Understanding Drill Down Reporting: Unlocking Insights for Data-Driven Decisions
Drill down reporting is a powerful tool that enables businesses to dissect their data, revealing granular details that can inform smarter decisions. By breaking down complex information into manageable segments, organizations can uncover trends, identify anomalies, and understand the underlying factors influencing performance. This article will guide you through the nuances of drill down reporting, illustrating how it can enhance your analytical capabilities and drive strategic initiatives. Whether you’re a seasoned data analyst or just starting your journey into data exploration, grasping the essence of drill down reporting is essential for unlocking deeper insights and fostering a culture of informed decision-making. Join us as we delve into the mechanisms of this powerful reporting technique and discover how it can propel your organization towards greater success.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
The Importance of Data-Driven Decision Making
In today’s fast-paced business environment, making decisions based on data rather than intuition is paramount. Data-driven decision making ensures that organizations leverage concrete evidence and insights to guide their strategies, leading to more accurate and effective outcomes. This approach minimizes the risks associated with guesswork and maximizes the potential for success by grounding decisions in real-world data.
One of the key advantages of data-driven decision making is its ability to provide a clear and objective picture of the business landscape. By analyzing data, companies can identify patterns and trends that might not be immediately apparent. This insight allows them to anticipate changes, adapt their strategies accordingly, and stay ahead of the competition. Furthermore, data-driven decisions are often more defensible, as they are based on empirical evidence rather than subjective judgment.
Moreover, data-driven decision making fosters a culture of accountability within organizations. When decisions are based on data, they can be tracked and evaluated, providing a clear record of what worked and what didn’t. This transparency encourages continuous improvement and helps businesses learn from their successes and failures. Ultimately, embracing data-driven decision making can lead to more sustainable growth and long-term success.
Key Components of Drill Down Reporting
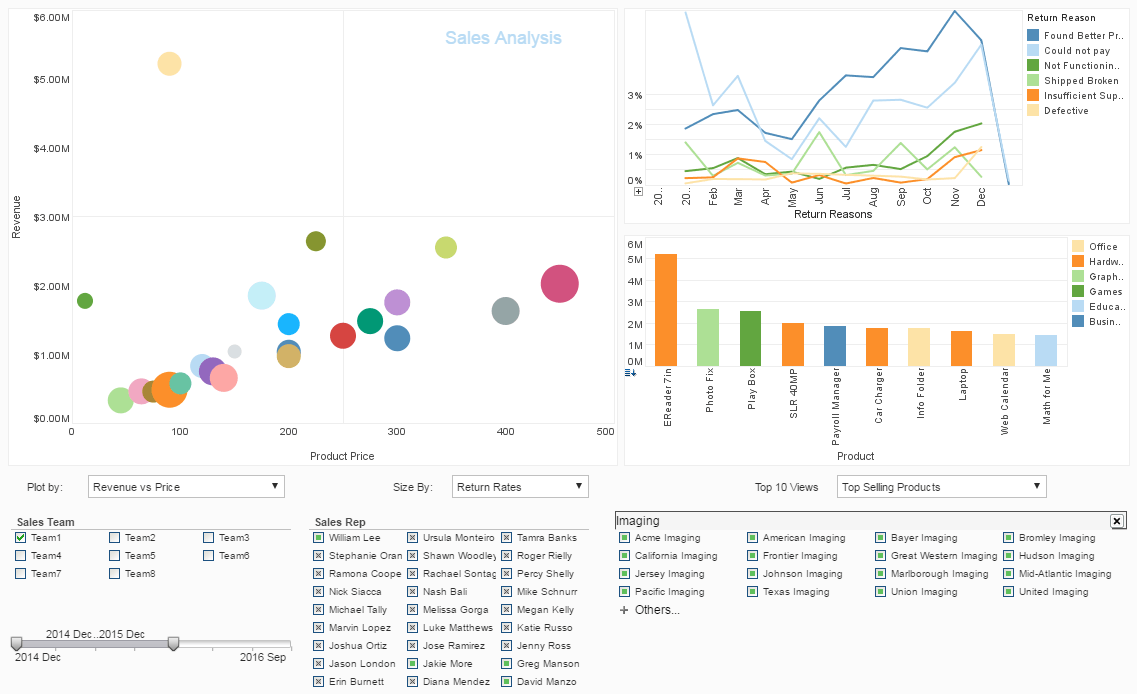
Drill down reporting is a method that allows users to navigate through layers of data, starting from a high-level summary and moving down to more detailed information. The key components of drill down reporting include hierarchical data structuring, interactive interfaces, and real-time data processing.
