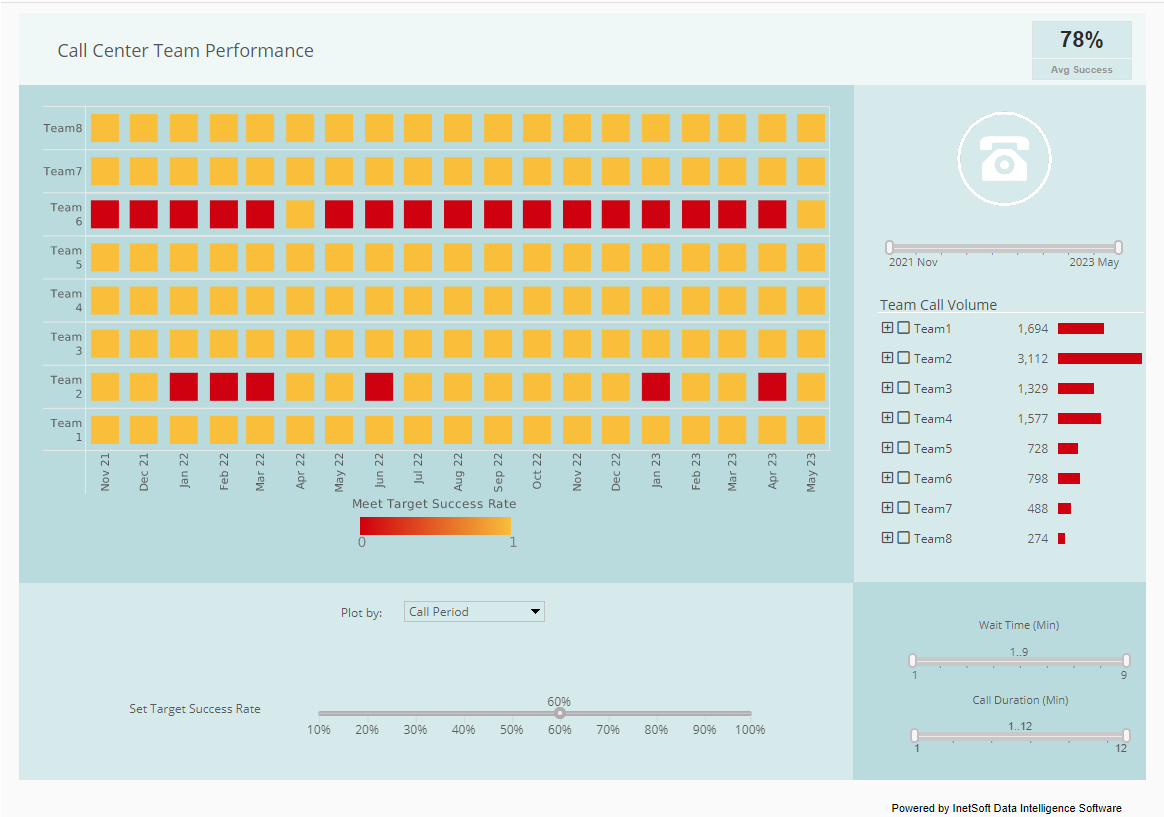
What Features Are Required for an SQL Server Dashboard Tool?
An effective SQL Server dashboard tool should possess a set of essential features to provide users with meaningful insights and facilitate data-driven decision-making. Here are key features required for an SQL Server dashboard tool:
- Data Connectivity and Integration:
- SQL Server Integration: Seamless integration with SQL Server databases to retrieve and visualize data directly.
- Support for Multiple Data Sources: Ability to connect to various data sources beyond SQL Server for comprehensive data analysis.
- User-Friendly Interface:
- Drag-and-Drop Design: Intuitive, drag-and-drop interface for building dashboards without extensive technical expertise.
- Customization Options: Flexibility to customize dashboard layouts, themes, and components to meet user preferences.
- Real-Time Data Updates:
- Live Data Streaming: Support for real-time or near-real-time data updates to provide users with the latest information.
- Scheduled Refresh: Ability to schedule automatic data refreshes at specified intervals.
