mapping and funnel analysis to visualize and comprehend the whole customer experience. Journey mapping is putting the interactions, touchpoints, and feelings of the consumer throughout their relationship with a firm into visual form. The evolution of the consumer through the various conversion process phases is tracked through funnel analysis. By using these strategies, analysts are better able to optimize the customer experience and increase conversions by discovering bottlenecks, drop-off spots, and places for improvement.
Average Resolution Time
The Average Resolution Time (ART) metric tracks how long it typically takes to address customer complaints or queries. This KPI aids analysts in determining how quickly and effectively customer care staff can resolve issues. Analysts may spot places where response or resolution times are longer than intended by monitoring ART, and then they can put initiatives in place to increase productivity, decrease wait times, and improve the overall customer experience.
Customer Retention Rate
The Customer Retention Rate (CRR) is the proportion of clients who stick with a business's goods or services over time. Analysts may assess the efficacy of client retention strategies and activities by measuring CRR. A high CRR suggests that consumers are happy and engaged, while a low rate might indicate possible problems that need to be addressed. Analyzing CRR directs efforts to retain important clients and identifies opportunities for development.
 |
Learn the advantages of InetSoft's small footprint BI platform. |
Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is the process of breaking the customer base into different categories according to a set of traits, habits, or preferences. Analysts working in customer experience operations employ segmentation to learn more about the wants, requirements, and preferences of their clients. Analysts may create more individualized and targeted interactions by breaking down each segment into its component parts and then tailoring their strategy, communication, and experiences to fit the specific needs of various client groups.
Customer Lifetime Value to Acquisition Cost Ratio
The Customer Lifetime Value to Acquisition Cost (CLV:CAC) ratio evaluates the value that a customer contributes to a business over the course of their relationship. This ratio aids analysts in determining how profitable and long-lasting client acquisition initiatives are. If the CLV:CAC ratio is high, the firm is likely outpacing the cost of acquiring new consumers in terms of value over time. Analysts may optimize return on investment by improving marketing and acquisition efforts by keeping an eye on this ratio.
Social Media Engagement Metrics
A important platform for client interactions and feedback is social media. On social media networks, customer experience operations analysts monitor different engagement metrics like likes, comments, shares, and mentions. These stats include information on the social media reach, influence, and sentiment of a company's name, goods, or services. Analysts can assess client opinion, spot patterns, and quickly resolve customer issues by examining social media interaction.
Customer Effort Analytics
Analyzing data pertaining to customer effort across various touchpoints and channels is known as customer effort analytics. Analysts may gauge the efficiency of customer support services and spot opportunities to minimize customer effort by measuring customer interactions, self-service adoption rates, and contact deflection. For improved customer experience, procedures can be streamlined, self-service alternatives can be improved, and support channels can be optimized.
Read what InetSoft customers and partners have said about their selection of Style Report as their production reporting tool. |
Customer Sentiment Analysis
Customer sentiment analysis entails assessing comments, reviews, and social media postings from customers to ascertain how they feel generally about a business, product, or service. Analysts may get insights into client satisfaction, preferences, and pain spots by classifying comments as positive, negative, or neutral using sentiment analysis methods. This analysis aids in pinpointing particular areas that need improvement and directs the formulation of plans to respond to customer complaints and improve the customer experience.
Customer Effort Score by Channel
Finding changes in customer effort levels across various touchpoints is made easier by channel-specific analysis of Customer Effort Score (CES). Analysts may identify which channels give the most smooth and seamless experiences and which may need work by comparing the CES ratings for different channels like phone assistance, email, chatbots, or self-service portals. This research helps prioritize improvements to channels that need more consumer effort and distribute resources efficiently.