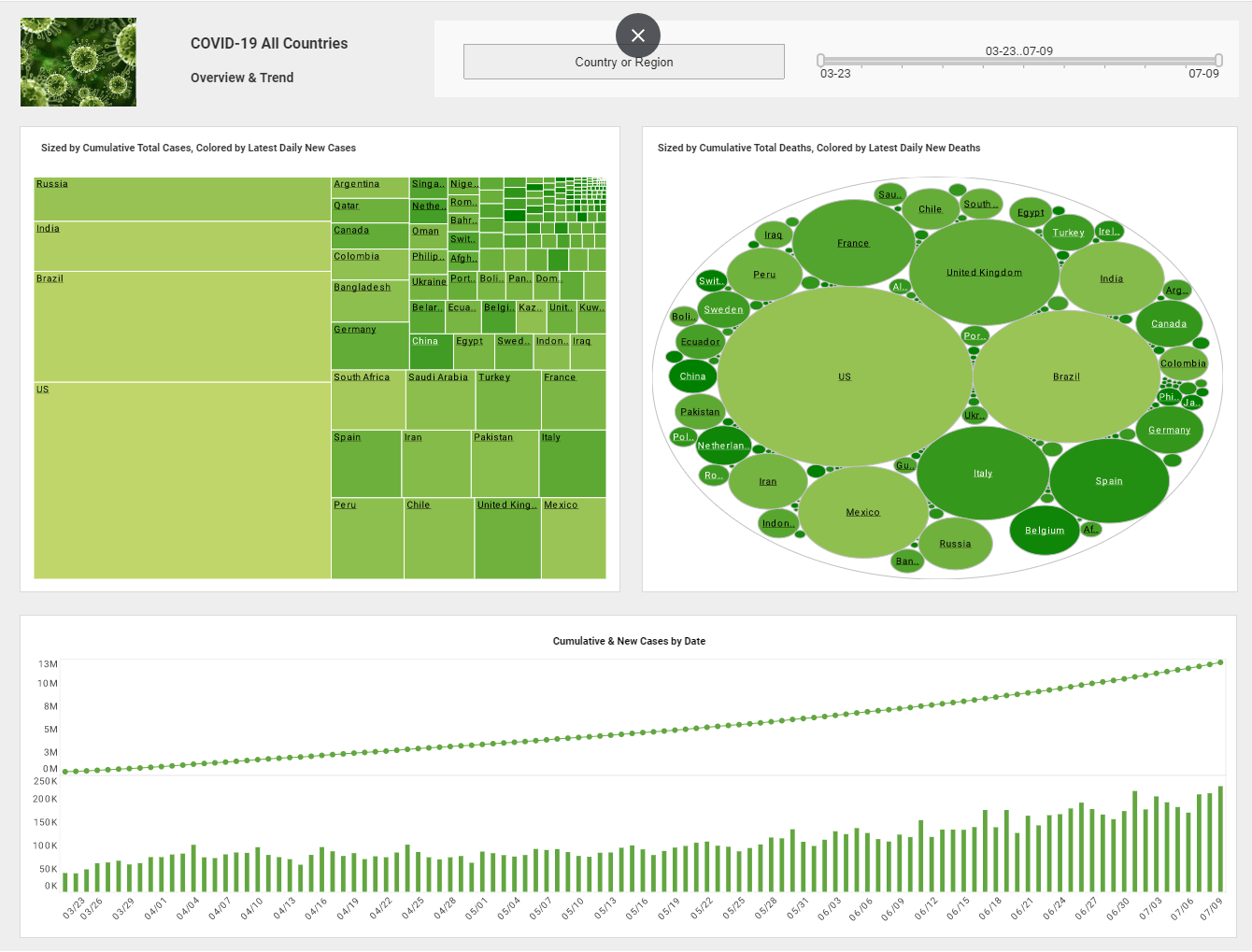
Tips for Data Visualization in Big Data
We are in a business environment in which around 3 trillion bytes of information are generated every day. This large amount of information has grown due, in part, to the Internet and the continuous technological increase in communications and data collection.
Such amount of data is generated and produced daily that it has been possible for organizations to analyze, discover and verify this enormous amount of information through specific technologies for it.
All this means that huge amounts of information come to us from multiple sources and what happens is that, on many occasions, there is not enough time for its correct interpretation.
At this point the field of big data visualization comes into play, the main objective of which is to show, through graphs and in a simple, measurable and understandable way, the information collected in the analysis and modeling of the same.
Although graphics have been used in business for decades, data visualization technologies have evolved according to the needs of the new business paradigm in which business analytics and big data systems proliferate.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
For this reason, we present in this post those most relevant aspects to take into account to get the most out of data visualization in our professional projects:
1. What are we going to tell. A common mistake when viewing information is trying to cover too much. We must know what we want to count and be precise in the information that we are going to show in the visualization.
2. Who is it aimed at (target audience). We must take into account what type of audience is going to work with the data to be shown in the visualization. Think about who is the user, who is going to interpret the graphs (if it is a data specialist, a marketer or a user without specialization) and based on this, decide what type of data we can show.
3. How are we going to tell it? This is where another aspect to take into account comes into play: storytelling with data, a new way of presenting and analyzing data. We recommend Cole Nussbaumer's book, "Storytelling with Data," in which he offers a practical guide to using the concepts of storytelling - telling a story with a beginning, middle and end - to communicate data visually and effectively.
 |
View a 2-minute demonstration of InetSoft's easy, agile, and robust BI software. |
4. Simplify. Although we have already mentioned it in the first point, we must give special importance to simplification. We must be concise and only show what is relevant, discard data that is not illustrious or is "noise" so that there is a correct visualization or good understanding.
