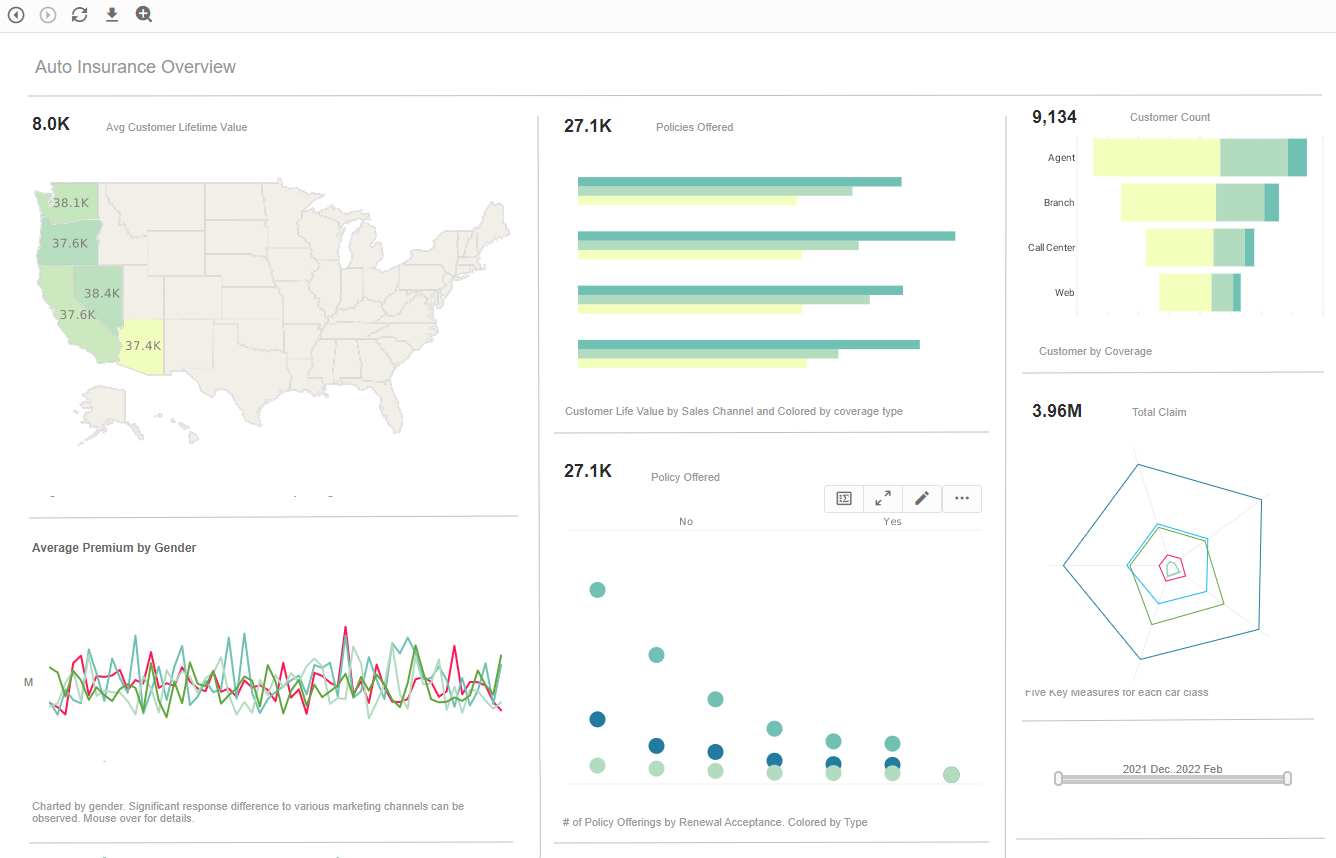
What Key Metrics Does an Insurance Operations Analyst Use?
By ensuring that diverse operational tasks run smoothly, insurance operations analysts play a significant role in the insurance sector. To gauge and track the effectiveness of insurance operations, these experts depend on key performance indicators (KPIs) and analytics.
In this article, we'll look at the important KPIs and data that insurance operations analysts use to boost productivity, raise client happiness, and improve financial results
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
Claims Processing Key Metrics
- Claim Cycle Time: This indicator gauges the typical processing time from claim filing to settlement. This KPI is monitored by insurance operations analysts to spot bottlenecks and speed up the claims process.
- Claims Settlement Ratio: Based on the total number of claims received, this KPI determines the proportion of claims that were successfully resolved. It aids analysts in assessing the efficacy of claims management procedures.
