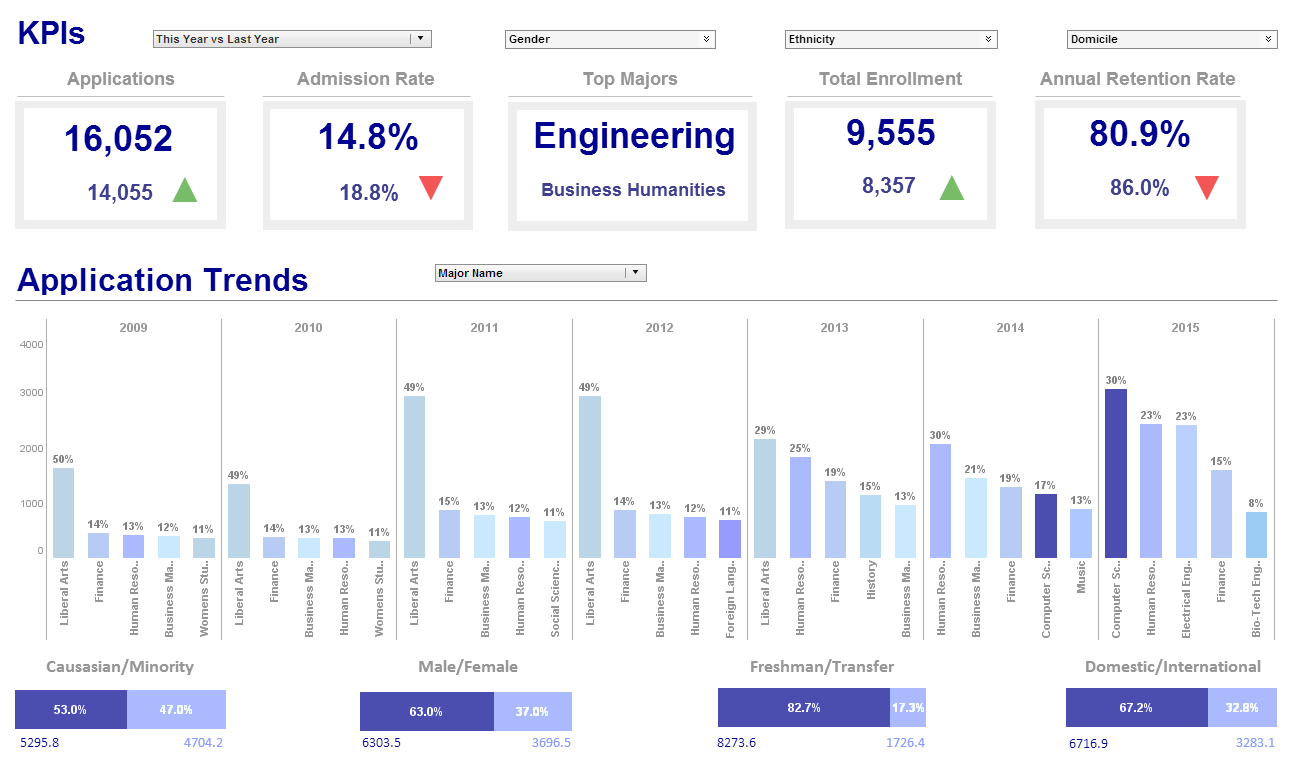
Visualization Software Companies: InetSoft Technology
Are you searching for visualization software companies? InetSoft offers a Web-based application that business user find intuitive to use and IT finds easy to deploy. Find evaluation resources to the left and additional articles on the topic below:
Visualized Data Powerful Persuasion - What makes visualized data, rather than static data, more powerful in persuading others in a business environment. I think that’s one of the shifts in -- well it's not even a shift, people have always used this information for these purposes because you don’t make organizational decisions in a vacuum. You typically have to convince other people that your definition of the problem, your understanding of the problem is right, but then you have to go on to convince people to take an action.And so the old model of BI was this publishing, saying, well here it is and then PowerPoint and Excel and things like that became the means to deliver it. And that environment was really great for explanation. It was great for things where you have known bounds because the exploration was already done for you by some IT analyst, who modeled the data and built a metadata layer in a particular way so, the known question, known bounds of the data for the answer. Then we get into the exploration which you didn’t really touch on there where visualization can enable that. And then you explore it. You explain it. You have got to educate people going from here it is to here is how it works and why we need to take an action, to persuasion: to this is the action I think we should take...
