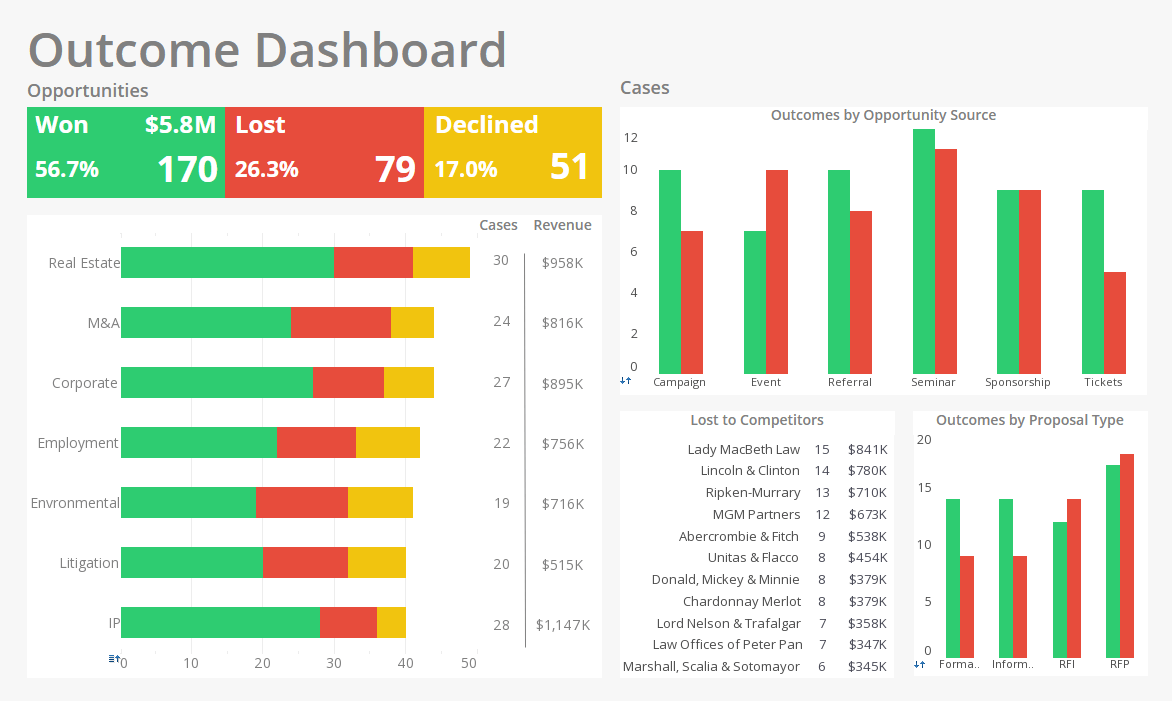
Product How-to: Report Table Elements
InetSoft's reporting software allows users to manage report table elements by filtering through complex data to deliver the desired results every time. View the example below to learn more about the Style Intelligence solution.
You can switch between tables and crosstabs (pivot tables) depending on your needs. Right-click on a Table element, and select �To Crosstab�. Note that the �Data Query� interface now permits crosstab grouping.
A crosstab or pivot table has row and column grouping, and displays a lot of information in a concise aggregated form. Right-click on a table, and select �To Crosstab� to change the grouping type and expose the crosstab options. All other functions, like formatting and properties, are just like a Table element.
Right-click on a Crosstab element, and choose ‘To Table’. Note the ‘Data Query’ interface now permits table grouping.
| #1 Ranking: Read how InetSoft was rated #1 for user adoption in G2's user survey-based index | Read More |
What Metrics and Data Are Contained in a Crop Production Report?
A comprehensive crop production report is a vital tool for farmers, policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders to assess the agricultural landscape and make informed decisions. Such reports are typically compiled by agricultural departments, organizations, and research institutions. They encompass a wide range of metrics and data that provide insights into the performance, trends, and challenges of crop production. Let's delve into the specifics of what metrics and data are commonly contained in a crop production report.
-
Crop Yield: Crop yield is a fundamental metric in any crop production report. It refers to the amount of harvested crop produced per unit of land area. This metric helps gauge the overall productivity of agricultural activities.
-
Acreage Planted and Harvested: The report includes information on the total land area allocated for planting a particular crop and the actual area that was eventually harvested. This data aids in understanding cropping patterns and efficiency.
-
Production Volume: The total quantity of the crop harvested is a key indicator of agricultural output. This metric provides an overview of the supply available for consumption, processing, and export.
-
Varietal Breakdown: Crop production reports often detail the specific varieties or cultivars of a crop that were planted and their respective yields. This information helps farmers and researchers assess the performance of different varieties under varying conditions.