- Average Claim Cost: Analysts may see trends and patterns that may affect the company's profitability by looking at the average cost of claims. For monitoring claim reserves and pricing rules, this KPI is important.
Policy Administration Key Metrics
- Policy Issuance Time: This statistic tracks how long it takes to process an application and issue a policy. To guarantee prompt policy issuance and enhance the client experience, insurance operations analysts track this KPI.
- Policy Renewal Rate: Analysts can gauge client loyalty and pinpoint opportunities for development by monitoring the proportion of policies that are renewed. The development of retention tactics and raising policyholder satisfaction are both aided by this KPI.
- Policy Underwriting Accuracy: This KPI examines the proportion of policies produced without mistakes or omissions in order to evaluate the precision of underwriting judgments. This statistic is used by insurance operations analysts to identify possible hazards and enhance the underwriting process.
Customer Service Key Metrics
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Through surveys or other forms of input, this statistic evaluates customer satisfaction levels. Insurance operations analysts review CSAT results to identify areas where customer service procedures need to be improved.
- First Contact Resolution (FCR): FCR gauges the proportion of customer questions or problems that are addressed after the first contact. This KPI is used by analysts to assess the effectiveness of customer service and identify areas where customers may exert less effort.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): The NPS gauges the possibility that consumers will refer other people to the insurance provider. Analysts of insurance operations monitor NPS to evaluate total customer loyalty and pinpoint tactics to increase brand advocacy.
Operational Efficiency Key Metrics
- Expense Ratio: This KPI aids analysts in evaluating the cost effectiveness of insurance operations by contrasting operational costs with net premiums received. Analysts may identify opportunities for cost-cutting and process improvement by keeping an eye on this ratio.
- Loss Ratio: The proportion of premiums that are used to pay claims is measured by the loss ratio. This KPI is examined by insurance operations analysts to assess underwriting profitability and identify opportunities for risk reduction.
- Productivity Metrics: These indicators of the operations team's productivity include claims per employee and policies handled per hour. These KPIs are monitored by analysts to identify areas where training or process improvements might increase efficiency.
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
Risk Management Key Metrics
- Risk Assessment Accuracy: This KPI assesses the precision of risk evaluations made throughout the underwriting procedure. Insurance operations experts look at this indicator to make sure that policy prices are correct and to spot any possible problems.
- Loss Development: The projected loss reserves are changed over time and are tracked through loss development analysis. This technique is used by analysts to assess the correctness of initial loss reserves and make the necessary adjustments.
- Loss Frequency and Severity: The frequency and severity of insurance losses are gauged by these KPIs. Insurance operations analysts keep an eye on these indicators to spot patterns and trends in claims, which may aid in developing risk-reduction plans.
Compliance and Regulatory Key Metrics
- Regulatory Compliance Rate: This statistic calculates the proportion of compliance with rules and regulations. In order to guarantee compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, insurance operations analysts monitor this KPI.
- Audit Findings: Analysts may spot areas of non-compliance, inadequate control measures, or ineffective processes by reviewing audit data. This knowledge aids in adopting remedial measures and enhancing operating procedures.
Fraud Detection and Prevention Key Metrics
- Fraud Detection Rate: The proportion of discovered fraudulent claims is measured by this statistic. In order to evaluate the efficiency of fraud detection procedures and enhance fraud prevention tactics, insurance operations analysts monitor this KPI.
- False Positive Rate: The proportion of instances that are initially marked as fraudulent but are subsequently shown to be authentic is measured by the false positive rate. This KPI is analyzed by analysts to improve algorithms for fraud detection and reduce false positives.
 |
Learn the advantages of InetSoft's small footprint BI platform. |
Sales and Marketing Key Metrics
- Conversion Rate: The conversion rate calculates the proportion of leads or prospects that result in the sale of real insurance. This KPI is monitored by insurance operations analysts to evaluate the success of sales and marketing initiatives.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV determines a customer's net profit over the course of their whole contract with the insurance provider. CLV is a metric that analysts use to identify high-value clients and create specialized retention plans.
- Channel Performance: Insurance operations analysts may identify opportunities for channel-specific improvements by examining the performance of various sales channels (such as agents, internet platforms, etc.).
Operational Risk Key Metrics
- Operational Risk Incidents: This indicator keeps tabs on the quantity and severity of events related to operational risk, such as system breakdowns, data breaches, or procedural mistakes. This data is used by analysts to identify possible operational issues and put risk-reduction strategies in place.
- Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR): The average amount of time needed to remedy operational problems or events is measured by MTTR. To guarantee prompt resolution and minimize the effect on operations, insurance operations analysts keep an eye on this KPI.