 |
View a 2-minute demonstration of InetSoft's easy, agile, and robust BI software. |
Visualizing Data on Google Map Charts - This page explains how you can use Google Maps in an InetSoft dashboard. By using a Google Map in your chart, you can lend a degree of realism to your geographical data, and provide important geographical context such as mountains, rivers, highways, and landmarks. In order to incorporate a Google Map in a dashboard, you must have an appropriate Google Maps Platform account. Obtain the API key from your Google Maps Platform account, and enter it in the InetSoft Enterprise Manager on the Web Map tab. Enable Use Web Map By Default to automatically use Google Maps when creating any Map Chart. Press Apply to save the settings. If you do not already have a data source with geographical data configured, begin by importing a data set into a Data Worksheet. The sample data we use here is from World Population Review which contains the top 200 US cities by population and has the structure shown below. The data set contains a lot of information about the different cities, but for this example we will just use the "pop2023" field as the measure. Create a new Dashboard based on the Data Worksheet (or other data source) you have created. To create a Google Map Chart using geographical regions such as states or cities or zip codes, add a new Chart to the Dashboard. Do not make the Chart size too large, because Google Maps have a 640px size limit imposed by Google. If the Chart component is too large, you will see a warning when you try to plot data on the map, and you will need to resize it...
Ways You Can Visualize Data - Some other ways you can visualize the data instead of a simple X and Y is multi dimensional visualization. Here we’re looking at data where we not only have an X and Y, but we have colored, sized and shaped our data. Again we can do explicit filtering. I can choose to look a specific region, say the west coast, and you notice that whenever you make a selection with the selection element all of the other selections are filtered based on the same underlying data. The reason for that is because within the west region there are only two divisions. So we’re saying, based on your initial selection, these are the other valid selections that you can make. So only this state would be considered based on your initial selection. With charting another possibility is that you can find outliers. You can see that we have this hover tool. It shows you what the data looks like. With that you can always highlight data points instead of doing a show details or instead of brushing it. You can also zoom in to see how those cluster of points relate to each other because those outliers are causing such a wide scaling of the X axis. So here we can highlight a little bit more of the movement toward collaboration. As long as you do not disable this option, any business user can actually make ad hoc changes, on the fly changes, on demand changes to the data binding...
What Are the Drawbacks of Amazon QuickSight Visualizations? While Amazon QuickSight offers numerous benefits as a business intelligence and data visualization tool, it also has its drawbacks. Here are some potential limitations and drawbacks of using Amazon QuickSight: Limited Advanced Analytics Capabilities: QuickSight is primarily focused on data visualization and dashboard creation, which means it may lack some of the advanced analytics features found in other BI tools. For users requiring complex statistical analysis, predictive modeling, or machine learning capabilities, QuickSight may not be the most suitable option. Limited Data Preparation Functionality: QuickSight's data preparation capabilities are not as robust as those offered by dedicated data preparation tools. While it allows for basic data cleaning, filtering, and transformation, users may find it lacking in more advanced data preparation functionalities such as data wrangling, join optimization, and data profiling. Limited Connectivity Options: While QuickSight integrates well with various AWS data sources such as Amazon Redshift, Amazon RDS, Amazon Aurora, Amazon S3, and others, its connectivity options to external data sources may be limited compared to other BI tools. Users may face challenges when trying to connect to on-premises databases or non-AWS cloud platforms...
What Are the Drawbacks of Hyperion Dashboards and Reporting? - Hyperion Dashboards and Reporting, often associated with Oracle Hyperion products, have been widely used for financial reporting, budgeting, and planning in enterprises. While they offer several advantages, it's essential to consider potential drawbacks as well. Here are some drawbacks associated with Hyperion Dashboards and Reporting: Complex Implementation: Hyperion solutions can be complex to implement. The setup and configuration may require specialized skills and expertise, and organizations might need to invest in training for their staff. Costly Licensing and Maintenance: The licensing and maintenance costs for Hyperion products can be significant. Small and medium-sized businesses might find it challenging to justify the expenses associated with these solutions. Resource Intensive: Running Hyperion Dashboards and Reporting can be resource-intensive, requiring robust hardware infrastructure. This might pose challenges for organizations with limited IT resources or those operating in cloud environments with cost considerations. Steep Learning Curve: Users, especially those not familiar with Hyperion products, might face a steep learning curve. This can impact productivity and hinder the adoption of the tools across different departments...