Hierarchical data structuring is essential for drill down reporting. It involves organizing data into different levels, where each level offers more detailed information than the previous one. For example, a sales report might start with a summary of total sales, then drill down to sales by region, and further drill down to sales by individual representatives. This structured approach allows users to explore data systematically and uncover specific insights.
Interactive interfaces are another crucial component of drill down reporting. These interfaces enable users to click on elements within a report and drill down into deeper levels of data. This interactivity makes the reporting process intuitive and user-friendly, allowing users to explore data dynamically and discover insights without needing advanced technical skills.
Real-time data processing ensures that the information presented in drill down reports is current and accurate. In fast-moving business environments, outdated data can lead to misguided decisions. By processing data in real-time, drill down reporting tools provide up-to-date insights that reflect the latest trends and changes, empowering users to make timely and informed decisions. div class="pt-4 pb-4">
 |
Read how InetSoft saves money and resources with deployment flexibility. |
How Drill Down Reporting Works
The mechanics of drill down reporting involve several steps that enable users to explore data in depth. The process typically starts with an aggregated view of data, presenting a high-level summary that gives an overview of key metrics and performance indicators. From this summary, users can initiate the drill down process by selecting specific data points or categories they wish to investigate further.
Once a user selects a data point to drill down into, the reporting tool retrieves the relevant data from the underlying database or data warehouse. This retrieval process involves querying the data source to extract more detailed information related to the selected category. The tool then presents this detailed information in a new report or visualization, offering a deeper layer of insight.
As users continue to drill down, they can navigate through multiple layers of data, each providing increasingly granular details. For example, starting from a high-level overview of company revenue, users might drill down to revenue by region, then further drill down to revenue by individual products or services. This layered approach allows users to pinpoint specific factors driving performance and identify areas for improvement.
Benefits of Utilizing Drill Down Reporting
Drill down reporting offers numerous benefits that enhance the analytical capabilities of organizations. One of the primary advantages is its ability to reveal hidden insights that might not be visible in aggregated data. By drilling down into detailed information, users can uncover trends, anomalies, and correlations that provide a deeper understanding of business dynamics.
Another significant benefit of drill down reporting is its contribution to more informed and precise decision making. With access to detailed data, decision-makers can base their strategies on comprehensive insights rather than superficial summaries. This precision can lead to better-targeted initiatives, optimized resource allocation, and improved overall performance.
Drill down reporting also enhances transparency and accountability within organizations. By providing a clear trail of data exploration, it allows stakeholders to track the decision-making process and evaluate the rationale behind specific choices. This transparency fosters trust and encourages a culture of data-driven thinking, where decisions are consistently backed by evidence. div class="pt-4 pb-4">
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
Common Use Cases for Drill Down Reporting
Drill down reporting is versatile and can be applied across various industries and business functions. In the retail sector, for instance, it can be used to analyze sales performance. Retail managers can start with a summary of total sales and drill down to sales by store, product category, and individual items. This detailed analysis helps identify top-performing products and stores, as well as areas needing improvement.
In the healthcare industry, drill down reporting can be utilized to monitor patient outcomes and operational efficiency. Healthcare administrators can begin with an overview of patient satisfaction scores and drill down to scores by department, treatment type, and individual practitioners. This granular analysis aids in pinpointing areas for enhancing patient care and operational processes.
