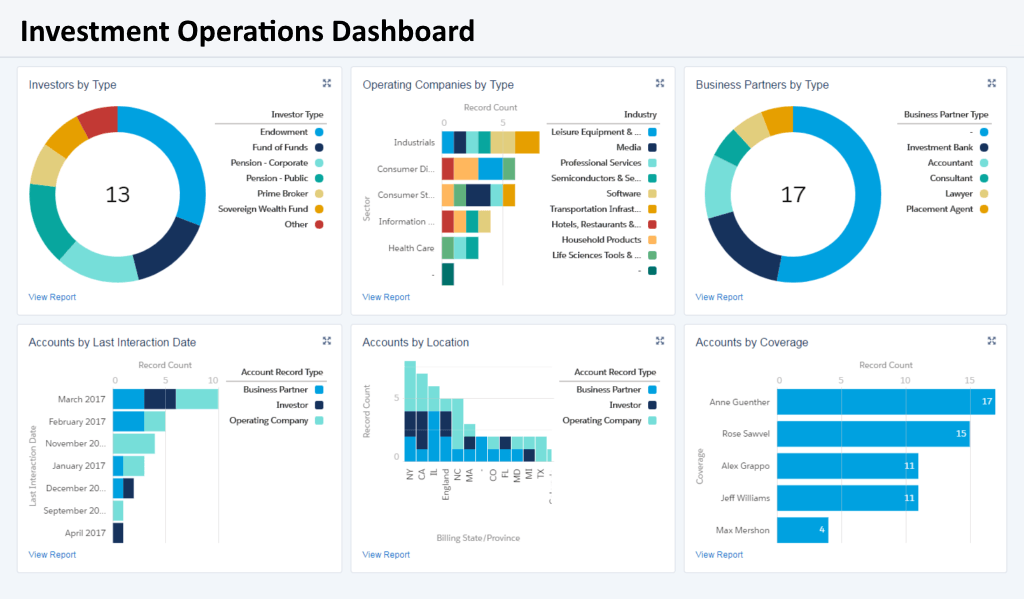
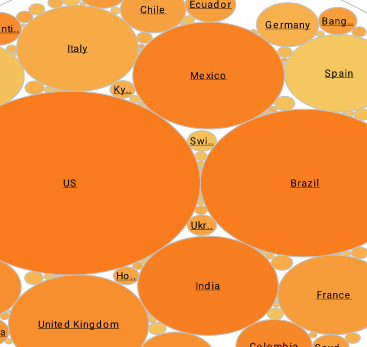
What KPIs and Analytics Does an Investment Operations Analyst Use?
Investment operations analysts are essential to the financial sector because they make sure that investment operations run smoothly and effectively. These experts depend on analytics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to oversee and improve investment processes. We will examine the crucial KPIs and analytics utilized by investment operations analysts in this post, emphasizing their importance and showing how they affect decision-making and performance assessment.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
Trade Execution Efficiency
The following KPIs and metrics are constantly monitored by investment operations analysts since efficient trade execution is essential to these activities:
- Trade Execution Speed: The time it takes to execute transactions is measured by this KPI. Analysts monitor the amount of time that passes between placing an order and the transaction being completed, striving for quick execution to take advantage of market opportunities and reduce exposure to market hazards.
- Fill Rate: The proportion of orders that are successfully performed is shown by the fill rate KPI. To evaluate the effectiveness of trade execution, spot any order routing or trade settlement concerns, and modify the procedure for better performance, analysts look at the fill rate.
- Trading Costs: For investment operations analysts, keeping an eye on trading expenses is essential. Analysts may find possibilities for cost savings, improve terms with brokers, and improve overall trade execution efficiency by evaluating transaction fees, bid-ask spreads, and other costs.
Portfolio Performance Evaluation
Analysts that specialize in investment operations also assess online portfolio performance using a variety of KPIs and analytics. Among the crucial metrics are:
- Return on Investment (ROI): ROI gauges how profitable an investment is in comparison to its cost. Analysts use ROI to evaluate the portfolio's overall performance and compare it to industry benchmarks. With the aid of this KPI, decision-makers may spot failing assets and maximize the returns on the portfolio.
- Risk-Adjusted Return: ROI gives a general picture of a portfolio's performance, while risk-adjusted return takes into account the degree of risk. In order to analyze various investment alternatives and successfully manage risk, analysts utilize metrics like the Sharpe ratio or the Treynor ratio to estimate the risk-adjusted return.
