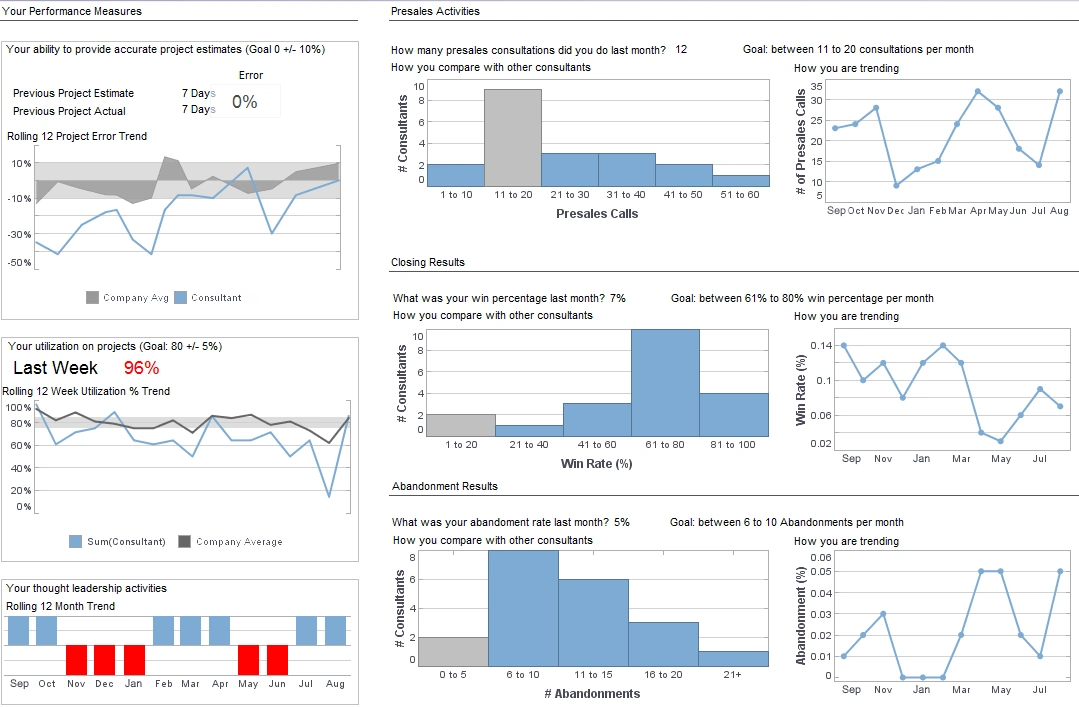
Product How-To: Changing Dashboard Layout Assets
InetSoft's dashboard software provides users with the flexibility to make changes to dashboard data assets in real-time as the need arises. View the example below to learn more about the Style Intelligence solution.
To modify a non-tabular asset (Named Condition, Named Grouping, Date Range, or Variable), right-click the asset title bar, and select 'Properties' from the context menu.
To mark an asset as the Primary asset, right-click on the asset's title row, and select 'Set as Primary' from the context menu. The Primary asset is displayed with a bold title.
The Primary asset is the “main result” of the Worksheet. It is this Primary asset that you will access from within reports or other Worksheets.
When you save a Worksheet, the Primary asset determines the appearance of the Worksheet in the Asset Repository, and how the Worksheet can be used.
You can delete an asset inside the Worksheet that contains it. You can also delete an entire Worksheet in the Asset Repository. To delete a table or other Worksheet asset, follow these steps:
- 1. Click the asset title row to select the asset.
- 2. Right-click the asset title row to open the context menu.
- 3. Select 'Remove' from the context menu.
Alternatively, press the 'Delete' key on the keyboard to remove the assembly. To delete an asset in the Asset Repository, do one of the following things:
- Select the asset name from the tree and press the Delete key on the keyboard.
- Right-click on the asset name in the tree and select the 'Remove' option.
Note: If an asset is used by other reports, the asset cannot be deleted.
What Are the Best Practices for Dashboard Layout?
Designing an effective dashboard layout requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure that it delivers actionable insights and a positive user experience. Here are some best practices for dashboard layout:
-
Clear Hierarchy and Organization: Organize the dashboard elements in a clear hierarchy, with the most important and relevant information prominently displayed. Use visual hierarchy techniques such as size, color, and placement to guide users' attention to critical elements first.
-
Consistent Layout and Design: Maintain consistency in layout and design across the dashboard to create a cohesive and visually appealing interface. Consistent use of fonts, colors, spacing, and alignment helps improve readability and usability.
