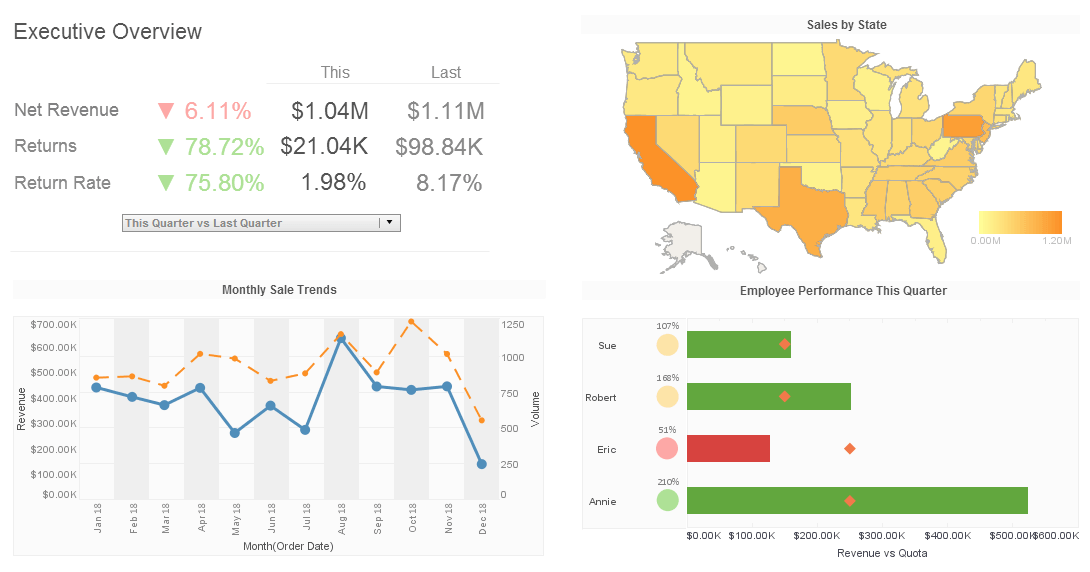
Business Intelligence Tools from InetSoft
InetSoft provides business intelligence tools that offer dashboards, analysis, and reporting that are easy, agile, and robust. InetSoft's flagship product, StyleBI™, goes beyond traditional business intelligence tools by providing a complete BI software platform which includes fine-grained security and administration for accessing diverse data sources.
In addition to pixel-perfect report publication, this advanced BI platform offers powerful yet easy-to-use Web-based applications for dashboard creation and interactive visual analysis.
If you've been searching for business intelligence tools that will make information access and reporting easier, look no further.
 |
View a 2-minute demonstration of InetSoft's easy, agile, and robust BI software. |
What KPIs and Metrics Do Rail Operators Monitor?
Rail operators monitor a wide range of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to assess the efficiency, safety, reliability, and financial performance of their operations. Some common KPIs and metrics monitored by rail operators include:
-
On-Time Performance (OTP): OTP measures the percentage of trains that arrive at their destinations on time. It is a critical metric for assessing service reliability and customer satisfaction. Delays can result from various factors such as track maintenance, equipment failures, weather conditions, and operational disruptions.
-
Schedule Adherence: Schedule adherence measures the extent to which trains adhere to their planned schedules. It evaluates the consistency and reliability of operations in terms of departure and arrival times. Deviations from schedules can lead to disruptions, inconvenience for passengers, and potential financial penalties for the operator.
-
Train Utilization: Train utilization metrics assess the efficiency of train utilization in terms of capacity utilization and frequency of service. It involves tracking metrics such as passenger or freight load factors, average passenger occupancy rates, and the number of trips per day or week. Optimizing train utilization helps maximize revenue potential while minimizing operational costs.
-
Safety Performance: Safety is a paramount concern for rail operators, and various safety metrics are monitored to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. These metrics may include accident rates, incidents of derailment or collision, employee injuries, level crossing accidents, and near-miss incidents. Monitoring safety performance helps identify potential hazards, implement preventive measures, and enhance safety protocols.
-
Asset Performance: Rail operators monitor the performance of critical assets such as locomotives, rolling stock, tracks, signaling systems, and infrastructure components. Asset performance metrics include metrics such as mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair (MTTR), asset availability, and reliability indices. Proactive maintenance and asset management strategies are implemented based on these metrics to optimize asset performance and minimize downtime.
