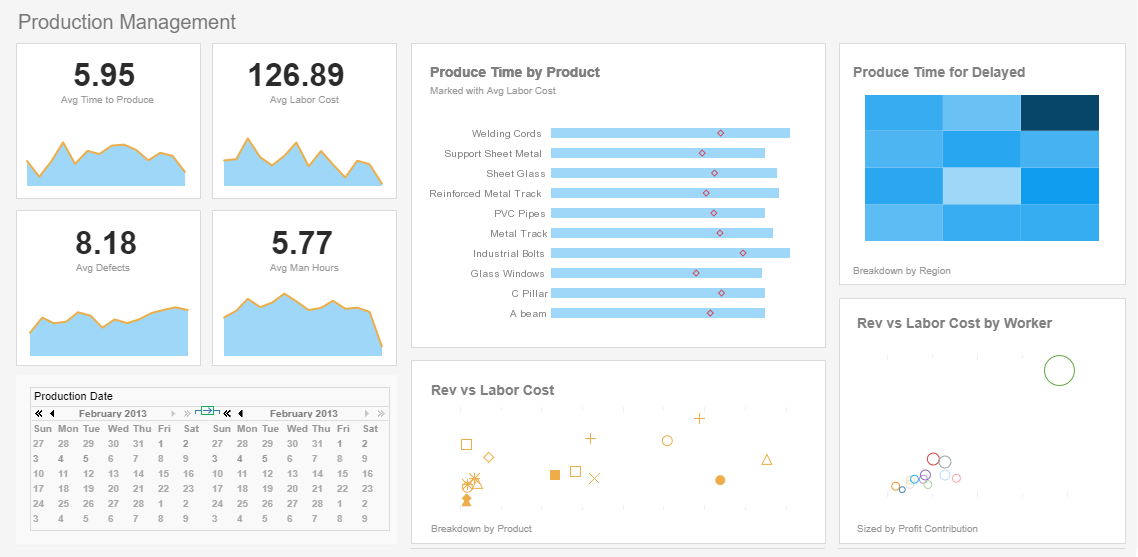
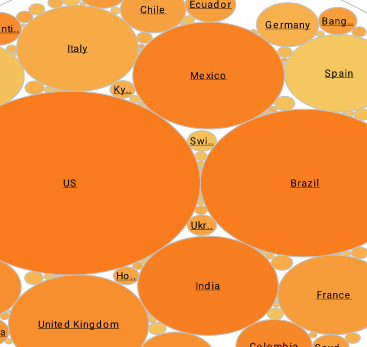
Operational Business Intelligence
InetSoft focuses on operational BI through an intuitive self-service user interface that facilitates the dissemination of information, and institutes accurate and timely decision making.
Requirements as diverse as reporting, OLAP, scorecards, dashboards, visualization, and ad hoc analysis are all met in a unified application that uses live key performance indicators to continually guide and gauge all business processes.
With cloud-based InetSoft's operational BI platform, businesses can:
- Explore data with self service solutions - The visualization driven approach of InetSoft allows users to perform their own reporting and analysis with very little IT support. By using familiar graphical objects and an intuitive Web 2.0 interface end users are empowered to easily explore, manipulate, and display data to gain new insights.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
What Is Operational Business Intelligence?
Operational business intelligence is defined as real-time business intelligence derived from ongoing business operations. In other words, it's business intelligence that fuels daily (or thereabout) decision-making. Regardless of your position or industry, having to make decisions informed by stale data is an enormous roadblock to success. Operational business intelligence is defined as real-time business intelligence derived from ongoing business operations. In other words, it's business intelligence that fuels daily (or thereabout) decision-making. Regardless of your position or industry, having to make decisions informed by stale data is an enormous roadblock to success.
 |
Learn the advantages of InetSoft's small footprint BI platform. |
What Are Some Examples of Operational Business Intelligence for a Credit Operations Analyst?
Operational business intelligence for a Credit Operations Analyst involves using data and analytics to gain insights and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of credit-related operations within an organization. Here are some examples of operational business intelligence initiatives that a Credit Operations Analyst may undertake:
-
Credit Application Processing Time: Analyzing the time taken to process credit applications can help identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the credit approval process. By tracking and measuring the processing time, the analyst can identify areas where the process can be streamlined, such as automating certain steps, reallocating resources, or improving communication channels.
