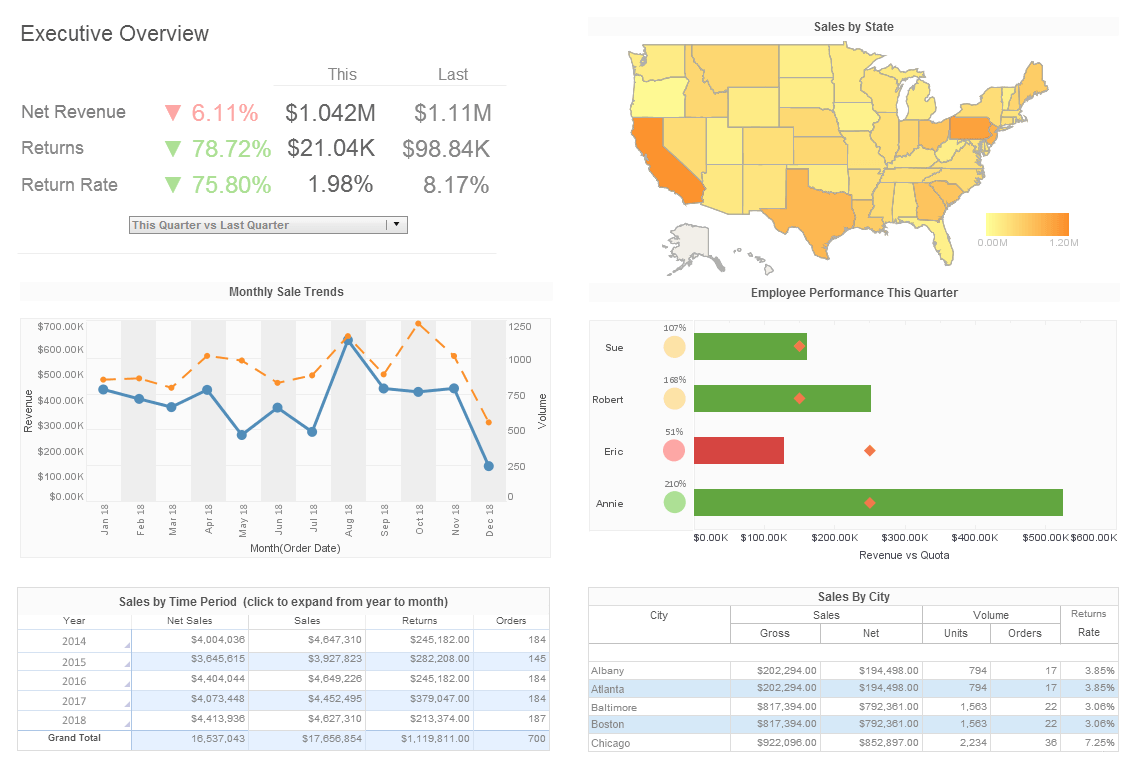
InetSoft's Ad Hoc Query Tool
Looking for an ad hoc query tool? InetSoft offers ad hoc query and reporting software to build ad hoc queries with a drag and drop designer. The query application includes powerful database access capabilities connecting to disparate data sources and permitting ad hoc query analysis for business users and database analysts alike. Based on a product that has won 8 JDJ Readers Choice Awards in a row, you have a great option to evaluate.
Style Report Enterprise provides a zero-client, Web-based application for:
- - production reports
- - interactive reports
- - ad hoc reports
- - data mashup
Style Report's small footprint, 100% Java, pure Web architecture delivers an embedding and integration-ready platform. This software, designed for ad hoc reporting, not only integrates with any Web user interface, it also leverages the same application server platform as that of the embedding application.
Style Report allows IT professionals to create sophisticated production reports that can be deployed for server based, or desktop based applications. The small footprint and 100% Java architecture makes it an ideal solution for embedded ad hoc reports. It is based upon XML, JavaScript, and other open standards technology that allows IT to fully leverage existing skills.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
What KPIs and Metrics Are Tracked Using Ad Hoc Query Tools in Beef Cattle Ranching?
