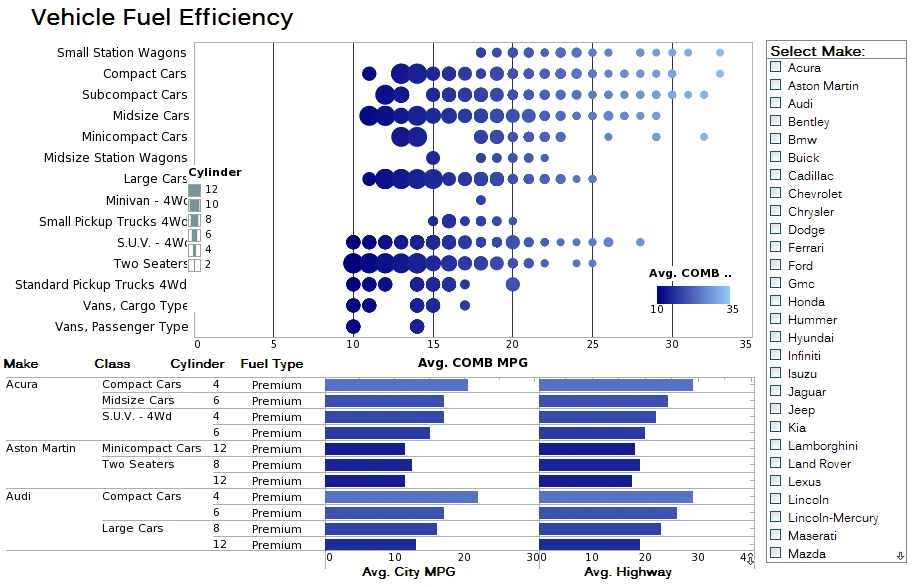
Pros and Cons of the Top 6 Data Visualization Vendors
InetSoft
- Strengths
- Strong support for a wide variety of data sources including relational databases, CSV, XML, JSON, web services and more
- Built in data mashup capabilities allow combining disparate data sets without heavy pre processing
- Data transformation tools are robust with built in ETL like functions such as joins, aggregations, calculations and cleansing
- Dashboards are interactive with easy filtering and parameter control for end users
- Scales well for mid sized deployments and supports multi tenant architectures
- Good support for embedding analytics into other applications or portals
- Metadata management helps ensure consistency across visualizations
- Scheduling and automation for data refresh supports operational reporting needs
- Visual design tools help create custom visualizations without coding
- Weaknesses
- Steeper learning curve for administrators and power users configuring data pipelines
- Limited real time streaming support compared with tools built around logs or event streams
- Integration with modern data lake architectures requires more custom work
- Not as strong in community driven plug ins and extensions as open source alternatives
- Data Pipeline
- Connects to many traditional data sources out of the box
- Supports incremental data refresh and scheduling
- Needs careful planning for high frequency updates
- Works better with batch oriented pipelines rather than real time streams
- ETL functions are embedded but not as powerful as standalone ETL tools
- Data Transformation
- In tool transformation allows cleansing and reshaping data before visualization
- Graphical transformation building reduces need for external scripting
- Complex transformations can become unwieldy if not documented well
- Some advanced transformations may require SQL knowledge
MetricFire
- Strengths
- Built for performance monitoring with strong time series data handling
- Deep integration with Prometheus makes it ideal for infrastructure metrics
- Supports long term storage of metrics while maintaining query performance
- Visualizations are optimized for monitoring and alerting contexts
- Alerting tools are mature with thresholds, notifications and escalation policies
- API driven approach makes integration with DevOps pipelines easier
- Scales well horizontally to handle high cardinality metrics
- Strong community and ecosystem around Prometheus standards
- Weaknesses
- Less suited for business intelligence style reporting with complex multidimensional data
- Customization outside of metric centric use cases can be limited
- Transformation capabilities focus on metric alignment not general ETL
- Steep learning curve for teams unfamiliar with time series concepts
- Dependency on Prometheus ecosystem means less flexibility for other data paradigms
- Data Pipeline
- Ingests metrics from exporters, agents and Prometheus instances
- Pipelines are optimized to store and retrieve high volume time series data efficiently
- Less focus on batch data or non time series sources
- Supports scraping targets at regular intervals for consistency
- Integrates with alerting and monitoring based workflows
- Data Transformation
- Transformation focused on aggregations over time, down sampling and roll ups
- Label based metrics allow flexible grouping and segmentation
- Limited general purpose transformation beyond time series operations
- Best practices often require preprocessing outside the tool for non metric data
Grafana
- Strengths
- Extremely flexible dashboarding platform connecting to many data sources
- Supports metrics, logs, traces and relational data depending on datasource plugins
- Open source with vibrant ecosystem of plugins and community contributions
- Alerting, annotations and sharing capabilities enhance real time observability
- Visualization library is broad and configurable
- Efficient for monitoring infrastructure, applications and business KPIs
- Provisioning as code allows stable automated deployments
- Team collaboration features with access control and shared dashboards
- Weaknesses
- Transformation abilities depend heavily on the capabilities of the datasource
- Does not include built in ETL to perform deep data reshaping before visualization