-
Credit Approval Rate: Monitoring the credit approval rate helps evaluate the effectiveness of credit risk assessment and decision-making processes. The analyst can identify factors that contribute to higher rejection rates, such as inconsistent credit policies, inadequate underwriting criteria, or incomplete documentation. This analysis enables them to recommend improvements to enhance the approval rate without compromising risk management.
-
Credit Portfolio Performance: Analyzing the performance of the credit portfolio provides insights into credit quality, delinquency rates, default rates, and overall portfolio health. The analyst can identify trends, patterns, and risk concentrations within the portfolio, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding credit risk management, collections strategies, or loan restructuring initiatives.
-
Aging of Receivables: Monitoring the aging of receivables helps assess the effectiveness of credit collection efforts. The analyst can analyze the aging buckets to identify accounts that require prioritized collections efforts or potential write-offs. This analysis facilitates the development of targeted collection strategies, such as implementing reminder campaigns, modifying payment terms, or initiating legal actions when necessary.
-
Customer Credit Utilization: Examining customer credit utilization patterns provides insights into how customers are utilizing their credit limits and whether they are nearing their credit capacity. The analyst can identify customers who may be at higher risk of default due to excessive credit utilization or changes in their repayment behavior. This analysis helps in proactively managing credit limits, establishing risk mitigation measures, or initiating customer outreach for risk assessment.
-
Credit Fraud Detection: Leveraging data analytics and machine learning techniques, the analyst can develop models to detect and prevent credit fraud. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns indicative of fraudulent activities, the analyst can build predictive models that flag suspicious transactions, unauthorized credit applications, or account takeovers. This proactive approach helps mitigate credit fraud risks and protect the organization's financial interests.
-
Customer Creditworthiness Assessment: Utilizing operational business intelligence, the analyst can develop credit scoring models to assess the creditworthiness of customers. By analyzing various customer data points, such as credit history, income levels, and repayment behavior, the analyst can develop models that provide insights into the risk associated with extending credit to different customers. This analysis helps optimize credit decision-making processes and minimize the risk of default.
-
Operational Efficiency Metrics: Apart from credit-specific metrics, the analyst can also track operational efficiency indicators, such as turnaround time for customer inquiries, accuracy of credit data entry, or completeness of credit documentation. Monitoring these metrics helps identify areas for process improvement, employee training needs, or system enhancements to enhance overall operational efficiency.
What KPIs Does a Credit Operations Analyst Use?
-
Collection Effectiveness: This KPI measures the effectiveness of credit collection efforts. It can include metrics such as the percentage of outstanding receivables, the aging of receivables, or the percentage of accounts in collections. The analyst can track these metrics to evaluate the performance of collection strategies, identify areas for improvement, and optimize collection processes.
-
Credit Loss Ratio: This KPI measures the ratio of credit losses (such as bad debts or write-offs) to the total amount of credit extended. It provides insights into the overall credit risk and helps the analyst evaluate the effectiveness of credit risk management strategies. Monitoring this KPI helps identify trends, assess portfolio performance, and refine underwriting criteria to minimize credit losses.
-
Customer Satisfaction: While not specific to credit operations, customer satisfaction is an important KPI to gauge the overall experience and perception of customers regarding credit processes and services. Feedback mechanisms, surveys, or Net Promoter Score (NPS) can be used to measure customer satisfaction. The analyst can track and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and enhance customer-centricity in credit operations.
-
Operational Efficiency Metrics: These KPIs assess the operational efficiency of credit processes. Examples include the average time to respond to customer inquiries, accuracy of credit data entry, turnaround time for credit limit changes, or completeness of credit documentation. By monitoring these metrics, the analyst can identify process bottlenecks, allocate resources effectively, and streamline operational workflows.
-
Compliance Metrics: These KPIs evaluate the organization's adherence to credit-related regulations, policies, and industry standards. They can include the number of compliance violations, regulatory fines or penalties, or the completion rate of compliance training programs. Monitoring compliance metrics helps the analyst ensure that credit operations align with legal and regulatory requirements.
-
Non-Performing Loans (NPLs): NPLs are loans that are past due and in default or at risk of default. They indicate borrowers who are experiencing financial difficulties or are unable to fulfill their repayment obligations. Monitoring the percentage of NPLs in the credit portfolio helps identify potential credit risks and assess the overall credit quality.
-
Delinquency Rate: The delinquency rate measures the percentage of loans or accounts that are past due but not yet in default. It indicates the number of borrowers who are experiencing payment delays. Tracking the delinquency rate helps identify early warning signs of potential credit problems and assess the effectiveness of collection strategies.