-
Financial Performance: Financial metrics such as revenue, operating expenses, profitability, cost per passenger-mile or ton-mile, and return on investment (ROI) are essential for assessing the financial health and sustainability of rail operations. These metrics help track revenue generation, cost efficiency, and profitability margins, enabling operators to make informed financial decisions and allocate resources effectively.
-
Customer Satisfaction: Customer satisfaction metrics such as passenger surveys, complaints, feedback ratings, and Net Promoter Score (NPS) are crucial for gauging the quality of service and customer experience. Positive customer satisfaction indicators indicate high service quality, reliability, and responsiveness, while negative feedback may signal areas for improvement and corrective action.
 |
Read how InetSoft was rated as a top BI vendor in G2 Crowd's user survey-based index. |
What KPIs and Metrics Do Managers at a Rail Yard Use?
Managers at a rail yard oversee the efficient operation of the yard's facilities, including the movement, storage, and maintenance of rail cars and cargo. To effectively manage these operations, rail yard managers monitor a variety of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics tailored to the specific needs of their facility. Some common KPIs and metrics used by rail yard managers include:
-
Yard Capacity Utilization: Yard capacity utilization measures the extent to which the available yard space and infrastructure are being utilized. This metric helps managers optimize space allocation, track inventory levels, and prevent congestion or bottlenecks within the yard. Monitoring yard capacity utilization enables managers to identify opportunities for process improvements and resource optimization.
-
Car Turnaround Time: Car turnaround time measures the time it takes for rail cars to enter the yard, undergo any necessary inspections or maintenance, and exit the yard for onward transportation. This metric is critical for assessing yard efficiency and throughput, as shorter turnaround times indicate faster processing and improved operational performance. Managers may track average turnaround times for different types of rail cars and prioritize measures to reduce delays and improve productivity.
-
Switching Efficiency: Switching efficiency measures the effectiveness of yard switching operations in terms of the number of cars handled per hour or shift. It evaluates the speed, accuracy, and reliability of switching activities such as classification, sorting, and assembling trains within the yard. Monitoring switching efficiency helps managers identify opportunities to streamline operations, optimize workforce allocation, and minimize dwell times for rail cars.
-
Equipment Availability and Reliability: Managers track the availability and reliability of critical equipment such as locomotives, cranes, and track maintenance vehicles to ensure uninterrupted yard operations. Metrics such as mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair (MTTR), and equipment uptime provide insights into equipment performance, maintenance needs, and resource allocation. Maximizing equipment availability and reliability is essential for minimizing downtime, preventing service disruptions, and maintaining operational efficiency.
-
Safety Performance: Safety is a top priority in rail yard operations, and managers monitor various safety metrics to promote a safe working environment for employees and prevent accidents or injuries. Safety performance metrics may include the number of safety incidents, near misses, compliance with safety protocols, and adherence to regulatory requirements. By tracking safety performance indicators, managers can identify potential hazards, implement preventive measures, and reinforce safety training and procedures.
-
Environmental Impact: Rail yard managers may also monitor environmental metrics related to energy consumption, emissions, waste generation, and compliance with environmental regulations. Sustainability initiatives such as reducing energy usage, implementing eco-friendly practices, and minimizing environmental impact align with corporate responsibility goals and contribute to a positive public image.
More Articles About Business Intelligence Operations
Building Comprehensive Analyses - StyleBI offers an interface for building comprehensive analyses in the form of interactive multidimensional charts, giving you direct access to insights that used to require several pages of reporting to put together...
How to Make a Funnel Chart in InetSoft - Creating a Funnel Chart with InetSoft software is extremely simple. The data can be arranged in two different ways. The first arrangement contains the aggregated data exactly as it should appear on the chart. For example...
Online Sentiment Analysis - An important KPI in reputation management is online sentiment analysis. It entails keeping an eye on internet reviews, news stories, and social media to gauge if a brand is being linked with good, negative, or neutral opinion. Businesses may react quickly to negative sentiment and magnify positive feedback by using this KPI to identify the general tone of talks about their goods or services...
Top Analytic Techniques for Business Users - Before the analysis of data can begin, it's best to meet and collaborate with all key stakeholders within your business to determine your primary campaign or strategic goals, thus gaining a comprehensive understanding of the types of insights that are needed to steer management directives and grow your organization...