- Complex queries can become hard to manage without abstraction layers
- User experience varies by plugin based on implementation quality
- Less suited for deep business analytics without integrated data warehousing
- Data Pipeline
- Primarily a visualization layer that connects to upstream data stores
- Supports time series DBs like Prometheus, InfluxDB as well as SQL engines and cloud sources
- Data ingestion handled externally which allows for best of breed pipeline choices
- Pipelines can be custom tailored using tools like Telegraf, Fluentd or custom scripts
- Enables layering of multiple data sources into unified dashboards
- Data Transformation
- Transformations rely on datasource query languages such as SQL, PromQL or others
- Grafana provides some transformation helpers but not full ETL workflow
- Best results achieved when pre transformed data is supplied from upstream
- Visualization side transformations focus on formatting, renaming and combining series
- Does not replace a dedicated transformation engine for complex cases
Kibana
- Strengths
- Seamlessly integrated with the Elastic Stack for logs, metrics and traces analytics
- Powerful search and filtering using the underlying Elasticsearch engine
- Visualizations are flexible with support for maps, charts, tables and more
- Dashboards can combine different visualization types into cohesive views
- Machine learning features can detect anomalies in data patterns
- Alerting and reporting features support operational use cases
- Useful for security analytics, observability and log exploration
- Weaknesses
- Tight coupling with Elasticsearch means less flexibility for other data platforms
- Scaling costs can grow with high volume indexing and storage needs
- Transformation outside of log ingestion pipelines is limited
- Elastic query language and mappings can be complex for novice users
- Visualization options can be overwhelming without clear governance
- Data Pipeline
- Logstash and Beats commonly used to ingest data into Elasticsearch
- Pipelines are real time oriented with streaming ingestion of logs and events
- Support for filtering, enriching and routing events before storage
- Batch import is possible but optimized performance is in streaming mode
- Pipelines can include custom scripts for advanced parsing
- Data Transformation
- Transformations performed in ingestion layer using Logstash, Beats processors or ingest pipelines
- Allows parsing, extracting fields and enriching records before indexing
- Once indexed, Elasticsearch provides aggregation and analytics capabilities
- Not ideal for heavy cross source joins compared with traditional BI tools
- Best suited for text and event oriented transformation workflows
Mozaik
- Strengths
- Designed for real time dashboards with a focus on DevOps and metric visualization
- Supports multiple data sources with widget based dashboards
- Open source and flexible to customize with code driven configurations
- Well suited for monitoring and status boards in operations centers
- Lightweight and simple for teams needing rapid setup
- Good integration with time series databases and REST APIs
- Weaknesses
- Not intended for heavy business intelligence reporting workflows
- Limited transformation tools compared with full BI platforms
- Customization requires coding rather than graphical design
- Smaller ecosystem compared with larger open source communities
- Less enterprise support and governance features
- Data Pipeline
- Typically pulls data from time series sources via APIs or native connectors
- Real time refresh is supported for up to the minute dashboards
- Pipelines are lightweight and often custom built by developers
- Not optimized for complex ETL or batch ingestion from varied sources
- Best used where simplicity and speed outweigh deep pipeline orchestration needs
- Data Transformation
- Transformation is usually handled by the data source before ingestion
- Mozaik focuses on presenting metrics that are already structured for visualization
- Some widget level formatting and calculations are available
- Not a substitute for dedicated transformation frameworks or engines
- Best fit when upstream systems provide data ready for consumption
More Articles About Data Visualization