What Are Some Projects That a Student Could Do With a Data Visualization Tool? - Students interested in data visualization can undertake a variety of projects to explore and showcase their skills using data visualization tools. Here are some project ideas across different domains and skill levels: Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) of Public Datasets: Students can choose a publicly available dataset from sources like Kaggle, UCI Machine Learning Repository, or government data portals and perform exploratory data analysis using a data visualization tool like InetSoft, Tableau, Power BI, or Plotly. They can create interactive visualizations to analyze trends, patterns, and relationships within the data. Public Health Dashboard: Develop a dashboard to visualize public health data, including cases, deaths, testing rates, and vaccination rates across different countries or regions. Students can use real-time data from sources like the World Health Organization (WHO) or Johns Hopkins University's dashboard and create interactive visualizations to track an illness' impact over time. Financial Portfolio Analysis: Students interested in finance can create a dashboard to visualize stock prices, portfolio performance, and financial metrics using historical stock market data. They can use APIs like Alpha Vantage or Yahoo Finance to retrieve stock data and visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) such as return on investment (ROI), volatility, and correlation...
What Are the Steps to Making a Data Visualization to Show Climate Zones in the United States? - Creating a data visualization to show climate zones in the United States can vary in complexity depending on the level of detail and interactivity you desire. Here's a breakdown of the steps and considerations for creating such a visualization: Data Collection: Obtain data on climate zones in the United States. This data may include temperature ranges, precipitation levels, and other relevant climatic factors. Sources like the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) or the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) provide climate zone maps. Data Preparation: Organize and clean the data. Ensure that it is in a format suitable for visualization. This may involve aggregating data by region or climate zone and converting it into a format compatible with your chosen visualization tool. Choose a Visualization Tool: Select a data visualization tool based on your preferences, skills, and the desired level of complexity. Tools like Tableau, Power BI, or D3.js offer varying levels of complexity and customization...
 |
Learn the advantages of InetSoft's small footprint BI platform. |
What Are the URLs for Some Good Government Data Sources to Use for Data Visualization Projects? - There are numerous government data sources available for data visualization projects, covering a wide range of topics such as demographics, economics, health, environment, education, and more. Here are some reliable URLs for accessing government data: Data.gov: This is a comprehensive repository of open government data from the United States federal government. It covers a vast array of topics and provides datasets in various formats. URL: Data.gov The World Bank Open Data: The World Bank offers free and open access to a comprehensive set of data about development in countries around the globe. It includes indicators on education, health, poverty, and many other aspects of development. URL: World Bank Open Data UN Data: The United Nations provides a wealth of data on global issues, including economic development, population, health, and more. It's a valuable resource for projects with an international focus. URL: UN Data Eurostat: Eurostat is the statistical office of the European Union and provides high-quality statistics on European countries across various topics such as economy, population, environment, and more...
What Are Visualization Tools - Visualization tools are software applications that allow users to create charts, images, diagrams, or animations to effectively communicate a message. When referring to business visualization tools, we need to creating visual guides of how our business is doing, that is easy understood by any level of employee at your company. Visualization is a technique that allows for the representation of data set graphically. When business data is large and very abstract, visualization tools help make the data easier to read and understand. Today, there are visualization tool for search, music, online communities, and almost anything, but none seem to be as vital as those used to dissect crucial business data, which also represent the greatest challenge...
What Data Visualizations Do Financial Reporting Managers Create? - Financial reporting managers utilize data visualizations to communicate complex financial information effectively, facilitate decision-making, and provide insights to stakeholders. Here are several types of data visualizations commonly used in financial reporting: Income Statements: Financial reporting managers use visualizations such as vertical bar charts or waterfall charts to represent income statements. These visualizations help stakeholders understand revenue, expenses, and profitability over a specific period, highlighting key components such as gross profit, operating income, and net income. Balance Sheets: Visualizations like stacked bar charts or treemaps are used to illustrate balance sheet data, including assets, liabilities, and equity. These visualizations enable stakeholders to see the composition of the company's financial position, identify trends in asset allocation, and assess liquidity and solvency...
