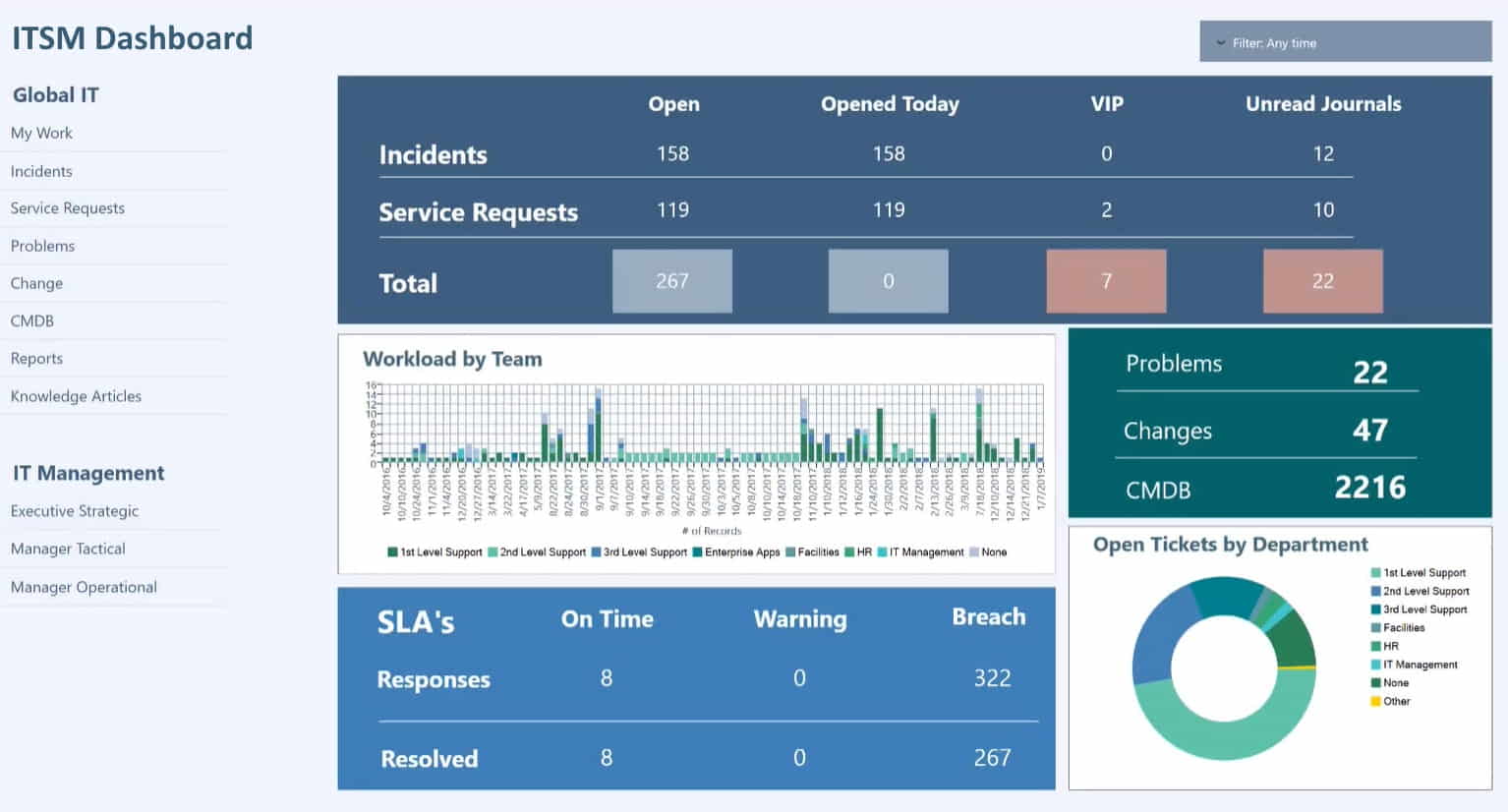
InetSoft's BI Software for Tracking KPIs in IT
InetSoft's BI software can be used to track IT KPIs. InetSoft's solution is true Software-as-a-Service for hosted and self-hosting, not a combination of client developer tools and a web-based delivery platform.
The dashboard application can be configured to access whatever data source contains your IT KPI data, and then with a drag and drop dashboard designer, anyone can quickly create and deploy a web-based interactive dashboard for tracking whatever IT KPIs they wish, such as service desk availability, datacenter power usage effectiveness (PUE), Corporate average data efficiency (CADE), or % of IT contribution in ROTA.
- Deployed in just weeks
- Learned by end users with minor training
- Adapt to however you define your IT KPIs
- Allow exploration for performance trends via visualization techniques
- Enable maximum self service
- Satisfy demanding executives
- Meet the requirements of power users
- Scale up for organizations of any size
StyleBI from InetSoft. It's Easy. Agile. Robust.
KPIs Used in IT: What They Mean and How to Use Them
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as the compass for IT organizations, providing measurable values that demonstrate how effectively teams achieve key business objectives. In the rapidly evolving technology landscape, IT departments must align their operations with business goals while maintaining operational excellence. Understanding and implementing the right KPIs enables IT leaders to make data-driven decisions, optimize resources, and demonstrate value to stakeholders.