Data Visualization How To Techniques - Today’s topic is data visualization how to techniques. Making pretty pictures, right? That’s part of it. Where did the concept originate? The idea of data visualization really came from a Yale professor named Edward Tufte. And so, I’m a software developer, and a lot of the applications I build are designed to capture data, and sometimes massive amounts of data. What’s the biggest problem with data? It’s trying to understand it once you capture it, trying to present that back in a meaningful way. Trying to curate it. There’s all kinds of books, podcasts, white papers and guidance on tools around how to store the data, how to create reports and nice, pretty graphs to go around it. But there isn’t a lot of guidance around what’s an effective way to display that data to the end user. And that’s really what data visualization, or at least effective data visualization, is all about. You don’t just slap data into a report. You don’t just export it into Excel, and run a wizard, and throw any graph up at all. Start thinking about that. Start thinking about what’s the best way to communicate this data through an image—maybe through a graph, or a chart, or something like that. That’s what data visualization’s all about. And like I said, I first started studying this when I read a book by Edward Tufte called The Visual Display of Quantitative Information...
Data Visualization Software Download - Are you looking to download data visualization software? Since 1996 InetSoft has been making business software that is easy to deploy and easy to use. Build self-service oriented dashboards and visual analyses quickly. View a 3-minute demo and download a free version...
Data Visualizations Are Quick at Solving a Problem - So that’s the second example of how data visualizations are quick at solving a problem. The concept here that you’ve seen in the demos is how charts that you put on pages address business issues. Combinations of visualizations then show a story of performance for a unit or for a problem. There is a set of charts we work with. You’ve seen bar charts that have a variety of looks and fields. A pie chart shows relative performance. Line chart show trends over time very well. The map shows distribution across a geographic area. It could also be a logical map. It can show links between things. So there’s a set of things that maps do really well. The heat map you just saw is another type. We have seen visualizations for text data. The text data would be selectable. There are different ways to cut the data down. A scatter plot you saw with the mutual funds but that can be turned into a bubble chart so you can resize and shape it for different kinds of data. Time table show transactions and in this case you actually see for this specific element. There are a set of clusters of transactions and then they stop and they pick up another areas over here...
Database Visualization Software - InetSoft’s unique and powerful business intelligence visualization software allows users to access a full set of databases along with a range of customization capabilities to visualize information at high quality and efficient level. It is said that a picture is worth a thousand words. If all the information we use everyday was presented in a visual format, we'd be observing pictures and graphs that compound multiple words, thoughts, and data. Although implementing that idea to our everyday lives is in the distant future, businesses can enjoy this idea in the present with a database visualization software. At InetSoft, we pride ourselves on business intelligence and providing organizations with the best solution. With our top of the line BI software, StyleBI, users will be able to access a slew of databases and convert the data into organized visuals...
Database Visualization Tools - InetSoft's StyleBI offers sophisticated software for database visualization. StyleBI is a small-footprint Java-based business intelligence software that maximizes self-service. It is unified, easy-to-deploy, and easy-to-use. Visualization makes data relationships distinguishable and most importantly, saves time. It also allows all users and decision makers to make new discoveries or spot trends so that the organization can stay 'ahead of the game.'...