-
Default Rate: The default rate measures the percentage of loans that have defaulted, typically defined as loans that are severely delinquent and unlikely to be fully repaid. It represents loans that have failed to meet repayment obligations, leading to a significant loss for the lender. Monitoring the default rate helps assess credit risk and evaluate the effectiveness of credit risk management strategies.
-
Charge-Off Rate: The charge-off rate measures the percentage of loans or credit balances that the lender has written off as uncollectible. It reflects the losses incurred by the organization due to defaults or severe delinquencies. Tracking the charge-off rate helps assess credit risk, evaluate the accuracy of credit risk assessments, and make provisions for potential losses.
-
Loan Loss Reserve Ratio: The loan loss reserve ratio measures the amount of money set aside by the organization to cover potential loan losses. It represents the provision made to account for credit risks within the portfolio. Monitoring this ratio helps ensure that sufficient reserves are allocated to mitigate potential losses and maintain financial stability.
-
Credit Concentration: Credit concentration refers to the extent to which credit exposures are concentrated within specific industries, geographic regions, or customer segments. Assessing credit concentration helps identify potential vulnerabilities and diversification needs within the portfolio. It ensures that the organization is not overly exposed to specific sectors or risks.
-
Recovery Rate: The recovery rate measures the percentage of the loan or credit balance that is recovered after default or charge-off. It reflects the organization's ability to recover funds through collection efforts, asset liquidation, or legal actions. Monitoring the recovery rate helps assess the effectiveness of collection strategies and evaluate the overall recovery performance.
-
Portfolio Mix: Portfolio mix refers to the distribution of credit exposures across different types of loans, credit products, or customer segments. Assessing the portfolio mix helps evaluate the risk profile of the portfolio and ensure a well-diversified credit portfolio. It helps manage concentration risks and align the portfolio with the organization's risk appetite and strategic objectives.
 |
View live interactive examples in InetSoft's dashboard and visualization gallery. |
More Articles About Operational BI for Analysts
Addressing Critical Operational Challenges - One of the biggest challenges facing Sell-side banks is the lack of visibility into their own trade execution processes. These blind spots limit their ability to successfully run their business. Some key questions are: How do you know what pricing strategy to quote if you can't determine how long it takes to generate a price and deliver it to the ECN? Can you win a competitive deal if you're the last person generating the quote? How are you going to increase trading volumes without visibility into the open-order status...
Articles About Tracking Business Performance Indicators - Do you need to track business performance indicators? InetSoft offers BI software for performance monitoring dashboards and balanced scorecards that can be easily deployed and used. View a demo and read reviews. Sales Management Application - Have you entertained thoughts of how you can further scale your business using your CRM if you began integrating an easy to use BI Tool? Then look no further, because it's possible with InetSoft's agile and robust software...
Best Practices in Measuring Businesses - There are many different approaches to measuring a business, and it can be difficult to know which metrics are the most important. There is no one metric that will tell you everything you need to know about your company, but there are some that provide insight into different aspects of your company's performance. The following are some of the most common metrics that measure a company's success: Revenue: The total amount of money made from a product or service within a certain time period; Net Income: The amount of money left over after all expenses have been paid...
Best Techniques For Managing Dashboards - Here are 8 recommended practices to follow no matter what kind of dashboard reports you're creating in order to remain efficient, effective, and well-organized: 1. Ensure that your data is relevant Who is watching your dashboard and getting your dashboard report? Only those metrics should be shown for those recipients. Additionally, avoid include any data that could look out of place or unnecessary if you group your dashboards by recipient, team, or subject...
BI Collaboration through Building Blocks - Traditional collaboration, achieved through a mixture of business intelligence reports, desktop application files, e-mails, and other means, is the equivalent of collaborative document editing. The limitations of this approach become apparent as the number of parties involved grows. Moreover, collaborating parties cannot easily build upon each other's work... BI Spans Applications And Databases /company/business_intelligence_suites/ - As Luke suggested, it spans applications and databases where all the information comes from. They are looking to, as I said before, put the processes in context. The second approach we find is that they are putting a BPM, a process strategy in place. The follow-on to that is sometimes the business intelligence strategy...
 |
Read how InetSoft saves money and resources with deployment flexibility. |
Continual Rise of Edtech - When exploring improved intelligence in the educational sector, it's important to look at the role EdTech plays in driving continual innovation. Before we continue, here's a practical definition of EdTech: EdTech-or education technology-is a branch of digital technology that focuses on the development of tools, applications, and processes dedicated to improving the learning experience both inside and outside of the classroom...
