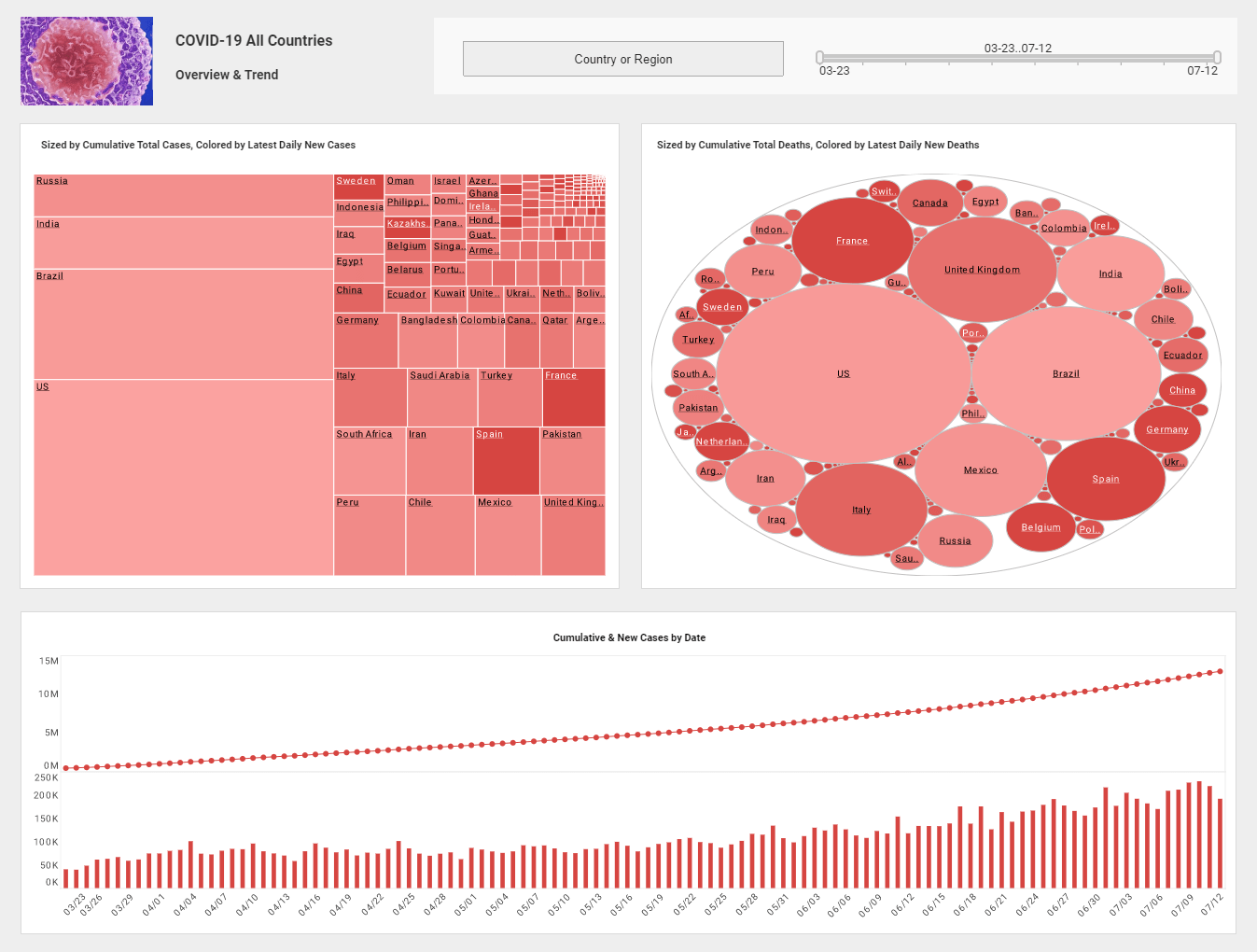
How Life Sciences Companies Use Analytics
Today, there's a much larger opportunity for health innovation than what's commonly considered in clinical informatics. But first, let's start with a brief historical comparison.
Around 300 BC, a library was established at the port city of Alexandria. This library was significant in that it was an attempt to collect as much of the world's information at one place as possible. At that time, it's believed that travelers through this city actually had to surrender their books temporarily so that they could be copied for the library.