-
Region-Specific Data: Crop production reports break down data by regions, states, or districts. This granularity enables stakeholders to identify localized trends, challenges, and successes in crop production.
-
Yield per Hectare/Acre: Calculating yield per unit of land area provides valuable insights into the efficiency of land utilization and production techniques.
-
Climatic and Weather Information: Weather data, including temperature, precipitation, and extreme events, plays a critical role in understanding the impact of climatic conditions on crop production. It helps identify trends related to climate change and adapt production strategies accordingly.
-
Pest and Disease Incidences: Reports often include information about pest and disease outbreaks affecting crop yields. This data highlights vulnerabilities in production systems and supports the development of effective pest management strategies.
-
Crop Management Practices: Information about irrigation methods, fertilizer usage, and other agronomic practices sheds light on the techniques employed by farmers to enhance production.
-
Price and Market Data: Crop production reports may also provide data on market prices for the harvested crops. This information is valuable for economic analysis, as it helps farmers decide when and where to sell their produce.
-
Historical Comparison: Comparing current data with historical records allows for the identification of trends, such as changes in crop productivity over time and the impact of various interventions.
-
Crop Rotation and Diversity: The report may include details about crop rotation and the diversity of crops planted in a particular region. Crop rotation practices are important for maintaining soil health and preventing disease buildup.
-
Sustainability Metrics: Increasingly, reports are incorporating metrics related to sustainable agricultural practices, such as water usage efficiency, carbon footprint, and soil conservation efforts.
-
Challenges and Recommendations: A comprehensive crop production report doesn't just provide data; it also analyzes challenges faced by the agricultural sector and suggests recommendations for improvement. This could encompass policy suggestions, technological innovations, and best practices.
What Metrics and Data Are Contained in a Forestry Management Report?
A forestry management report is a crucial tool for assessing the health, sustainability, and productivity of forest ecosystems. These reports provide valuable insights for forest managers, policymakers, conservationists, and other stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding forest management and conservation efforts. Here's a detailed overview of the metrics and data commonly found in a forestry management report:
-
Forest Cover and Land Use: The report begins with an assessment of the total forest cover and its distribution within the designated area. It may also include information on land use changes, such as deforestation, afforestation, and reforestation efforts.
-
Tree Species Inventory: A comprehensive inventory of tree species present in the forest is a core component. This data helps assess biodiversity, monitor changes in species composition, and identify endangered or invasive species.
-
Tree Age and Growth Rates: Information about the age distribution of trees and their growth rates provides insights into the overall health and regeneration potential of the forest. This data aids in planning for sustainable timber harvesting and ecosystem restoration.
-
Timber Volume and Harvesting: Timber volume data indicates the amount of wood available for harvest. This metric is essential for sustainable forest management, ensuring that harvesting rates do not exceed regeneration rates.
-
Wildlife and Biodiversity: Forestry management reports often include data on wildlife populations and biodiversity within the forest. This information helps assess the impact of management practices on animal habitats and supports conservation efforts.
-
Carbon Sequestration: With growing emphasis on climate change mitigation, carbon sequestration data highlights the forest's role as a carbon sink. This metric quantifies the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by trees and the potential contribution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Forest Health and Disease Incidences: Reports may provide information on the health status of trees, including the prevalence of diseases and pests. Monitoring forest health helps prevent the spread of infections and enables timely interventions.
-
Soil Quality and Erosion: Data on soil composition, erosion rates, and nutrient content contribute to understanding the long-term sustainability of the forest ecosystem. Healthy soils are essential for maintaining tree growth and overall ecosystem vitality.
-
Protected Areas and Conservation Zones: The report may outline designated protected areas, conservation zones, and areas of ecological significance. This information informs management strategies to preserve critical habitats.
-
Fire Risk and Management: In regions prone to wildfires, forestry management reports include data on fire risk factors, historical fire occurrences, and strategies for fire prevention and management.
-
Recreation and Tourism Data: Forests often serve as recreational areas for hiking, camping, and other outdoor activities. Reports may include data on visitor numbers, infrastructure, and the impact of tourism on the ecosystem.
-
Socioeconomic Impact: Forestry management reports can analyze the socioeconomic impact of forest management on local communities, including employment, income generation, and cultural significance.
-
Illegal Logging and Enforcement: Information on illegal logging activities and enforcement efforts helps identify areas of concern and assess the effectiveness of regulations.
-
Long-Term Monitoring: Many forestry management reports provide data collected over multiple years to track trends, changes, and the effectiveness of management interventions over time.