Critical BI Success Factors - What are some of the critical success factors when you're implementing a business intelligence solution? From an operational BI viewpoint, you need a good infrastructure to support the kind of data volumes that are involved. You also need operational BI to coexist with other kinds of business intelligence applications such as tactical BI. Therefore you...
Evaluate InetSoft's All in One Business Dashboard Software - Looking for a good all in one business dashboard solution? InetSoft is a pioneer in self-service dashboard software with a drag-and-drop designer for business users. View a demo and try interactive examples. Key for a successful BI strategy and to maximize adoption, our BI solution is easier to deploy and use and supports advanced data mashups for maximum self-service...
Examples of KPM's - To visualize how some common KPM's can be charted and analyzed in InetSoft's application look at the examples to the left. The Marketing Department of any products or services company needs to track leads as one of its KPMs. This screenshot shows the weekly count of the number of new leads generated. In addition, thanks to mutli-dimensional charting ...
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
Good MongoDB Reporting Tool - Looking for a good MongoDB reporting tool? InetSoft's pioneering dashboard reporting application produces great-looking web-based reports and dashboards with an easy-to-use drag-and-drop designer. View a demo and try interactive examples. A defining highlight of this release is upgraded data visualization capabilities for geographic charting...
How Many Phases of Data Analytics Are There? - Data analytics is the process of looking at and analyzing data to draw conclusions and make wise judgments. In order to gather, process, and analyze data from diverse sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and internet platforms, a range of approaches and technologies are used. To make data-driven decisions and optimize operations, data analytics is employed in a range of industries, including business, finance, healthcare, and government... Link All Your Metrics /business/solutions/how_to_avoid_making_common_mistakes_when_measuring_performance/ - Here are some of the biggest mistakes I've seen organizations make. Probably one of the most common ones is coming up with some vague vision statement and then trying to link all your metrics and your scorecard to the vision. In fact, some of the books on balanced scorecards even suggest that that's how you should do it...
Make Sure Your Kpis Are Measurable - It's important to select KPIs that you can actually measure. There's no point in tracking a metric if you can't accurately track and report on it. When in doubt, err on the side of simplicity and choose a KPI that you can easily track and report on without too much hassle. Measuring KPIs involves more than just data collection...
Scorecard Metrics in Action - The foundation of a scorecard is that business does not happen in a vacuum. All aspects of a business are interconnected and all decisions permeate throughout an organization. Common scorecard metrics are chosen based on different business perspectives such as financial, customer, process, and innovation. They can measure anything from monthly turnover to the installation date of new machinery...
 |
View live interactive examples in InetSoft's dashboard and visualization gallery. |
Simple Point-And-Click Access - The Marketing Department of any products or services company needs to track leads as one of its KPIs. This screenshot shows the weekly count of the number of new leads generated. In addition, thanks to mutli-dimensional charting of the source of leads by colors in the vertical bars, the reasons for a KPI's increase or decrease can be seen. The checkboxes to the right provide simple point-and-click access to filtering to explore further the reasons for change, or for slicing and dicing different campaigns, so that multiple KPIs can be tracked in a single report..
Transitioning Into Operational Business Intelligence - We are here today to talk about operational business intelligence, or BI, what also people call enterprise intelligence. We certainly see more and more companies finding a critical role for BI in their day-to-day decision making, and this isn't just in their strategic planning as it may have been in the past...
Way For Users To Create A KPI Dashboard - The key to creating an effective KPI dashboard is selecting the right tool, and InetSoft offers a simple and powerful way for users to create a KPI dashboard in order to meet the needs of any business. Key Performance Indicators, or KPI's, are measurable values that indicate how effectively business goals are being met. It is crucial for businesses to keep track of their most important KPI's to ensure ongoing quality performance and overall efficiency...
What Are the KPIs in IT? - This is a relatively new area for the use of KPIs. IT has had some traditional ones such as the five nines for uptime, server availability, for instance, or are processes running fast or slow. But now that IT is doing things that are customer-facing like powering a company's online presence and the performance of the Web site is a point of competitive differentiation, that's where there new performance indicators that need to be tracked...
What Exactly is a Metric? - A metric is a quantitative measure. They are used to track certain operations, such as a marketing or sales initiative's conversion rate. Metrics allow organizations to evaluate the effectiveness of these processes To apply our previous example of kilometers traveled, you can only ascertain how far a person has traveled by using the measure...