Data Visualizer Software - Data is like ore, raw and valuable, however companies are using data visualizer software to transform their raw data into actionable information... InetSoft's StyleBI, a premium BI software that can handle thousands of rows and columns...
Easy Data Visualization - InetSoft offers data visualization tools that are easy, agile, and robust. InetSoft has pioneered the evolution from static reporting towards interactive visualization of data. Visuals are fast becoming a highly valued tool for gaining a a true sense of business performance. Previously, a manager might have been able to see how each of his sales people were doing in a quarter. With the power of visuals, that same manager may compare each quarter, each sales person, and further, find the answers to exploratory questions such as "What are the characteristics and trends among our highest paying customers?" Further, a manager may not remember exactly how much revenue each department made in a quarter, but he or she may very well remember how big or small a visual bubble representing each department was. Visuals lead to improved management...
Easy Visual Analytics Tool - Another question is if we already have a BI Platform set up, does it takes less time to set up this kind of visual analytics tool? If you have another BI Platform set up, and if you have data warehouse with an accessible format of data, then yes, actually it’s really easy. It's more the individual analysis scenario where you can just load a table and work with it. And if the tables are well formatted, it’s easy enough for an individual end-user could bring in a couple, two or three tables, link them together and work with them. If you have formatted data such as in a data warehouse, the setup is really not that hard. If the data is in more of a transaction table that has got tables that somebody stuck in 10 years ago that nobody knows about, that has to be removed. If you’ve got no descriptions in the tables, or you’ve got transactions calculations that haven’t been working, then it’s another story. That sort of set up usually takes about five to 10 days to get prepared. Another case is we have really clean data warehouses. We try to figure that out before we start. Once we are accessing a number of tables, we can do many things. Say there’s a transaction table with six million transactions and you are trying to get purchase totals by customer, we can create another table with the roll up of the transaction table. So we’re going to roll up on customer and sum the transactions so we get the total...
Eli Manning Sports Stats Visualization - Interactively analyze the Giant's quarterback's performance versus any opponent. Built using InetSoft's free data visualization app, Visualize Free...
Example of an Advanced Visualization - Let’s look at one example of an advanced visualization, so you can see what is meant by more insight per pixel. Think of a regular gauge chart. It’s very familiar. Some people would call this the executive eye candy. Everyone likes to see this in a dashboard because we’re familiar with the idea of the speedometer style gauge. So if the needle is either in red or yellow then we’re below target for something. Now the challenge with this is this single gauge is taking up a lot of space. The other problem is 10% of the population is color blind. So is that the red on the right or the green? One solution to this problem is the bullet graph. This does a couple of things. First, it doesn’t rely on the red-yellow-green so everyone...
Examples of How Data Visualization Yields Faster Insights - What are some examples of how data visualization yields faster insights? I can think of a few examples in the marketing realm. Day of the week patterns can easily be identified in Web site traffic. Very quickly, looking at a daily traffic chart the troughs on the weekend are obvious, if you're a company serving businesses, for instance. Comparing current performance to the previous year is another example. When the lines normally trace each other following the typical day of the week seasonality, a change in the pattern is quickly spotted when the lines move in different directions or even change slope. Finding best performing ads in PPC campaigns such as with Google AdWords is another good example in the marketing realm. There is so much data captured, ad position, click-through rates, conversion rates. With the tabular reporting that comes with such a service, there's a limit to what you can see just by doing some filtering and only be able to sort on one column at a time. So this where multi-dimensional visual analysis really is necessary. If you make a bubble chart out of this data, you can easily look at 6 dimensions at once because not only do you have the x and y-axes, but you can size the bubbles by another dimension, and color them by another. Then the best performing, most valuable ads will pop out, and just by hovering the mouse over a bubble, you can read the details like which ad group, which ad creative each one represents...