In beef cattle ranching, tracking specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics is essential for optimizing operations, improving productivity, and ensuring profitability. Here are some key KPIs and their definitions, along with their significance in performance management:
1. Calving Rate
- Definition: The percentage of cows that give birth to healthy calves in a given period.
- Significance: High calving rates indicate good herd fertility and effective breeding practices, crucial for maintaining or increasing herd size and productivity.
2. Calf Mortality Rate
- Definition: The percentage of calves that die before weaning.
- Significance: Low mortality rates reflect good herd health management and care practices, directly impacting the number of calves that reach maturity.
3. Weaning Weight
- Definition: The average weight of calves at weaning age.
- Significance: Higher weaning weights suggest good maternal care, nutrition, and overall calf health, leading to better growth rates and market readiness.
4. Average Daily Gain (ADG)
- Definition: The average weight gain per day of a calf or cow.
- Significance: ADG is a critical measure of growth efficiency and feed conversion, influencing the time required to reach market weight and overall productivity.
5. Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR)
- Definition: The amount of feed required to gain a unit of weight.
- Significance: Lower FCR values indicate more efficient feed usage, reducing feed costs and increasing profitability.
6. Breeding Stock Replacement Rate
- Definition: The percentage of breeding animals replaced annually.
- Significance: This rate helps maintain genetic diversity and herd health, ensuring long-term productivity and resilience.
7. Pregnancy Rate
- Definition: The percentage of cows that become pregnant during the breeding season.
- Significance: High pregnancy rates indicate successful breeding practices and good reproductive health.
8. Culling Rate
- Definition: The percentage of cattle removed from the herd due to health, age, or productivity issues.
- Significance: Effective culling strategies help maintain a healthy and productive herd, improving overall herd performance.
9. Herd Health Metrics
- Definition: Includes measures such as disease incidence, vaccination rates, and veterinary costs.
- Significance: Good health metrics ensure the well-being of the herd, reducing mortality and enhancing productivity.
10. Pasture Utilization Rate
- Definition: The percentage of available pastureland effectively used for grazing.
- Significance: Optimizing pasture utilization helps maintain sustainable grazing practices and reduces feed costs.
11. Carcass Yield
- Definition: The amount of usable meat obtained from a slaughtered animal.
- Significance: Higher carcass yields increase profitability and indicate good animal growth and health management.
12. Cost of Gain
- Definition: The total cost incurred to produce a unit of weight gain in cattle.
- Significance: Understanding the cost of gain helps in managing expenses and improving the economic efficiency of the operation.
13. Feed Costs per Head
- Definition: The total feed cost for each animal over a specific period.
- Significance: Managing feed costs is crucial for profitability, as feed is typically the largest expense in cattle ranching.
14. Average Market Weight
- Definition: The average weight of cattle at the time of sale.
- Significance: Achieving optimal market weight ensures maximum revenue from sales, reflecting effective growth and management practices.
15. Revenue per Head
- Definition: The total income generated per animal sold.
- Significance: Indicates the financial performance and market value of the cattle, essential for assessing overall profitability.
16. Labor Efficiency
- Definition: The ratio of labor hours to the number of cattle managed.
- Significance: Higher labor efficiency reduces costs and improves operational productivity.
17. Water Usage Efficiency
- Definition: The amount of water used per unit of weight gain or per head.
- Significance: Ensures sustainable water usage, essential for long-term viability, especially in regions with water scarcity.
18. Environmental Impact Metrics
- Definition: Includes measures like greenhouse gas emissions, manure management efficiency, and land use.
- Significance: Monitoring environmental impact is vital for sustainable practices and regulatory compliance.
19. Net Profit Margin
- Definition: The percentage of revenue remaining after all expenses are deducted.
- Significance: A key measure of overall financial health and profitability of the ranching operation.
20. Return on Investment (ROI)
- Definition: The profitability ratio calculated by dividing net profit by the total investment.
- Significance: Indicates the efficiency of investment and helps in making informed financial decisions.
