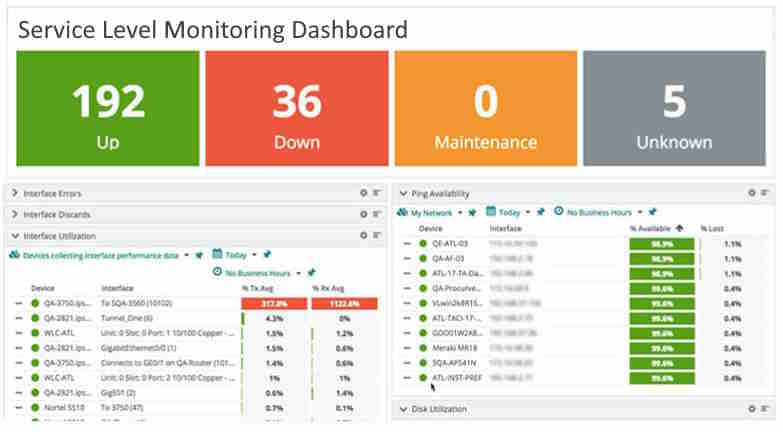
What KPIs and Analytics Are Used on a Service Level Monitoring Dashboard?
In order to guarantee ideal service levels and client happiness, it is essential to monitor the functioning of these services. An efficient way for organizations to manage and assess service performance is via the use of a service level monitoring dashboard, which offers a thorough overview of key performance indicators (KPIs) and analytics.
The key KPIs and analytics used on a service level monitoring dashboard are examined in this article.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
Availability and Uptime Metrics
- Service Uptime: The proportion of time a service is operational is measured by this KPI. It offers information on the service's dependability and accessibility.
- Downtime Duration: The length of service outages is measured by this statistic. Analysis of downtime patterns reveals recurrent problems and areas for development.
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): The average interval between servicing failures is calculated using MTBF. It helps in the identification of patterns and possible regions for improving service stability.
Response Time and Performance Metrics
- Average Response Time: This KPI calculates how quickly a service responds to user queries. Reduced response times increase customer happiness and experience.
- Latency: The time difference between the beginning of a request and the beginning of a response is known as latency. Analyzing latency helps in identifying bottlenecks and improving service effectiveness.
- Throughput: The throughput of a service is the volume of requests it can process in a given amount of time. Monitoring throughput helps in determining the capacity and scalability of the service.
Error and Incident Management Metrics
- Error Rate: The proportion of unsuccessful requests or transactions is determined by this KPI. Monitoring mistake rates enables the discovery of possible problems that may be hurting customer satisfaction and service performance.
- Incident Count: The number of service issues reported during a certain time period is quantified by this measure. Finding reoccurring issues and prioritizing your troubleshooting efforts are made easier by analyzing incident patterns.
- Mean Time to Recover (MTTR): The average amount of time needed to restore a service after an event is measured by MTTR. The effect on customers is reduced while service availability is improved by reducing MTTR.
User Satisfaction Metrics
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): CSAT measures how satisfied consumers are with the service. Surveys and ratings are used to collect customer input and determine how well the service is regarded.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Customers' propensity to suggest the service to others is measured by NPS. It demonstrates the service's capacity to develop devoted supporters who actively market the company.
- Customer Effort Score (CES): CES evaluates how simple it is to use the service and carry out requested tasks. Reduced customer effort results in an enhanced user experience and more satisfaction.
Capacity Planning Metrics
- Utilization Rate: This KPI gauges how much of the service's resources are really used. Monitoring use enables the detection of possible capacity issues and resource allocation optimization.
- Scalability: Metrics on scalability evaluate the service's capacity to meet rising customer demand. Planning for future development and making sure the service can handle growing user bases are both aided by scalability analysis.
Security and Compliance Metrics
- Security Incident Count: This measure provides a numerical representation of the service's security incidents or breaches. Monitoring security occurrences helps to spot weaknesses and improve security procedures.
- Compliance Adherence: Monitoring compliance metrics makes ensuring the service abides with organizational and industry norms. It lessens the likelihood of violations and associated fines.
Service Usage and Adoption Metrics
- Active Users: This indicator keeps tabs on how many distinct users actively utilize the service during a certain period of time. Monitoring active users helps in evaluating service engagement and uptake.
- Session Duration: The amount of time that users typically spend engaging with the service during a session is measured by session length. Understanding user engagement levels requires analysis of session length.
- Feature Adoption: This measure assesses how often users use certain features or functions of the service. It assists in determining popular features and potential improvement areas.
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
Service Level Agreement (SLA) Metrics
- SLA Compliance: This KPI calculates the proportion of service-level agreements that are fulfilled within the predefined SLA limits. Making ensuring service delivery complies with SLAs guarantees that it meets consumer expectations.
- Response and Resolution Time: These metrics assess how long it takes to recognize and address consumer questions or problems. Monitoring response and resolution times helps in achieving SLA goals and enhancing client satisfaction.
Cost and Efficiency Metrics
- Cost per Transaction: This statistic figures out the typical cost involved in handling a single transaction or service request. Monitoring the cost per transaction helps in increasing operational effectiveness and finding areas for cost-savings.
- Resource Utilization: Metrics for resource utilization evaluate how well infrastructure, hardware, or software resources are allocated and used. It aids in resource underutilization and cost-efficiency optimization.
Service Outage Impact Metrics
- Revenue Impact: This statistic calculates the cost of service interruptions or outages on revenue production. Prioritizing investments in service dependability and resilience is made easier with an understanding of revenue losses.
- Customer Churn Rate: Churn rate counts the number of customers that stop using a service because they are unsatisfied or experience service disruptions. Determine the effect of interruptions on client retention by tracking churn rate.
 |
Learn the advantages of InetSoft's small footprint BI platform. |
Trend Analysis and Forecasting
- Service Performance Trends: Finding patterns, abnormalities, and possible service performance enhancements is made easier by analyzing previous data and trends. The predicting of future service needs is aided by trend analysis.
- Predictive Analytics: To predict service performance, identify anomalies, and proactively handle future problems, predictive analytics makes use of historical data and machine learning algorithms.
Service Level Monitoring Benchmarking
- Industry Comparisons: Comparing service performance to industry benchmarks and rivals reveals relative performance and potential improvement areas.
- Internal Benchmarking: In order to find best practices and chances for standardization, departments or business units within an organization might compare service performance.