-
Recommendations and Management Strategies: Similar to crop production reports, forestry management reports often conclude with recommendations for sustainable practices, conservation efforts, and policy considerations.
 |
View live interactive examples in InetSoft's dashboard and visualization gallery. |
More Resources for Report Managers
Map One of These Columns to a Geographic Field - So to create a map, I no longer have a map component on the left hand side. I simply have a chart, and then there's a special map type. So if I select chart style I can choose map. Now for my data, I need to map one of these columns to a geographic field. So for example, State here will simply be set as a geographic field and it asks me what map to associate it with - what level of detail within that map - and then I can also have different sets of mappings...
Need Comprehensive Reporting Software - Does your business need comprehensive reporting software that covers all of your informational and data needs InetSoft's comprehensive Style Report allows non-technical users to easily create reports that display vital information in the most clear and communicative way possible. Tables, charts, and other tools can all be used in a single display environment and modified for the user's preference...
Potential For Geographic Business Intelligence - The potential for geographic business intelligence is significant. Geographic intelligence and business intelligence are natural partners. Organizations that use geographic information intelligently stand to benefit. The business intelligence platform that InetSoft provides starts with access to enterprise information management systems such as CRM systems, any relational database...
Tool to Make a Heat Map Online for Free - The data source for the chart (data block, query, or data model) should represent dimensions and measures as independent columns or fields, including a date column, as shown below. See Prepare Your Data for information on how to manipulate your data, if it is not currently in this form. (Note: A properly designed data model will already have the correct structure...
Tool to Make a Regional Map Online for Free - To easily and quickly create regional maps online for free, create a Free Individual Account on the InetSoft website. You will then be able to upload a spreadsheet data set. Once you have done that, you will be able to proceed past the Visualization Recommender, which can usually get you started creating a dashboard. Since the Recommender does not allow you to create a map chart, press the Full Editor button...
Trend for Adding Geographic Intelligence - Today we see this trend continuing. One of the models, you might call a federated model, where a GIS is shared with many other enterprise applications. Here is a chart from a market research firm. They surveyed 60 enterprise managers from the private and public sectors. The light bars are showing what people perceive as an increase in GIS applications, and the darker bars are where people have reported they see a trend towards GIS integrating with other enterprise systems...
 |
Read how InetSoft saves money and resources with deployment flexibility. |
User-friendly BAM Software - BAM software diminishes the havoc of having to manually pull out data and the risk of missing important data in the process. With BAM, rules are predefined and automatically perform; canceling out human error. The software simply gathers relevant data (which can come from multiple sources) that can be meaningfully used, then processed to identify and categorize factors to specific concerns...
You're Getting a Lot More Data - Of course, there are exceptions to that. I would call myself one of those, but really you know it's all about the same stuff. It's about taking data that maybe transactional and was captured operationally for tactical purposes and doing analysis and aggregation on top of it for strategic purposes. The difference is in the granularity of the data, and typically in Big Data scenarios the granularity is a lot lower so you're getting a lot more data...
Ways InetSoft Dashboard Chart Creator Helps - Our software allows you to quickly manage your data in a clear and concise way. Key benefits include the ability to: Use a small-footprint server that delivers web based interactive flash dashboards Share your information within your organization Have dashboards that range from monitoring and executive to sophisticated interactive visual analysis and business management Enhance manageability and agility...
What are some examples of how location enhances business intelligence? - Location information is valuable to most organizations, but it becomes critical to organizations where geography has a dramatic impact on business operations, such as in the areas of marketing, planning, asset tracking, resource assignments, and the delivery of services. Understanding how location impacts your organization is important. It can give a company a powerful competitive advantage in their market. Spatial analysis answers questions that are "where" related...
 |
Learn about the top 10 features of embedded business intelligence. |
What is a dashboard report in the consulting industry? - A dashboard report represents the aggregated data from information obtained across every facet of a company. In essence, dashboard reporting involves analyzing the company's KPIs based on data obtained in real-time. For a consulting firm, the information on a dashboard report summarizes a client's business decisions over a specific period. It is similar to a still-frame of the company's position at a given point in time...
What Is Happening In The Geographic Business Intelligence World - Quite a lot is happening in the geographic business intelligence world. If you take things like geoprocessing, it allows a much richer what-if capability, something that models more closely the decision-making process people use in the real world. So there are some interesting opportunities for making these types of decisions with what geographic business intelligence can offer you today...
What Is Spatial Data? - Spatial data or GIS Systems store spatial data. And what is spatial data? It's points, lines, and polygons. So, a point might be a store on a map or a ZIP code. It could be a house. A line is perhaps a road, a pipeline, or a utility transmission line. And the polygon is simply a shape. We have some standard shapes of state, country, ZIP codes or we can also create them using GIS Systems. These are custom shapes such as a custom sales territory, a floodplain, the path of a tornado and even shadows of a skyscraper...
| Previous: Managing Report Elements |
Next: Report Chart Elements
|