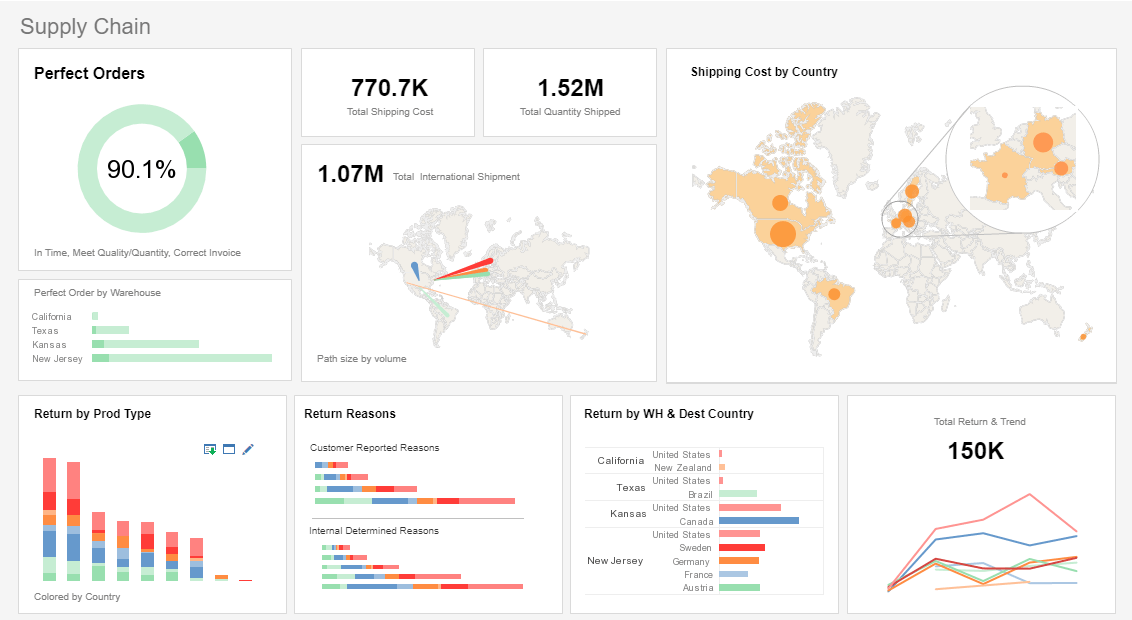
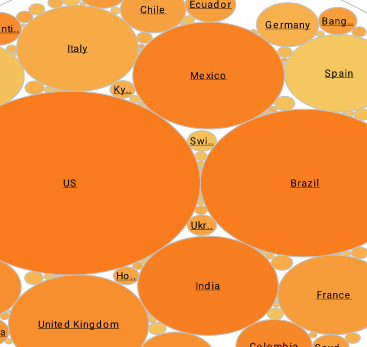
What Metrics Does a Supply Chain Operations Analyst Use?
The effective flow of products and services from suppliers to end consumers is ensured in large part by supply chain management.
Supply chain operations analysts play a significant role in this process' optimization by keeping an eye on key performance indicators (KPIs) and using analytics to spot potential areas for development.
The performance of supply networks may be improved by supply chain operations analysts using key KPIs and analytics, which we shall discuss in this article.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
Inventory Turnover Ratio
The effectiveness of a company's inventory management is gauged by its inventory turnover ratio. It is derived by dividing the average inventory value by the cost of goods sold (COGS). A high inventory turnover ratio implies that the firm is not retaining extra stock and that its items are selling rapidly, which may lower carry costs and boost cash flow.
Order Fill Rate
An important KPI to measure how successfully a business satisfies client demand is the order fill rate. It calculates the proportion of client orders that are fully and promptly fulfilled. A supply chain that is capable of satisfying customer expectations and reducing backorders or stockouts has a high order fill rate.
On-Time Delivery (OTD)
The proportion of orders that are delivered to clients on time or earlier than the specified delivery date is measured by the crucial indicator known as on-time delivery. A dependable supply chain with efficient planning and execution that produces happy customers and improved reputation is indicated by a high OTD rate.