- Data Visualization:
- Rich Chart Types: Availability of a variety of chart types (bar charts, line charts, pie charts, etc.) for diverse data representation.
- Maps and Geographic Visualization: Capability to incorporate maps and geospatial visualizations for location-based insights.
- Interactive Elements: Interactive features such as drill-downs, tooltips, and filters for a dynamic user experience.
- Dashboard Components:
- Widgets and Gauges: Different types of widgets and gauges for displaying key performance indicators (KPIs) in a visually appealing manner.
- Tables and Grids: Support for displaying tabular data with sorting and filtering options.
- Mobile Responsiveness:
- Responsive Design: Ensuring that dashboards are accessible and user-friendly on various devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Security and Access Control:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Granular control over user access based on roles and permissions.
- Data Encryption: Implementation of encryption mechanisms to secure sensitive data.
- Alerts and Notifications:
- Threshold Alerts: Ability to set thresholds for key metrics and receive alerts when predefined thresholds are breached.
- Notification Channels: Support for various notification channels such as email or in-dashboard alerts.
- Embedding and Sharing:
- Embeddable Dashboards: Capability to embed dashboards seamlessly into other applications or portals.
- Sharing Options: Easy sharing of dashboards with colleagues or stakeholders through links or exports.
- Performance Optimization:
- Caching Mechanisms: Efficient caching strategies to enhance dashboard loading speed.
- Query Optimization: Optimized SQL queries for improved performance with large datasets.
- Scalability:
- Scalable Architecture: Ability to scale to handle growing data volumes and user demands.
- Integration with Other Tools:
- Integration with BI Tools: Compatibility with popular business intelligence tools for extended analytics capabilities.
- API Support: Availability of APIs for integration with external applications and services.
- Documentation and Support:
- User Documentation: Comprehensive documentation for users and administrators.
- Customer Support: Responsive customer support for assistance with technical issues.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
What Levels of Security Does InetSoft Offer?
InetSoft places a strong emphasis on security to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data within its business intelligence and reporting solutions. The platform offers multiple levels of security features to safeguard sensitive information. Here are some key aspects of the security levels provided by InetSoft:
- Authentication Mechanisms:
- User Authentication: InetSoft supports robust user authentication mechanisms, ensuring that only authorized users can access the platform.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Integration with SSO solutions for seamless and secure user access across multiple applications.
- Authorization and Access Control:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Granular control over user permissions based on roles, allowing administrators to define who can access specific features and data.
- Object-Level Security: Fine-grained control over access to individual reports, dashboards, or data sources.
- Data Encryption:
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): Encryption of data in transit through the use of TLS protocols, ensuring secure communication between clients and the InetSoft server.
- Data-at-Rest Encryption: Options for encrypting stored data to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Secure Data Handling:
- Data Masking: Capability to mask or anonymize sensitive data to protect privacy and comply with regulations.
- Secure Data Transmission: Ensuring secure transmission of data between components within the InetSoft platform.
- Audit Trail and Logging:
- Audit Logging: Recording and logging of user activities, system events, and access attempts for auditing purposes.
- Log Management: Centralized management of logs to facilitate monitoring and investigation.
- Secure Integration and APIs:
- API Security: Security measures for APIs, including authentication and authorization, to ensure secure integration with external applications.
- Secure Connectivity to Data Sources: Secure connections to various data sources, including SQL Server databases, with options for encrypted communication.
- Secure Administration:
- Admin Console Security: Protection of the administrative console through secure authentication and authorization mechanisms.
- Configuration Security: Ensuring secure configuration settings to prevent unauthorized changes.
- Secure Deployment Options:
- On-Premises Security: Security measures for on-premises deployments, including network security and server hardening.
- Cloud Security: Ensuring security best practices for cloud-based deployments, including compliance with cloud provider security standards.
- Compliance and Certifications:
- Regulatory Compliance: Alignment with industry regulations and compliance standards to meet data protection and privacy requirements.
- Certifications: Adherence to security certifications and standards to demonstrate a commitment to security best practices.
- User Education and Training:
- Security Awareness Training: Educational resources and training materials to promote security awareness among users and administrators.