InetSoft Technology: Free and Commerical Business Intelligence Products - Dashboard, Analysis and Reporting Tools
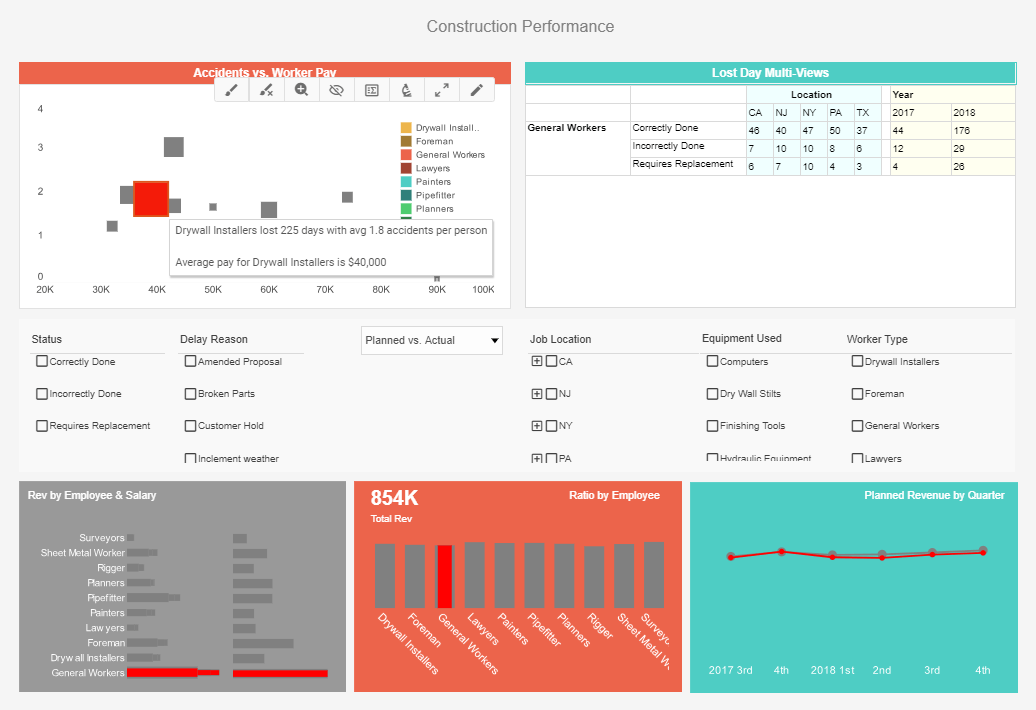
InetSoft offers an Operational BI platform that features visualization-driven: reporting, dashboards, and analytics. It is backed by Data Block technology that provides user-defined data mashup and transformation, and performance benefits like streaming, caching, and materialized view pre-aggregation.
Our products are easy, agile, and robust: easy to implement initially, and easy for users to learn; agile to adjust to changing business requirements quickly; and robust in terms of feature-set and scalability. Your budget benefits from fast implementations and flexible licensing while your users receive greater self-service, exploration, and collaboration. InetSoft's innovative products have won awards from developers every year since 1999.
Commercial Products
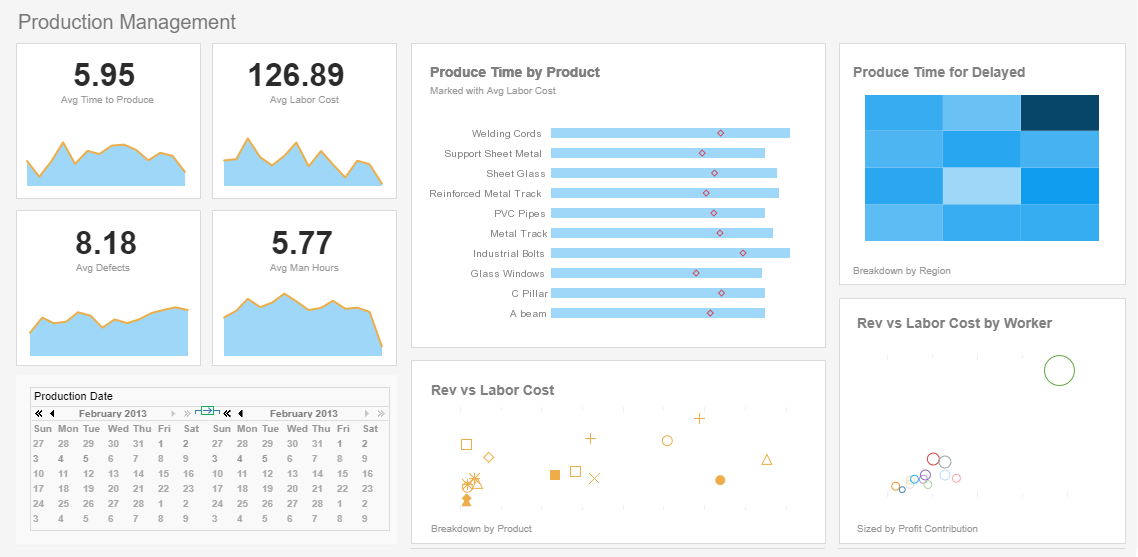
Style Intelligence - Business Intelligence Software
Style Intelligence is a complete operational business intelligence platform. It provides a visualization-driven approach to reporting, dashboards, and visual analysis, all in a single small footprint deployment.