Perfect Order Fulfillment
The proportion of orders that are delivered without any mistakes or problems, such as erroneous products, damaged goods, or delayed shipments, is measured by the flawless order fulfillment statistic. A supply chain that is well-organized and excels in precision and dependability will have a high percentage of flawless order fulfillment.
Supplier Performance Metrics
The performance indicators of suppliers are regularly monitored by supply chain operations analysts to make sure they fulfill requirements for quality, cost, and delivery. The lead time variability, supplier failure rate, and on-time delivery from suppliers are important supplier KPIs. Building solid supplier relationships and minimizing supply chain interruptions are made possible by analyzing these indicators.
Transportation Cost per Unit
A cost-related KPI called transportation cost per unit counts the costs associated with transporting items from one place to another. Supply chain operations experts may pinpoint inefficient transportation practices and put into place cost-cutting strategies like streamlining shipping routes or grouping shipments by studying this parameter.
Warehouse Utilization Rate
The effectiveness of using warehouse space is gauged by the warehouse utilization rate. It is computed by dividing the total volume of inventory by the total amount of warehouse storage. A high warehouse utilization rate shows efficient use of the available space, whilst a low rate may point to the need for better warehouse structure or inventory control techniques.
Lead Time
From the moment an order is placed until it is delivered, the lead time measures how long it takes for a product to travel through the complete supply chain. Supply chain operations experts may identify bottlenecks and reduce procedures by analyzing lead time, which leads to quicker order fulfillment and more customer satisfaction.
Return Rate
The proportion of items returned by consumers is measured by the return rate. High return rates may indicate poor product quality, incomplete orders, or unsatisfied customers. Supply chain operations analysts can address underlying problems and lower return rates, which will result in cost savings and enhanced customer loyalty.
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
Forecast Accuracy
A key analytics statistic called forecast accuracy assesses how well demand estimates compare to actual sales. Supply chain operations analysts use accurate forecasting to efficiently manage production schedules, optimize inventory levels, and coordinate resources. This statistic helps companies to reduce unnecessary inventory expenses and stockouts, which boosts profitability.
Cash-to-Cash Cycle Time
The time it takes for a business to turn its cash investments in inventory back into cash via sales is known as the cash-to-cash cycle time. It entails figuring out how long, on average, it takes to be paid by clients after paying suppliers for raw materials. The working capital management and liquidity are enhanced when the cash-to-cash cycle time is decreased.
Supply Chain Cost as a Percentage of Revenue
By calculating the overall supply chain expenses as a proportion of total revenue produced, this KPI assesses the effectiveness of the supply chain. A decreased supply chain cost % shows that the chain is running more cost-effectively, making the most of costs, and improving the company's total profitability.
 |
Learn the advantages of InetSoft's small footprint BI platform. |
Fill Rate vs. Forecasted Demand
How closely the actual demand matches the predicted demand is gauged by fill rate vs. expected demand. While a considerable difference between actual and expected demand may indicate problems with forecasting accuracy, production planning, or inventory management, a high fill rate indicates that the supply chain is successfully satisfying demand.
Customer Service Level
Customer service level is a statistic that measures a company's capacity to execute orders in accordance with customer expectations. It takes into account things like order accuracy, on-time delivery, and customer service response. A high degree of customer service improves client retention, satisfaction, and brand loyalty.
Supply Chain Resilience
An analytics method called supply chain resilience evaluates a supply chain's capacity to resist interruptions and bounce back fast after them. Supply chain operations analysts may create plans to improve the resilience of the supply chain and lessen the effects of interruptions by identifying weaknesses and possible threats.
Transportation Lead Time
The amount of time it takes for items to go from the supplier to the warehouse or from the warehouse to the customer is known as the transportation lead time. Analyzing transportation lead time enables improved coordination between suppliers, carriers, and distribution hubs and aids in spotting inefficiencies in logistics procedures.
Sustainability Metrics
Sustainability indicators assess the supply chain's effects on the environment and society. The utilization of renewable resources, water consumption, waste production, and carbon emissions are some examples of important sustainability indicators. Supply chain operations analysts can put eco-friendly procedures in place and link the supply chain with sustainable company goals by keeping an eye on these measures.