Financial services organizations can leverage drill down reporting to assess risk and performance. Starting with a summary of portfolio performance, analysts can drill down to performance by asset class, individual assets, and specific transactions. This detailed insight supports better risk management and investment strategies, ensuring optimal financial outcomes.
Tools and Software for Effective Drill Down Reporting
Several tools and software solutions are designed to facilitate effective drill down reporting. These tools offer various features that enhance data exploration and analysis. One popular option is Tableau, a powerful data visualization tool that enables users to create interactive dashboards and drill down into detailed data layers. Tableau’s intuitive interface and robust data processing capabilities make it a favorite among data analysts. The most common complaint about Tableau is its frustrating dashboard layout and formatting limitations, especially the lack of responsive design and multi-object alignment tools
StyleBI is popular because it combines a lightweight, cloud-native architecture with powerful data transformation and visualization capabilities. Its modular microservices can be deployed flexibly—on Docker, in the cloud, or embedded into other applications—making it ideal for developers and enterprises alike. Users appreciate its gentle learning curve and machine-assisted design tools, which accelerate dashboard creation without sacrificing sophistication. It supports interactive dashboards and scheduled reports, catering to both self-service users and enterprise reporting needs. Finally, its fine-grained security controls and multi-tenant support in the enterprise edition make it a trusted choice for secure, scalable analytics
Another widely-used tool is Microsoft Power BI, which provides comprehensive reporting and visualization features. Power BI allows users to connect to multiple data sources, create interactive reports, and drill down into data with ease. Its integration with other Microsoft products and services further enhances its utility for businesses operating within the Microsoft ecosystem. The top complaint about Power BI is its performance issues with large datasets, especially when complex DAX calculations or inefficient data models are involved.
For organizations seeking advanced analytics capabilities, tools like Qlik Sense and Looker offer sophisticated data exploration features. Qlik Sense provides associative data models that allow users to explore data dynamically, while Looker offers powerful querying and visualization options. Both tools support deep drill down analysis, empowering users to uncover actionable insights. The most common complaint about Qlik is its steep learning curve and limited collaboration features, especially the cumbersome process for multiple users to edit dashboards.
 |
View the gallery of examples of dashboards and visualizations. |
Best Practices for Implementing Drill Down Reporting
Implementing drill down reporting effectively requires following several best practices. Firstly, it is essential to establish clear objectives for the reporting process. Understanding what insights are needed and the questions to be answered will guide the design and structure of drill down reports, ensuring they meet specific business needs.
Secondly, data quality and integrity must be prioritized. Accurate and reliable data is the foundation of effective drill down reporting. Organizations should implement robust data governance practices to ensure the data used in reports is clean, consistent, and up-to-date. Regular data audits and validation processes can help maintain high standards of data quality.
Thirdly, designing intuitive and user-friendly interfaces is crucial for successful drill down reporting. Reports should be easy to navigate, with clear visualizations and interactive elements that allow users to explore data effortlessly. Providing training and support to users can further enhance their ability to utilize drill down reporting tools effectively.
Challenges and Limitations of Drill Down Reporting
While drill down reporting offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges and limitations. One common challenge is the complexity of data management. Organizing and maintaining hierarchical data structures can be resource-intensive, requiring significant effort to ensure data is properly categorized and accessible.
Another limitation is the potential for information overload. As users drill down into deeper layers of data, they may encounter vast amounts of detailed information. Without proper guidance and context, this abundance of data can become overwhelming, making it difficult to extract meaningful insights. Designing reports that balance detail with clarity is essential to mitigate this issue.
Additionally, drill down reporting may require significant computational resources, especially when dealing with large datasets and real-time processing. Ensuring the reporting infrastructure can handle the demands of drill down analysis is crucial for maintaining performance and responsiveness. Investing in scalable and robust technology solutions can help address these challenges.