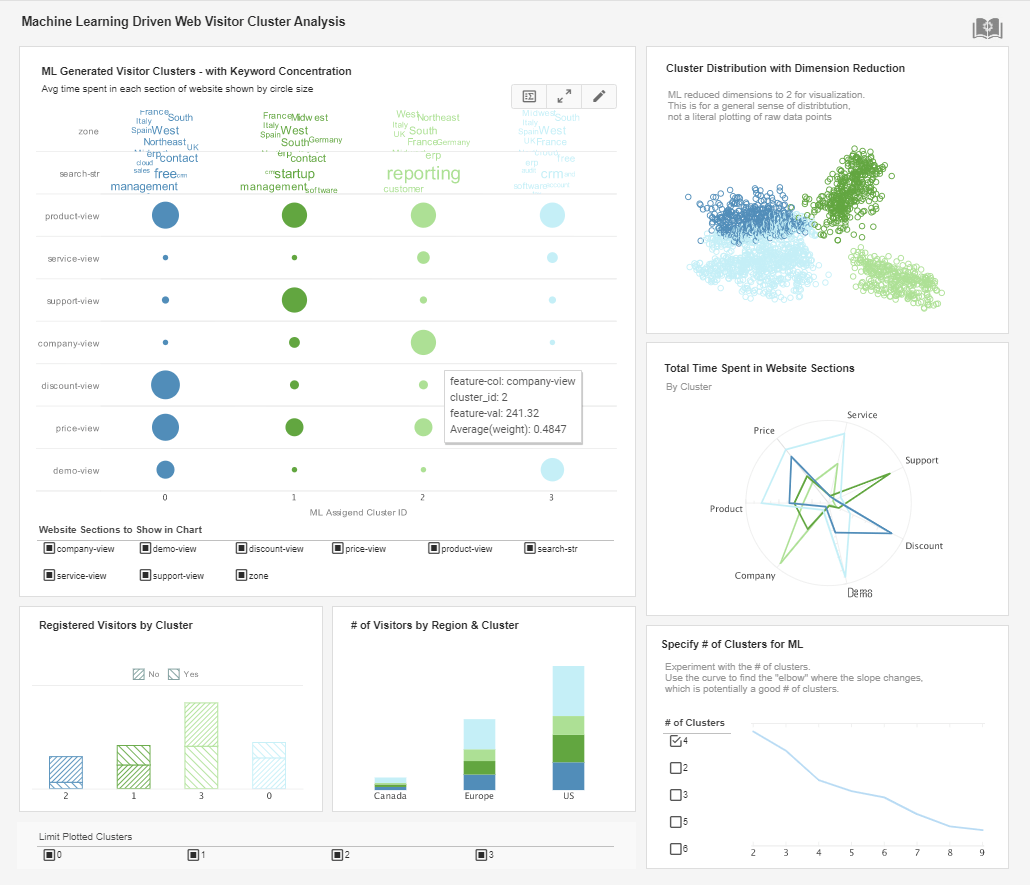
Style Scope - Dashboard Software
Style Scope is an edition of Style Intelligence that includes the patent-pending Data Block technology that is focused on data visualization, plus monitoring and analytic dashboards.