What Data Visualizations Does a Quality Control Supervisor Use? - Control Charts: Control charts are essential tools in quality control. They display process data over time and include control limits that represent acceptable variation. QC supervisors use control charts to monitor variations in a process and detect any special causes of variation that may lead to defects or deviations from the desired quality standards. Histograms: Histograms are graphical representations of the distribution of a set of data. QC supervisors use histograms to analyze the frequency and spread of measurement values in a sample, helping them understand the distribution of defects or quality characteristics. Scatter Plots: Scatter plots are used to visualize the relationship between two variables. In quality control, supervisors may use scatter plots to identify correlations between process parameters and product quality. They can use this information to optimize process settings and reduce variability. Pareto Charts: Pareto charts display the frequency of occurrences of various defects or issues in descending order. QC supervisors use Pareto charts to prioritize the most significant quality issues, enabling them to focus efforts on addressing the most critical problems first...
What Do Directors of Parks and Recreation Facilities View with a Dashboard Tool for Visualizing Data? - Directors of parks and recreation facilities utilize dashboard tools for visualizing data to gain insights into various aspects of park operations, visitor engagement, facility usage, and resource management. These dashboards help directors make data-driven decisions, monitor performance metrics, and enhance the overall experience for park visitors. Here are some key elements that directors may view with a dashboard tool: Attendance and Visitor Trends: Directors can track attendance metrics to understand visitor trends, peak visitation periods, and popular attractions within the park. This data helps in planning staffing levels, programming schedules, and resource allocation to accommodate fluctuations in visitor traffic. Facility Utilization: Dashboards provide insights into the usage of park facilities, including sports fields, picnic areas, playgrounds, and event venues. Directors can analyze reservation data, usage patterns, and peak hours to optimize facility scheduling, maintenance, and rental revenue...
What Is the Difference Between InetSoft's Visualize Free and InetSoft's StyleBI? - InetSoft offers two distinct products: Visualize Free and StyleBI. Here are the key differences between InetSoft's Visualize Free and StyleBI: Product Type and Purpose: Visualize Free: Visualize Free is a free, entry-level data visualization tool provided by InetSoft. It is designed for individual users or small teams who need basic data visualization capabilities without the need for advanced business intelligence features. StyleBI: StyleBI is a comprehensive business intelligence platform offered by InetSoft. It is a full-featured, enterprise-grade solution designed for organizations with more extensive data analysis, reporting, and dashboard requirements. Capabilities and Features: Visualize Free: Basic Data Visualization: Visualize Free offers fundamental data visualization capabilities, allowing users to create simple charts, graphs, and dashboards. Limited Advanced Features: The free version is limited in terms of advanced features and functionalities compared to enterprise-grade solutions...
What Is The Difference Between a Visualization and a Dashboard? - Making sense of data in a way that is simple to understand is becoming more and more crucial as organizations continue to gather enormous volumes of data. Dashboards and visualizations may help with this. There are important distinctions between visualizations and dashboards, despite the fact that they both convey data visually. In this post, we'll examine the distinctions between dashboards and visualizations and explain why companies would want to use them. What Is a Visualization? A visualization is a graphic depiction of facts that makes it simple and fast to comprehend. Data is presented in an understandable fashion using visualizations, which might include charts, graphs, and diagrams. Data patterns, trends, and linkages that may not be readily obvious from a spreadsheet or database can be found using visualizations...
 |
Read the top 10 reasons for selecting InetSoft as your BI partner. |
What Is the Role of a Marketing Operations Professional? - A Marketing Operations professional plays a critical role in optimizing and streamlining the internal processes, technologies, and strategies within a marketing department. Their primary goal is to enhance the efficiency, effectiveness, and overall performance of marketing campaigns and initiatives. Here are some key responsibilities and roles of a Marketing Operations professional: Technology Management: Marketing operations professionals are responsible for managing marketing technology tools and platforms. They evaluate, implement, and integrate various software solutions such as customer relationship management (CRM), marketing automation, analytics, content management, and more. They ensure that these tools work together seamlessly to support marketing efforts. Data Management: Effective marketing relies on accurate and clean data. Marketing operations professionals oversee data collection, validation, integration, and cleansing processes. They ensure that data is structured in a way that enables meaningful analysis and informed decision-making. Analytics and Reporting: These professionals play a role in measuring the performance of marketing campaigns and initiatives. They develop key performance indicators (KPIs), set up tracking mechanisms, analyze data, and create reports to provide insights into the effectiveness of marketing efforts. This information helps marketers make data-driven decisions...