5. Use appropriate graphics according to the type of data. We must use graphic resources wisely. Not all graphics are good for everything. For example, always use column charts to make comparisons instead of pie charts, as it is visually better appreciated. To make it easier to organize graphics, using BI software is highly recommended.
6. Do not abuse tables. Tables should only be used when we need to show accurate values. Likewise, it must be taken into account that the tables are designed at an appropriate scale so that there is no confusion in the data analysis.
 |
View live interactive examples in InetSoft's dashboard and visualization gallery. |
7. Use appropriate colors to facilitate the perception and understanding of the data. Selecting colors seems straightforward, but not all colors are effective at displaying data. It is advisable to use pastel colors or different shades of the same color instead of bright colors such as red, fuchsia, yellow and orange in the same graph. On the other hand, using color correctly can make a graph more understandable.
8. Clear and memorable statements. We must choose a good headline to contextualize and direct attention to the most important information. The use of human-readable fonts and the use of easy-to-read labels, axes, and legends can be an important factor in visualizing the data.
9. Organize the data logically. We ensure that the different graphics and screens on the display are aligned horizontally and vertically so that they can be accurately compared and not create any misleading optical illusions.
10. Cite sources from which information is extracted. Being transparent gives you greater credibility. If we have extracted information or data from other sources, we must cite them to give credibility to the information we show.
Visualizing Big Data in Baseball
Visualizing big data in baseball has revolutionized the sport, providing teams with unprecedented insights into player performance, strategy optimization, and fan engagement. Let's explore an example of how big data visualization has transformed the way baseball is played and experienced:
Player Performance Analysis
Imagine a scenario where a baseball team is leveraging big data analytics to evaluate player performance and make informed decisions on lineup composition and player development strategies. Through advanced statistical analysis and visualization techniques, the team's analytics department collects vast amounts of data on player performance metrics such as batting average, on-base percentage, slugging percentage, and defensive metrics like fielding percentage and defensive runs saved.
Using interactive dashboards and heat maps, the team visualizes this data to identify patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent through traditional scouting methods. For example, they might use a scatter plot to visualize the relationship between a player's batting average and their performance against specific types of pitches or pitch velocities. This allows coaches to tailor their coaching strategies and provide targeted feedback to players to improve their performance in key areas.
Strategy Optimization
Big data visualization also plays a crucial role in optimizing in-game strategies and decision-making. Imagine the team's coaching staff using real-time data feeds and interactive dashboards to analyze opposing pitchers' tendencies and identify potential weaknesses in their pitching repertoire. By visualizing pitch location heat maps and batter-pitcher matchup data, coaches can make data-driven decisions on pitch selection, defensive positioning, and pinch-hitting strategies to maximize their team's chances of scoring runs and winning games.
Furthermore, big data visualization enables teams to conduct "what-if" scenarios and simulations to evaluate the potential outcomes of different strategic decisions. For example, they might use a simulation model to analyze the impact of bringing in a relief pitcher in a high-pressure situation versus sticking with the starting pitcher for another inning. By visualizing the projected win probability and expected run outcomes of each decision, coaches can make more informed decisions under pressure and increase their team's chances of success.
Fan Engagement
Big data visualization isn't just limited to the front office and coaching staff—it also enhances the fan experience both inside and outside the ballpark. Imagine fans using mobile apps or interactive stadium displays to access real-time statistics, player profiles, and immersive visualizations of in-game action. For example, they might use augmented reality overlays to visualize the trajectory of a home run ball or the spin rate of a pitcher's curveball in real-time.
Additionally, big data visualization enables teams to personalize the fan experience by providing targeted content and promotions based on individual fan preferences and behavior. For example, they might use data analytics to analyze fan demographics and purchasing history to offer personalized ticket offers, merchandise discounts, and exclusive experiences tailored to each fan's interests.
 |
View a 2-minute demonstration of InetSoft's easy, agile, and robust BI software. |
More Articles About Visualization
Best Investment for My Data - The other thing I would add is I think it's important to spend more time on the use case and figuring out what would be the best investment for my data because there is so much data. Obviously you have to get it clean what. Where do I want to start? What's going to give me the biggest bang for my buck? Is it that predictive analytics the best use case, or is it more about customer behavior? Taking the time to figure that out will ultimately drive more success in the future...
Dashboard for Stakeholder Reach and Impressions - The first step in stakeholder involvement is reach. A baseline for evaluating the initial effect is established by counting the people who have been exposed to the organization's messaging, information, or events. Impressions provide a more precise estimate of the audience's potential size that has seen or engaged with the organization's activity. These metrics provide information on how well the company can engage its stakeholders and how well the communication channels work...
Data-driven marketing: Connecting the dots - To adopt a sustainable culture of analytic reporting and strategy when it comes to developing marketing communications that matter, working with the right tools is essential. Working with cutting-edge BI tools and analysis solutions will empower you to curate and visualize your most vital marketing metrics in one centralized location. Not only will accessing your data in a visual format help improve your decision-making, but it will also allow you to interact with your insights and develop targeted campaign strategies that make a genuine impact...
Using AI for Career Path Predictions - Machine learning will soon help students determine what careers they want to get into, and what colleges to consider enrolling in. Instead of high school students feeling the pressure of having to choose a school and a career, AI will be able to suggest schools and careers based on their skillset, interests, and abilities. And with those objectives, students can pick a college and career with ease...
What Is Media Analytics? - Media Analytics involves taking media data (a.k.a. Statistics or big data) you have collected and studying its trends. It may take time to learn what certain patterns of numbers, times, dates, amounts are telling you. Once you figure out what the data means, you can use it to improve your business. Learning how to evaluate the data you have will lead to better business decisions. For instance, you can keep track of how many people have viewed your video content and for how long. These metrics are highly beneficial if you're a publisher, a digital agency, or even a content creator...