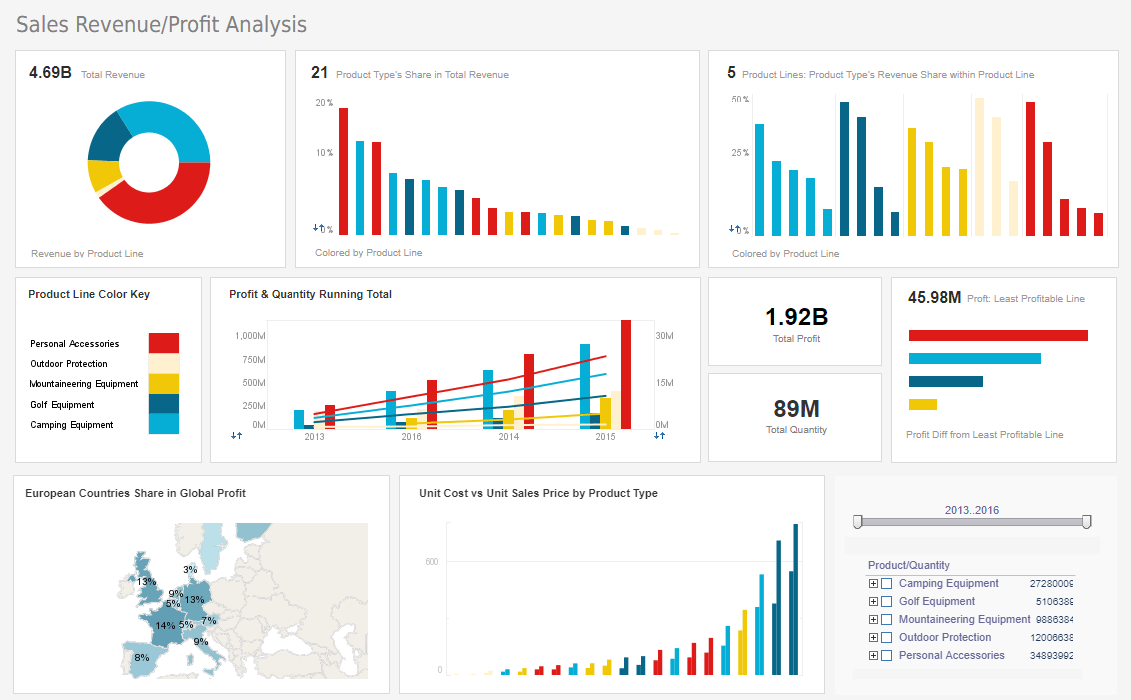
Style Report Enterprise - Reporting Software
Style Report Enterprise is an edition of Style Intelligence that focuses on high performance, scalable enterprise reporting. Deliver carefully formatted information to a wide business user community.
Free Business Intelligence Applications
The Start Free button gives you two options for using InetSoft's free dashboard visualization software.
Individual Account
Register with any email address, including free email services such as Google and Yahoo. There is no credit card required. Use the 100% web app with no desktop install. Collaborate online in real time. Use data sources such as uploaded Excel or CSV files or connect to live Google sheets. Publicly share dashboards, if you wish, via URL link. All advanced data visualization types and interactive controls are available.
Business Account
Register with any organizational (business, university, or organization) email address. There is no credit card required. Use the 100% web app with no desktop install. Collaborate online in real time. Use data sources such as uploaded Excel or CSV files or connect to live Google sheets, plus more Google apps, Facebook, databases and many other online data sources. Publicly share dashboards, if you wish, via URL link. Privately share dashboards and analyses within your organization (same email domain). All advanced data visualization types and interactive controls are available.
How Does a Port Authority Use Wind Rose Charts?
Port authorities use wind rose charts as an essential tool for understanding and managing the influence of wind patterns on port operations and safety. A wind rose chart provides a graphical representation of the frequency and direction of wind at a particular location over a specific period. This information is crucial for various aspects of port management, including navigation, ship scheduling, infrastructure planning, and environmental monitoring. Here's a detailed look at how port authorities utilize wind rose charts:
1. Navigational Safety and Vessel Management
a. Berthing and Mooring Operations:
- Optimal Berthing Conditions: Wind rose charts help port authorities determine the safest and most efficient berthing conditions for vessels. They can identify periods when strong winds from specific directions might make docking difficult or unsafe, helping in scheduling and planning berthing operations accordingly.
- Mooring Strategies: Understanding prevailing wind directions and speeds is essential for selecting the appropriate mooring arrangements to ensure vessels remain securely fastened. This is particularly critical for large vessels or those carrying hazardous materials.
b. Navigation and Piloting Assistance:
- Navigational Hazards: Wind patterns can significantly impact navigation within a port, particularly in narrow channels or areas with high vessel traffic. Wind rose charts enable pilots and port authorities to anticipate challenging conditions and prepare accordingly.
- Guidance for Inbound and Outbound Traffic: Port authorities use wind rose data to provide guidance to incoming and outgoing vessels about the best times and routes to use, reducing the risk of accidents caused by sudden wind shifts or high wind speeds.