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
How Is Artificial Intelligence Used by Beef Cattle Ranchers?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly important in beef cattle ranching, offering numerous benefits that enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability. Here are several key ways AI is used by beef cattle ranchers:
1. Precision Livestock Farming
Smart Sensors and Wearables:
- Definition: AI-powered sensors and wearable devices monitor the health and activity of cattle.
- Significance: These devices collect data on vital signs, movement patterns, and behavior, allowing for early detection of health issues and reducing the need for manual monitoring.
Automated Data Analysis:
- Definition: AI algorithms analyze data from sensors to provide insights into cattle health, growth, and behavior.
- Significance: Enables ranchers to make informed decisions about feeding, breeding, and medical treatments, improving overall herd management.
2. Health Monitoring and Disease Detection
Predictive Health Analytics:
- Definition: AI systems predict potential health issues by analyzing historical and real-time data.
- Significance: Early detection of diseases and health problems allows for timely interventions, reducing morbidity and mortality rates.
Behavioral Analysis:
- Definition: AI analyzes cattle behavior to identify signs of illness or distress.
- Significance: Changes in behavior, such as reduced movement or abnormal feeding patterns, can indicate health problems that require attention.
3. Feeding Optimization
Automated Feeding Systems:
- Definition: AI-controlled feeding systems adjust the quantity and type of feed based on individual cattle needs.
- Significance: Optimizes feed usage, ensuring that each animal receives the appropriate nutrients, leading to better growth rates and reduced waste.
Nutritional Analytics:
- Definition: AI analyzes feed composition and cattle growth data to develop optimal feeding strategies.
- Significance: Enhances feed efficiency and reduces costs, improving profitability.
4. Breeding and Genetic Improvement
Genomic Selection:
- Definition: AI analyzes genetic data to identify the best breeding candidates.
- Significance: Accelerates genetic improvement, leading to healthier, more productive herds.
Reproductive Management:
- Definition: AI systems monitor and predict optimal breeding times for cows.
- Significance: Increases conception rates and improves calving intervals, enhancing reproductive efficiency.
5. Pasture and Resource Management
Pasture Monitoring:
- Definition: AI-powered drones and satellite imagery monitor pasture health and usage.
- Significance: Provides insights into pasture conditions, allowing for better grazing management and sustainable land use.
Water Resource Management:
- Definition: AI systems optimize water usage by monitoring water sources and cattle hydration levels.
- Significance: Ensures efficient water use, crucial for sustainability, especially in regions with limited water resources.
6. Operational Efficiency
Labor Management:
- Definition: AI schedules and optimizes labor tasks based on operational needs and data analysis.
- Significance: Increases labor efficiency, reducing costs and improving productivity.
Supply Chain Optimization:
- Definition: AI predicts demand and optimizes the supply chain from farm to market.
- Significance: Enhances logistics and ensures timely delivery of products, reducing costs and increasing customer satisfaction.
7. Environmental Sustainability
Emission Monitoring:
- Definition: AI tracks and analyzes greenhouse gas emissions from cattle.
- Significance: Helps ranchers implement strategies to reduce their environmental footprint, ensuring compliance with regulations and promoting sustainability.
Waste Management:
- Definition: AI optimizes manure management and nutrient recycling.
- Significance: Reduces waste and improves soil health, contributing to sustainable farming practices.
8. Market and Financial Analysis
Price Forecasting:
- Definition: AI models predict market trends and cattle prices.
- Significance: Helps ranchers make informed decisions about when to buy or sell cattle, optimizing revenue.
Financial Performance Analysis:
- Definition: AI analyzes financial data to provide insights into profitability and cost management.
- Significance: Improves financial planning and resource allocation, enhancing overall business performance.
9. Animal Welfare
Welfare Monitoring:
- Definition: AI assesses cattle welfare through behavioral and physiological data.
- Significance: Ensures high standards of animal welfare, which is increasingly important for consumer trust and regulatory compliance.
Stress Detection:
- Definition: AI identifies signs of stress in cattle, such as abnormal vocalizations or movement patterns.
- Significance: Addressing stress improves cattle health and productivity, as well as ethical standards in farming.
 |
Read how InetSoft saves money and resources with deployment flexibility. |