Example of the Use of Visual Discovery and Reporting - This is another example of the use of visual discovery and reporting where this shows the patterns of a problem very visually, and a team can discuss it and quickly get insight that the problem is in the Northeast. If you were poring through PDF reports, you could get a different answer. If you tried to sort by worst flights, they’re not all in the North East. The problem is when they group together, and that’s another example of seeing something because of the visual reporting and analysis capability, which gives you the ability to act on the fly and needing to answer the questions that come up. You killed the cycle of pain, and you reach better and faster decision making. We’ve seen a couple of good examples of dashboards here and good dashboard design. It really is a balancing act. A good dashboard has a very clean design, and what we mean by that is that it is not too dense. You don’t want the dashboard to be overwhelming with too much information. Nor should it be too sparse so that the information on the page doesn’t let you get to the detail that you need to know in order to take the action...
Examples of How Data Visualization Yields Faster Insights - What are some examples of how data visualization yields faster insights? I can think of a few examples in the marketing realm. Day of the week patterns can easily be identified in Web site traffic. Very quickly, looking at a daily traffic chart the troughs on the weekend are obvious, if you're a company serving businesses, for instance. Comparing current performance to the previous year is another example. When the lines normally trace each other following the typical day of the week seasonality, a change in the pattern is quickly spotted when the lines move in different directions or even change slope. Finding best performing ads in PPC campaigns such as with Google AdWords is another good example in the marketing realm. There is so much data captured, ad position, click-through rates, conversion rates. With the tabular reporting that comes with such a service, there's a limit to what you can see just by doing some filtering and only be able to sort on one column at a time. So this where multi-dimensional visual analysis really is necessary. If you make a bubble chart out of this data, you can easily look at 6 dimensions at once because not only do you have the x and y-axes, but you can size the bubbles by another dimension, and color them by another. Then the best performing, most valuable ads will pop out, and just by hovering the mouse over a bubble, you can read the details like which ad group, which ad creative each one represents...
Example of the Use of Visual Discovery and Reporting - This is another example of the use of visual discovery and reporting where this shows the patterns of a problem very visually, and a team can discuss it and quickly get insight that the problem is in the Northeast. If you were poring through PDF reports, you could get a different answer. If you tried to sort by worst flights, they're not all in the North East. The problem is when they group together, and that's another example of seeing something because of the visual reporting and analysis capability, which gives you the ability to act on the fly and needing to answer the questions that come up. You killed the cycle of pain, and you reach better and faster decision making. We've seen a couple of good examples of dashboards here and good dashboard design. It really is a balancing act. A good dashboard has a very clean design, and what we mean by that is that it is not too dense. You don't want the dashboard to be overwhelming with too much information. Nor should it be too sparse so that the information on the page doesn't let you get to the detail that you need in order to take the action...
Excellent Data Visualization Types Added - With addition of the following chart types, InetSoft offers as wide an advanced data visualization library as any analytics solution available. Enhancement for Using R Data Sources Among many user-driven improvements to administrative functions, users of external version control systems get more efficient access to the changes on InetSoft platform assets that concern them. Security management gets additional capabilities including SSO login defaults and user/role/group lookups. Dashboard and Chart Features Tooltips offer more options such as displaying more data point details than just the one selected and the ability to provide more information about a field, including name, alias, and description. Radar charts can now display in pivoted orientations. A new gauge type provides a colored sweep area based on desired data ranges. For example: sweep dashboard gauge Facebook Ad Insights Enhancement Advertisers can better report on their Facebook performance statistics with the ability to use all of the available data parameters. User Portal Functionality Foldering has been added for data asset organization, and intelligent search makes finding dashboards, reports, and worksheets easier For the Full Release Notes To review the complete list of new features and improvements, please see: https://inetsoft-cdn.s3.amazonaws.com/literature/2021_Minor_Features.pdf...