In healthcare today, we are actually taken on a very similar challenge, though not centralized in one physical place. We are now collecting massive amounts of information. Information that people did not have access to before.
The following questions arise: How do you use all of this information? How do you find it? How do you ensure that you can read and interpret it, and how can you use it to make new kinds of decisions?
Those are the questions that fall into the domain of analytics. The keys to health industry innovation will not be found in simply trying to aggregate and report retrospective views of data collective. Nor will they be found in systems that reflect an old way of delivering care.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
Data-Based Decision Making
We need a different kind of information science, clinical practice, and health businesses. Information science should drive data-based decision making; information science that is tailored to the unique attributes of patients, as well as acknowledges the current world of technological opportunity.
No single market segment or institution can be successful in shifting to a new health model without shared
data and insights from other market segments.
So a health plan cannot optimize treatment costs without understanding the clinical outcomes from providers.
At the same time, researchers can't develop more tailored therapeutics without richer insights from patients.
If you want to transform healthcare, you have to share data and insights.
If we talk about health analytics, this is not about business intelligence, web reports or policy, and practice-oriented informatics. It's all aboutadvanced analytical methods that capture and interpret the interdependencies that we all know exists between clinical financial operational and individual perspectives. It is also about mathematical and statistical techniques that do not just focus on describing what has happened in the past. Instead, they model, predict, and optimize the future.
 |
View a 2-minute demonstration of InetSoft's easy, agile, and robust BI software. |
The Four V's of Big Data
In big data, people talk about the four V's:
1. Volume
Healthcare generates a large volume of data. For example, for genomic data, each human genome requires 200 gigabytes of raw data or 125 megabytes if we store just SNPs. For medical imaging data, a single MRI is about 300 gigabytes. Medical imaging data generated in the U.S. per year was estimated to be 100 petabytes.
2. Variety
Healthcare also generates a lot of different kinds of information. It includes clinical information, patient demographics, diagnosis, procedure, medication, lab results, and the clinical notes. Patients also generate a lot of data, such as information coming out of arm body sensors and other devices that patients wear.
3. Velocity
Healthcare also generates a lot of real-time data, such as blood pressure measures, temperature, heart rate, drug dispensing levels at intensive care units.
4. Veracity
Unfortunately, healthcare data often comes with a lot of noise, a lot of missing data, a lot of errors, and a lot of false alarms. It is a big challenge in healthcare data analytics.
Today, the landscape is changing for healthcare big data analytics as more organizations figure out how to harness big data. They also implement the right infrastructure for generating actionable insights from a slew of new sources. However, some providers may still be wondering how big data can actually work for them.
 |
View live interactive examples in InetSoft's dashboard and visualization gallery. |
The Benefits of Analytics In Life Sciences
Everything that we do, whether it's science or medicine things that existed fifty years ago, no longer exists today. But change is slow. With the help of technology in the right ways at the right time, we can make the journey better for people. What does that mean to us?
Imagine that someone's going to fall. What the analytics does is it takes different pieces of information and compiles them together. It gives the healthcare sector a true definition of risk for the patients so that they can hopefully prevent them from falling. Or, at least, implement an intervention. The analytics impact on medicine is fundamentally to transform the physicians' ability to personalize care directly to you.
The benefits of analytics in life sciences are manifested in significant areas:
- Early detection of prescription and treatment patterns;
- Strategizing the intent of the patient to real-world results;
- Achieving operational excellence to drive through the intellectual journey of patient centricity.
 |
Read the top 10 reasons for selecting InetSoft as your BI partner. |
Why Do Life Science Companies Need A Modern Analytics Platform?
The present 'savvy' customers have wellbeing data readily available. They are taking a gander at expert guidance and proactive consideration from the healthcare business. Hence, life sciences organizations are attempting to stay up with the client.
They are moving from treatment to preventive research. Much the same as different ventures, it is time that the life sciences organizations receive information, examination, and influence they experience deliberately for their potential benefit.
Many life science companies want to adopt an integrated analytics platform to:
- Make their analytics capabilities more efficient, scalable, and adaptive to emerging data sources.
- Leverage increasing amounts of data and accelerate insight generation.
- Accelerate analytics programs for R&D to commercial terms.
- Enhance ad hoc analytics capabilities by leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Optimize costs by leveraging cloud and proven solutions in the industry.