Understanding IT KPIs
IT KPIs differ from general business metrics in that they focus on technology-specific outcomes that directly impact business operations. These indicators must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). The most effective IT KPIs bridge the gap between technical performance and business value, translating complex technical metrics into language that executives and stakeholders can understand and act upon.
System Performance and Availability KPIs
System Uptime/Availability: This fundamental KPI measures the percentage of time systems are operational and accessible to users. Calculated as (Total Time - Downtime) / Total Time × 100, this metric typically targets 99.9% or higher for critical systems. Organizations use this KPI to assess infrastructure reliability and plan maintenance windows effectively.
Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): MTTR measures the average time required to restore service after a failure occurs. This KPI helps evaluate incident response effectiveness and guides investments in monitoring tools, automation, and staff training. Lower MTTR values indicate more efficient problem resolution processes.
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): This metric calculates the average operational time between system failures, providing insights into system reliability and helping predict future maintenance needs. MTBF helps IT teams schedule preventive maintenance and budget for hardware replacements.
Security and Compliance KPIs
Security Incident Response Time: This KPI measures how quickly the IT security team responds to and resolves security incidents. Faster response times reduce potential damage from breaches and demonstrate the effectiveness of security procedures and training programs.
Patch Management Compliance: This metric tracks the percentage of systems that receive security patches within defined timeframes. High compliance rates indicate effective vulnerability management and reduce security risks across the organization.
Data Backup Success Rate: This KPI measures the percentage of successful backup operations, ensuring business continuity and disaster recovery capabilities. Regular monitoring prevents data loss and ensures recovery objectives can be met.
User Experience and Support KPIs
First Call Resolution Rate: This metric tracks the percentage of support tickets resolved during the initial contact. Higher rates indicate effective knowledge management, skilled support staff, and well-designed self-service options, leading to improved user satisfaction and reduced support costs.
Average Response Time: This KPI measures how quickly IT support responds to user requests, directly impacting user productivity and satisfaction. Organizations typically set different response time targets based on ticket priority levels.
User Satisfaction Scores: Through surveys and feedback mechanisms, this KPI gauges user perception of IT services quality. High satisfaction scores correlate with effective service delivery and help identify areas for improvement.
Financial and Resource Management KPIs
IT Cost per Employee: This metric calculates total IT spending divided by the number of employees, helping organizations benchmark against industry standards and identify cost optimization opportunities. It provides insights into IT investment efficiency and scaling patterns.
Project Budget Variance: This KPI measures the difference between planned and actual project costs, indicating project management effectiveness and financial control. Consistent budget adherence demonstrates strong project governance and resource planning.
Return on IT Investment (ROI): This metric evaluates the financial return generated by IT investments, helping justify technology expenditures and prioritize future investments. ROI calculations should include both direct cost savings and productivity improvements.
Implementation Strategies
Start with Business Alignment: Begin by identifying how IT services directly support business objectives. Select KPIs that demonstrate IT's contribution to revenue generation, cost reduction, or competitive advantage. This alignment ensures stakeholder buy-in and resource allocation.
Successful KPI implementation requires establishing baseline measurements before setting targets. Historical data provides context for realistic goal-setting and helps identify trends over time. Organizations should focus on a balanced scorecard approach, combining operational, financial, and strategic metrics to provide comprehensive performance visibility.
Data collection and reporting mechanisms must be automated wherever possible to ensure consistency and reduce manual effort. Dashboard tools and monitoring systems should provide real-time visibility into KPI performance, enabling proactive management and quick response to emerging issues.
Best Practices for KPI Management
Regular review and adjustment of KPIs ensures continued relevance as business needs evolve. Quarterly assessments should evaluate whether existing metrics still align with strategic objectives and identify new KPIs that may be needed. This iterative approach prevents metric stagnation and maintains focus on value creation.
Communication plays a crucial role in KPI success. Regular reporting to stakeholders should highlight achievements, explain variances, and outline improvement plans. Visual dashboards and executive summaries help translate technical metrics into business language that resonates with different audiences.
Training and accountability ensure that team members understand how their work contributes to KPI performance. Clear ownership assignments and regular performance discussions help maintain focus on continuous improvement and goal achievement.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Organizations often struggle with measuring too many KPIs simultaneously, leading to confusion and diluted focus. The solution involves prioritizing metrics based on business impact and focusing on a core set of indicators that drive meaningful action. Quality trumps quantity in KPI selection.
Another common challenge involves setting unrealistic targets that discourage teams rather than motivate improvement. Successful KPI programs use incremental target-setting, celebrating progress while maintaining stretch goals that encourage innovation and efficiency gains.
Finally, organizations must avoid the trap of managing to metrics rather than managing for results. KPIs should guide decision-making and improvement efforts, not become ends in themselves. Regular validation ensures that improved KPI scores translate into genuine business value and user satisfaction.
Effective IT KPI management transforms technology departments from cost centers into strategic business partners. By carefully selecting, implementing, and managing the right performance indicators, IT organizations can demonstrate value, optimize operations, and contribute meaningfully to organizational success. The key lies in balancing technical excellence with business outcomes, ensuring that every metric tells a story of value creation and continuous improvement.