-
Use of White Space: Incorporate sufficient white space between dashboard components to avoid clutter and improve visual clarity. White space helps separate different elements, making it easier for users to focus on individual insights and data points.
-
Responsive Design: Ensure that the dashboard layout is responsive and adapts to different screen sizes and devices. Designing for responsiveness ensures that users can access and interact with the dashboard seamlessly across desktops, tablets, and mobile devices.
-
Prioritize Key Metrics: Identify and prioritize the most important metrics and KPIs relevant to the dashboard's objectives. Place these key metrics prominently at the top or center of the dashboard to provide users with immediate insights into performance and trends.
-
Use of Visualizations: Choose appropriate data visualizations that effectively communicate insights and trends. Use a mix of charts, graphs, tables, and other visual elements to present data in a meaningful and easily understandable format. Select visualizations based on the type of data and the insights you want to convey.
-
Contextual Information: Provide contextual information and annotations to help users interpret the data effectively. Use labels, tooltips, annotations, and descriptions to provide additional context, explain key findings, and highlight important trends or outliers.
-
Interactive Elements: Incorporate interactive elements such as filters, drill-downs, and hover effects to enable users to explore data in more detail. Interactive features empower users to customize their views, filter data based on specific criteria, and uncover deeper insights.
-
Performance Considerations: Optimize dashboard performance by minimizing the number of data points, limiting the use of complex visualizations, and optimizing data queries and processing. Ensure that the dashboard loads quickly and responds promptly to user interactions to provide a smooth and responsive user experience.
-
Feedback and Iteration: Gather feedback from users regularly and iterate on the dashboard design based on their input. Continuously refine and improve the layout, content, and functionality of the dashboard to better meet the needs and preferences of users over time.
What Are the Best Interactive Features to Add to a Dashboard and Why?
Interactive features in a dashboard can significantly enhance user experience, making the data more accessible, understandable, and actionable. Here are some of the best interactive features to consider adding to a dashboard, along with explanations of why they are valuable:
1. Drill-Down Capability
- Why: Allows users to explore detailed data behind high-level summaries. This feature helps in identifying root causes and understanding data at a granular level.
- Example: Clicking on a bar in a sales chart to see sales performance by individual products or regions.
2. Filter and Search Options
- Why: Enables users to focus on specific data subsets by applying various filters. This helps in personalized data exploration and quicker insights.
- Example: Filtering data by date ranges, product categories, or geographic regions.
3. Dynamic Data Updates
- Why: Ensures that users are always working with the most current data, which is crucial for real-time decision-making.
- Example: Live data feeds for stock prices or social media mentions.
4. Customizable Views
- Why: Allows users to tailor the dashboard to their specific needs and preferences, enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
- Example: Letting users select which metrics to display or how they want data visualized (e.g., charts vs. tables).
5. Interactive Charts and Graphs
- Why: Makes data exploration more intuitive and engaging. Users can interact with the visual elements to uncover deeper insights.
- Example: Hovering over a line graph to see specific data points or clicking on a segment of a pie chart to highlight related information.
6. Data Export Options
- Why: Facilitates sharing and further analysis outside the dashboard environment. Users can take the data with them in a preferred format.
- Example: Exporting charts or tables to Excel, PDF, or CSV.
7. Annotations and Commentary
- Why: Provides context to the data, helping users understand key points and the story behind the numbers. It's especially useful for collaborative environments.
- Example: Adding notes or comments directly on the dashboard to explain spikes in data or trends.
8. Trend Lines and Forecasting
- Why: Helps users identify patterns and predict future performance, which is essential for strategic planning.
- Example: Showing trend lines on sales data to forecast future sales based on historical trends.
9. Geographic Mapping
- Why: Enhances the visualization of spatial data, making it easier to see geographic patterns and distributions.
- Example: Heat maps showing sales performance across different regions or locations of service incidents.
10. Responsive Design
- Why: Ensures that the dashboard is accessible and usable across various devices and screen sizes, from desktops to smartphones.
- Example: Adapting the layout and visual elements automatically to fit the screen size and resolution of the device in use.
11. Alerts and Notifications
- Why: Keeps users informed of significant changes or anomalies in the data, allowing for timely interventions.
- Example: Email or in-dashboard alerts for sudden drops in website traffic or spikes in error rates.
12. User Access Controls
- Why: Ensures that sensitive data is protected and only accessible to authorized users, enhancing data security.
- Example: Role-based access controls that provide different data visibility levels based on user roles.
13. Interactive Legends
- Why: Enhances data comprehension by allowing users to interact with the legend to highlight or isolate specific data series in a chart.
- Example: Clicking on legend items to toggle the visibility of corresponding data series in a multi-line chart.