What Is Visual Analysis? - Today we are here to talk about visual analysis and specifically working with data. What is visual analysis? The origin of visual analysis goes back to two of the success stories of computers in this world. One of them was databases. Back in the ‘60s, there were many different approaches to databases. In the ‘70s, relational algebra was developed, and relational databases emerged as a standard. This gave databases the property that they could support a high level query language. And in particular, they could support parallel and transactional queries, which allowed us to use them for everything. We use them for finance. We use them for medicine, retail, education, on and on like that. In the ‘90s, once we had all our data online, people started realizing they could do analytical reporting using data warehousing technologies. And then now, in this decade, there has been a focus on ad-hoc querying. Data is absolutely essential to our business. I would say that part of the financial problem we are having right now is because people took their eyes off the data. So this is the one huge success story of computer science...
What Kinds of Visual Analytics Does an HR Professional Do? - Human resources (HR) professionals utilize visual analytics to gain insights into various aspects of workforce management, employee engagement, performance, and organizational health. Visual analytics tools help HR professionals to analyze and communicate complex data in a visual format, enabling better decision-making and strategic planning. Here are several types of visual analytics commonly used by HR professionals: Employee Demographics: HR professionals use visual analytics to analyze and visualize employee demographics such as age, gender, ethnicity, education level, and tenure. Visual representations like pie charts, bar graphs, or heat maps can provide insights into the diversity, composition, and distribution of the workforce, helping HR teams identify trends, disparities, and areas for improvement in diversity and inclusion initiatives. Recruitment and Hiring Metrics: Visual analytics can help HR professionals track recruitment and hiring metrics such as time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, source of hire, applicant demographics, and recruitment funnel effectiveness. Dashboards and reports with visualizations like funnel charts, recruitment pipelines, and geographic heat maps enable HR teams to assess the efficiency and effectiveness of their recruitment efforts, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions to optimize the hiring process...
When Should You Use a Monochromatic Palette? - A monochromatic color palette involves using different shades, tones, and tints of a single color. This creates a harmonious and visually cohesive look. Here are situations where using a monochromatic palette is particularly effective: Creating a Calm and Serene Atmosphere: Monochromatic palettes, especially in lighter tones, can evoke a sense of tranquility and calmness. They are excellent choices for spaces where relaxation and a peaceful ambiance are desired, such as bedrooms or meditation rooms. Emphasizing Texture and Form: In design, using a monochromatic palette allows for a focus on texture, form, and shape. Without the distraction of multiple colors, the eye is drawn to the subtleties and details within the design elements. Achieving a Minimalist Aesthetic: Monochromatic palettes are a hallmark of minimalist design. They create a clean, uncluttered look that emphasizes simplicity and functionality. This is often used in modern and contemporary interior design...
Who in the Team's Organization Use Data Visualization Software? - Many different people within a professional baseball team may work with data visualization software to analyze and present data effectively. Here are some key roles: Data Analyst: Data analysts collect, clean, and analyze various data sets related to player performance, scouting reports, game statistics, and more. They utilize data visualization software to create visual representations of the data, uncover insights, and communicate findings to coaches, managers, and other stakeholders. Data Scientist: Data scientists apply statistical and machine learning techniques to explore and derive insights from baseball data. They work with complex data sets and leverage data visualization tools to present their findings in a clear and concise manner. Data scientists help identify patterns, build predictive models, and optimize strategies based on data-driven insights. Performance Analyst: Performance analysts focus on analyzing player performance metrics, both individually and collectively. They use data visualization software to create charts, graphs, and heat maps to identify performance trends, strengths, weaknesses, and improvement areas. Performance analysts collaborate with coaches and players to optimize training programs and game strategies...
| Previous: Exploratory Visual Analysis Software |