2. Port Infrastructure and Design Planning
a. Design of Port Structures:
- Breakwaters and Piers: Wind rose charts are used to assess how wind-driven waves and currents may impact breakwaters, piers, and other structures. This information is crucial during the design phase to ensure these structures can withstand the environmental conditions.
- Crane and Equipment Placement: Wind data is essential for determining the optimal placement and operation of cranes and other heavy equipment, which can be affected by high winds. This helps in minimizing downtime and ensuring the safety of port operations.
b. Layout of Port Facilities:
- Orientation of Runways and Storage Areas: In ports with air transport facilities, wind rose data can influence the orientation of runways. Similarly, the layout of storage areas for sensitive cargo that might be affected by wind (e.g., open storage for bulk goods) can be optimized based on wind patterns.
- Building Design and Wind Load: Wind rose charts help architects and engineers design port buildings and warehouses to withstand local wind conditions, taking into account factors like wind load and the potential for wind-driven debris.
3. Operational Efficiency and Scheduling
a. Minimizing Downtime:
- Predicting Disruptions: Port authorities use wind rose charts to anticipate potential disruptions to loading, unloading, and transportation activities due to adverse wind conditions. By understanding typical wind patterns, they can schedule operations during periods of lower risk.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Maintenance and repair work, especially on high structures like cranes and communication towers, is scheduled during periods when wind conditions are forecasted to be calm, reducing the risk to workers and equipment.
b. Optimizing Shipping Schedules:
- Scheduling Ship Movements: Accurate knowledge of wind patterns enables port authorities to schedule ship movements more efficiently, avoiding times when strong winds could complicate navigation or make cargo handling unsafe.
- Fuel Efficiency for Vessels: Understanding wind patterns helps ships entering and leaving the port to plan their routes and speeds, optimizing fuel use and minimizing environmental impact.
4. Environmental and Hazard Management
a. Air Quality Monitoring:
- Dispersion of Pollutants: Wind rose charts are used to predict how pollutants, such as emissions from ships and industrial activities, will disperse. This information helps in monitoring air quality and implementing measures to mitigate environmental impact.
- Managing Dust and Particulate Matter: For ports handling bulk goods like coal or grain, wind patterns influence the spread of dust and particulates. Wind rose data can guide the positioning of dust suppression systems and the scheduling of cargo handling to minimize dust emissions.
b. Emergency Response Planning:
- Spill and Hazardous Material Response: In the event of an oil spill or release of hazardous materials, wind rose charts help predict the spread of airborne contaminants. This is crucial for coordinating emergency response efforts and protecting the health and safety of workers and nearby communities.
- Fire Management: Knowledge of wind patterns is vital in managing and containing fires, especially in ports where flammable materials are stored or transported. It helps predict the potential spread of fire and smoke, enabling more effective firefighting strategies.
5. Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
a. Adherence to Safety Regulations:
- Safety Standards Compliance: Ports are subject to international and local safety regulations, many of which include requirements related to wind conditions (e.g., maximum allowable wind speeds for certain operations). Wind rose charts provide the necessary data to demonstrate compliance with these standards.
- Environmental Regulations: Ports must also comply with environmental regulations regarding emissions and pollutant dispersion. Wind rose charts help in the assessment and reporting of compliance with these regulations, especially in relation to air quality and pollutant control.
b. Data for Environmental Impact Assessments:
- Impact on Local Ecosystems: Wind rose data is often used in environmental impact assessments to understand how port activities might affect local ecosystems, particularly through the dispersal of pollutants or noise.
- Public Reporting and Transparency: Many ports publish wind data as part of their transparency initiatives, providing stakeholders and the public with information on how the port manages environmental and safety concerns.
6. Long-Term Strategic Planning
a. Climate Adaptation Strategies:
- Adapting to Climate Change: As climate patterns change, understanding historical wind data becomes essential for adapting port infrastructure and operations. Wind rose charts can indicate shifts in wind patterns over time, informing long-term planning and investment in infrastructure.
- Forecasting and Scenario Planning: Wind rose data helps in developing scenarios for future port operations, considering potential changes in weather patterns. This is particularly relevant for ports that are planning expansions or new facilities.
b. Investment and Resource Allocation:
- Infrastructure Investment: Port authorities use wind data to prioritize investments in infrastructure, such as wind barriers, enhanced mooring systems, or improved navigation aids, based on the anticipated wind conditions.
- Resource Allocation for Operations: Wind rose charts help allocate resources more effectively, such as positioning tugs, pilots, and maintenance crews where they are most likely to be needed based on wind forecasts.