- Portfolio Diversification: The key to controlling risk in investing portfolios is diversification. Analysts of investment operations evaluate portfolio diversity using a variety of metrics, including sector allocation, beta, and correlation coefficient. These analytics assist in identifying concentration hazards and portfolio rebalancing to improve risk-return profiles.
Operational Efficiency
Investment operations analysts depend on the KPIs and data listed below to ensure operational efficiency:
- Trade Settlement Cycle: The duration needed to complete and settle deals is measured by the trade settlement cycle. To ensure fast settlement and lower operational risks, analysts track this KPI to spot any delays or bottlenecks in the settlement process.
- Trade Errors: Trade mistakes may have a big financial impact. For the purpose of determining the reasons, putting preventative measures in place, and boosting operational effectiveness, analysts keep track of the quantity and kinds of trade mistakes, such as inaccurate order inputs or unsuccessful deals.
- Straight-Through Processing (STP) Rate: STP rate is a measurement of the proportion of transactions that can be handled entirely online. High STP rates are the goal of investment operations analysts since they lower the risk of mistakes, increase efficiency, and simplify operational processes.
Compliance and Regulatory Monitoring
In investing activities, adherence to laws and professional standards is crucial. KPIs and analytics are used by analysts to monitor compliance requirements:
- Regulatory Reporting Accuracy: The correctness of regulatory reports presented to regulating organizations is monitored by analysts. This KPI assists in ensuring reporting requirements are followed and indicates any problems that can call for remedial action.
- Transaction Monitoring: Analytical tools are used by investment operations analysts to track transactions and spot possible cases of fraud, money laundering, or other illegal activity. Analysts may quickly alert compliance teams to worrisome trends or anomalies by using data analytics.
- Audit Trail Analysis: A thorough record of all transactions and activities connected with investing operations is referred to as an audit trail. Analytics are used by analysts to examine the audit trail and spot any inconsistencies, promoting regulatory compliance and maintaining transparency.
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
Risk Management
One of the most important aspects of investing operations is managing and reducing risks. The following KPIs and analytics are used by analysts:
- Value at Risk (VaR): VaR calculates the potential value loss of a portfolio or investment over a certain time horizon and with a given degree of confidence. In order to evaluate and efficiently manage market risk exposure, investment operations analysts compute VaR.
- Tracking Error: Tracking error calculates how much portfolio results deviate from a reference index. This KPI is used by analysts to measure the effectiveness of active investing strategies and determine their capacity to provide returns that are consistent with the specified benchmark.
- Counterparty Risk: The danger of financial loss brought on by a counterparty's failure or default is referred to as "counterparty risk." By examining credit ratings, collateral requirements, and exposure restrictions, analysts keep an eye on this risk to make sure that suitable risk mitigation measures are in place.
Cost Efficiency
For investment operations analysts, cost management is a top priority. The following KPIs and analytics are used by them:
- Expense Ratio: The proportion of assets under management (AUM) utilized to pay operational expenditures is determined by the expense ratio. To guarantee cost effectiveness, analysts track this ratio and evaluate it against standards set by the industry.
- Cost per Trade: This KPI gauges the typical expense related to carrying out a single deal. The goal of tracking the cost per transaction is to help investment operations analysts find possibilities for cost reduction, improve the conditions on which they are paid by service providers, and streamline trade execution procedures.
- Operational Cost Analysis: Operational costs, such as those related to infrastructure, technology, and staff expenditures, are thoroughly examined by analysts. To increase total cost efficiency, this study aids in identifying inefficient areas and putting cost-cutting measures into place.
 |
Read the top 10 reasons for selecting InetSoft as your BI partner. |
Client Servicing and Satisfaction
Operations involving investments must provide top-notch customer service. The following KPIs and analytics are used by analysts:
- Client Satisfaction Surveys: Surveys and other forms of feedback are used by analysts to gauge customer satisfaction. This qualitative data aids in pinpointing problem areas and enhancing the customer experience as a whole.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): SLAs describe the performance measurements and service standards that have been agreed upon between investment operations teams and their customers. To make sure service delivery meets or exceeds customer expectations, analysts keep an eye on SLAs.
- Turnaround Time: Turnaround time gauges how long it takes to respond to customer questions, requests, or problems. Analysts who work in investment operations monitor this KPI to guarantee prompt reaction and resolution, which boosts customer satisfaction.